10+ Av8b Harrier Facts: Mustsee Jump Jet Secrets Unveiled

Introduction to the Iconic AV-8B Harrier

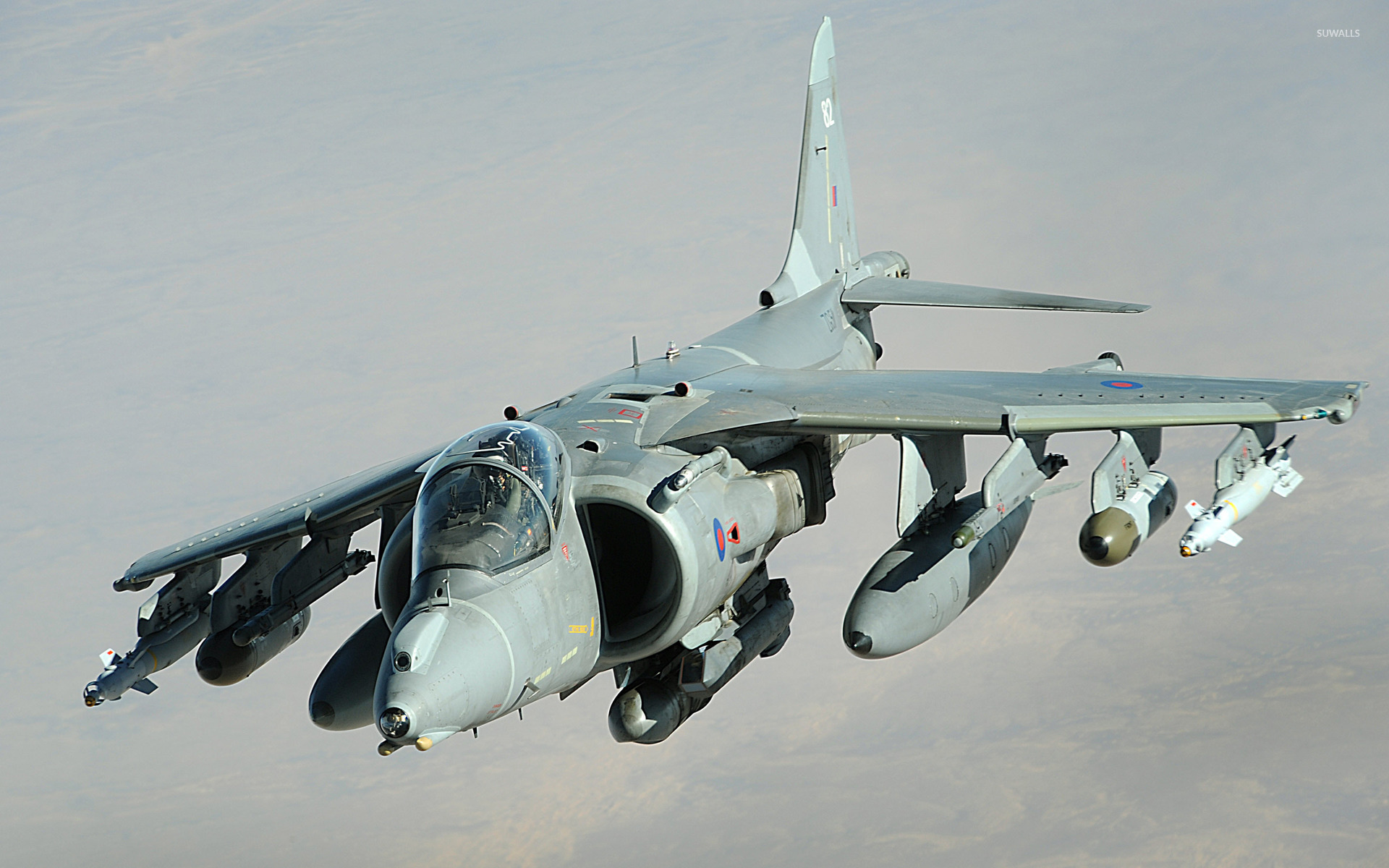
The AV-8B Harrier, often referred to as the “Jump Jet,” is an incredible aircraft that has captured the imagination of aviation enthusiasts worldwide. With its unique capabilities and an impressive history, the Harrier has left an indelible mark on military aviation. In this blog post, we delve into over 10 fascinating facts about the AV-8B Harrier, uncovering its secrets and exploring why it remains an iconic aircraft to this day.
The Harrier’s Vertical Takeoff and Landing (VTOL) Capability

One of the most distinctive features of the AV-8B Harrier is its ability to perform Vertical Takeoff and Landing (VTOL). This remarkable capability allows the aircraft to take off and land vertically, much like a helicopter. The Harrier achieves this through its unique vectoring engine nozzles, which can be directed downward, enabling it to hover and maneuver with exceptional precision.
The Origin of the Harrier’s Name

The name “Harrier” is derived from a species of bird known as the “harrier hawk.” These birds of prey are known for their agility and hunting prowess, which inspired the aircraft’s name. Just like its namesake, the AV-8B Harrier is renowned for its exceptional maneuverability and ability to strike with precision.
A Legacy of Innovation: The Harrier’s Development

The AV-8B Harrier is the latest iteration of the Harrier family, which began with the Hawker Siddeley Harrier in the 1960s. This groundbreaking aircraft was the world’s first successful vertical/short takeoff and landing (V/STOL) jet fighter, revolutionizing military aviation. The AV-8B, developed by British Aerospace and McDonnell Douglas, builds upon this legacy, incorporating advanced technology and improved performance.
The Harrier’s Role in Modern Warfare

The AV-8B Harrier has played a crucial role in modern warfare, particularly in close air support and ground attack missions. Its ability to operate from small, improvised airfields and even aircraft carriers makes it an invaluable asset for military operations. The Harrier’s versatility and agility have made it a preferred choice for various combat scenarios.
Engine Technology: The Pegasus Powerplant

At the heart of the AV-8B Harrier’s performance is the Pegasus powerplant, a remarkable engine designed specifically for VTOL aircraft. The Pegasus engine features four vectoring nozzles, allowing the aircraft to redirect its thrust for vertical takeoff and landing. This engine technology is a key factor in the Harrier’s exceptional maneuverability and responsiveness.
The Harrier’s Service with the U.S. Marine Corps

The AV-8B Harrier has been an integral part of the U.S. Marine Corps’ aviation capabilities since its introduction. The Marine Corps operates a significant fleet of Harriers, utilizing them for a range of missions, including close air support, reconnaissance, and combat search and rescue. The Harrier’s ability to operate from forward operating bases makes it an ideal choice for the Marine Corps’ rapid deployment and expeditionary operations.
Stealth Features: The Harrier’s Low Observable Design

While not a stealth fighter in the traditional sense, the AV-8B Harrier incorporates several design features to reduce its radar signature. The aircraft’s angular shape, combined with radar-absorbent materials, helps to minimize its radar cross-section. This low observable design enhances the Harrier’s survivability and mission effectiveness, especially when operating in hostile environments.
The Harrier’s Unique Thrust Vectoring System

One of the most critical components of the AV-8B Harrier’s VTOL capability is its thrust vectoring system. This system allows the aircraft to redirect its engine thrust in multiple directions, enabling vertical takeoff and landing. The Harrier’s vectoring nozzles can be adjusted to provide forward, downward, or upward thrust, providing exceptional control and maneuverability during flight.
The Harrier’s Impressive Performance Specifications

The AV-8B Harrier boasts impressive performance specifications, making it a formidable aircraft. With a maximum speed of over 700 mph and a service ceiling of approximately 50,000 feet, the Harrier can outmaneuver many modern fighter jets. Its range of over 1,000 miles and ability to carry a variety of weapons and sensors make it a versatile and deadly force on the battlefield.
The Harrier’s Retirement and Legacy
After decades of service, the AV-8B Harrier is gradually being retired from active duty. The U.S. Marine Corps is transitioning to the F-35B Lightning II, which offers advanced stealth capabilities and improved performance. However, the Harrier’s legacy will live on, having proven its worth in numerous conflicts and leaving an indelible mark on military aviation history.
Conclusion
The AV-8B Harrier, with its unique VTOL capability and exceptional performance, has earned its place as an iconic aircraft. From its innovative design to its crucial role in modern warfare, the Harrier has left an enduring legacy. As we bid farewell to this remarkable aircraft, we can reflect on its impact and the advancements it inspired in the world of aviation.
FAQ

What is the significance of the Harrier’s VTOL capability?

+
The Harrier’s VTOL capability allows it to operate from a variety of locations, including small airfields and even aircraft carriers. This versatility makes it an invaluable asset for military operations, as it can rapidly deploy and provide close air support where needed.
How does the Harrier’s engine work for VTOL?

+
The Harrier’s Pegasus engine features vectoring nozzles that can direct thrust downward, enabling vertical takeoff and landing. This unique design allows the aircraft to hover and maneuver with precision, making it highly agile and responsive.
What are some notable conflicts the Harrier participated in?

+
The AV-8B Harrier has seen action in numerous conflicts, including the Gulf War, the Kosovo War, and the Iraq War. Its ability to provide close air support and conduct precision strikes has made it a vital asset in these operations.
Is the Harrier still in active service today?

+
While the Harrier is being phased out, it is still in active service with some military forces. The U.S. Marine Corps, for example, continues to operate a fleet of Harriers, although they are gradually being replaced by the F-35B Lightning II.
What is the future of VTOL aircraft like the Harrier?

+
VTOL technology continues to evolve, and we can expect to see further advancements in the future. The Harrier’s legacy has paved the way for more advanced VTOL aircraft, such as the F-35B Lightning II, which offers improved stealth capabilities and performance.