1. 12 Steps To Becoming A Veterinarian: The Ultimate Guide

12 Steps to Becoming a Veterinarian: Your Comprehensive Guide

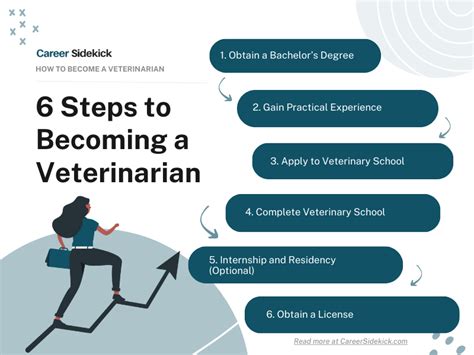
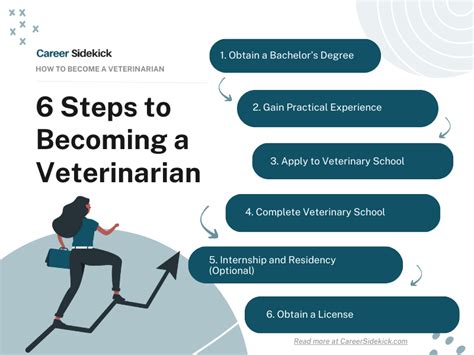
Are you passionate about animals and considering a career as a veterinarian? It's an exciting and rewarding path, but it requires dedication and a clear plan. In this ultimate guide, we'll walk you through the 12 essential steps to becoming a veterinarian, ensuring you're well-prepared for this noble profession.
Step 1: Explore Your Passion
Before embarking on your veterinary journey, it's crucial to evaluate your passion for animals. Spend time volunteering at animal shelters, assisting veterinarians, or even just observing wildlife. This hands-on experience will help you understand if a career in veterinary medicine is truly your calling.
Step 2: Excel in Your High School Studies

Veterinary programs typically have rigorous admission requirements. Focus on excelling in your high school courses, particularly in the sciences. Strong grades in biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics will give you a solid foundation for your future studies.
Step 3: Gain Relevant Experience

Veterinary schools highly value practical experience. Seek out opportunities to work or volunteer at veterinary clinics, farms, or animal research facilities. This experience not only enhances your application but also provides valuable insights into the daily life of a veterinarian.
Step 4: Choose the Right Undergraduate Program

While some veterinary schools offer direct-entry programs, most require a bachelor's degree. Choose an undergraduate program that aligns with your interests and provides a strong foundation in the sciences. Consider majoring in biology, zoology, or a related field.
Step 5: Prepare for the Admissions Process

The admissions process for veterinary schools is competitive. Start preparing early by researching the requirements of your chosen schools. Most programs require standardized tests like the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) or the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT). Familiarize yourself with the test content and consider preparatory courses or study guides.
Step 6: Craft a Compelling Application

Your application is your chance to showcase your passion, experiences, and potential as a veterinarian. Highlight your academic achievements, relevant work or volunteer experiences, and any leadership roles you've held. Write a compelling personal statement that demonstrates your dedication to the field.
Step 7: Choose the Right Veterinary School
With your applications submitted, it's time to choose the right veterinary school. Consider factors such as location, program curriculum, research opportunities, and clinical rotations. Visit the schools if possible, and speak with current students and alumni to get a feel for the culture and environment.
Step 8: Complete Your Veterinary Curriculum

Veterinary school is an intense and challenging journey. Expect a rigorous curriculum covering anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and various veterinary specialties. Balancing your studies with practical experiences, such as clinical rotations and research projects, is essential for a well-rounded education.
Step 9: Gain Clinical Experience

Clinical rotations are a vital part of your veterinary education. These rotations provide hands-on experience in different areas of veterinary medicine, such as small animal practice, large animal care, surgery, and emergency medicine. Embrace these opportunities to refine your skills and gain valuable insights into the veterinary profession.
Step 10: Prepare for Licensing Exams
To practice as a veterinarian, you must pass licensing exams. In the United States, this includes the North American Veterinary Licensing Examination (NAVLE). Familiarize yourself with the exam format and content, and consider study resources and practice exams to ensure you're well-prepared.
Step 11: Explore Specialization Options
Veterinary medicine offers a wide range of specializations, from internal medicine and surgery to exotic animal care and research. During your studies or early in your career, explore these specializations to find your niche. Consider pursuing additional training or certifications to become an expert in your chosen field.
Step 12: Start Your Veterinary Career
With your education and training complete, it's time to embark on your veterinary career. Seek out job opportunities in your desired field, whether it's a small animal practice, a research facility, or a zoo. Remember, continuing education and professional development are essential to staying current in this ever-evolving field.
Conclusion
Becoming a veterinarian is a challenging yet rewarding journey. By following these 12 steps, you'll be well-prepared to pursue this noble profession and make a positive impact on the lives of animals and their owners. Remember, your passion and dedication will guide you through every step of this exciting path.
What are the key skills needed to become a successful veterinarian?
+
Successful veterinarians possess a unique blend of skills, including strong scientific knowledge, excellent communication and interpersonal skills, empathy and compassion for animals and their owners, and the ability to make quick and informed decisions in high-pressure situations.
How long does it typically take to become a veterinarian?
+
The time it takes to become a veterinarian varies depending on the educational path and specialization chosen. On average, it takes around 8-10 years, including undergraduate studies, veterinary school, and any additional training or residency programs.
What are some common challenges faced by veterinarians?
+
Veterinarians often face emotional challenges, such as dealing with the loss of patients or difficult conversations with pet owners. They must also stay updated with the latest advancements in veterinary medicine and manage the financial aspects of running a practice.
Can I become a veterinarian if I don’t have a strong background in science?
+
While a strong foundation in science is beneficial, it’s not always a requirement. Many veterinary schools offer pre-veterinary programs or bridge courses to help students strengthen their scientific knowledge. Dedication and a willingness to learn can help overcome initial challenges.
What are some alternative career paths within veterinary medicine?
+
Veterinary medicine offers a range of career paths beyond clinical practice. These include veterinary research, public health, animal welfare advocacy, and even careers in the pharmaceutical or biotechnology industries.

