10+ Built Environment Innovations: Unlocking Urban Potential

The built environment is a crucial aspect of modern society, shaping the way we live, work, and interact with our surroundings. As urban populations continue to grow, the need for innovative solutions to enhance the livability and sustainability of our cities becomes increasingly evident. From smart infrastructure to green architecture, here are some of the most exciting innovations in the built environment that are unlocking the full potential of our urban spaces.
1. Smart Cities and IoT Integration
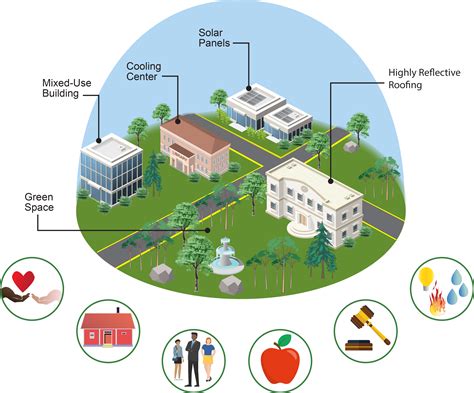
The concept of smart cities is revolutionizing urban planning and management. By integrating the Internet of Things (IoT) into city infrastructure, we can create connected and efficient urban ecosystems. Smart sensors and devices collect real-time data on various aspects of city life, including traffic flow, energy consumption, and environmental conditions.
- Smart Traffic Management: Sensors embedded in roads and vehicles optimize traffic flow, reducing congestion and travel times.
- Intelligent Lighting Systems: LED streetlights adjust brightness based on ambient light and motion detection, saving energy and enhancing safety.
- Smart Waste Management: IoT-enabled waste bins send notifications when they need to be emptied, optimizing collection routes and reducing costs.
2. Green and Sustainable Architecture

Sustainable architecture focuses on minimizing the environmental impact of buildings while maximizing energy efficiency and comfort. Green building practices are gaining traction worldwide, and some of the key innovations include:
- Passive Design: Utilizing natural lighting, ventilation, and temperature control to reduce the need for mechanical systems.
- Green Roofs and Walls: Installing vegetation on rooftops and vertical surfaces improves insulation, absorbs rainwater, and enhances urban biodiversity.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Incorporating solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal systems to generate clean energy for buildings.
- Wastewater Recycling: Implementing systems to treat and reuse wastewater for non-potable purposes, reducing strain on water resources.
3. Vertical Farming and Urban Agriculture
As urban spaces become more congested, vertical farming offers a sustainable solution to meet the growing demand for fresh produce. By utilizing advanced hydroponic and aeroponic techniques, crops can be grown in controlled environments, often stacked in layers.
- Increased Food Production: Vertical farming can produce higher yields per square foot compared to traditional agriculture.
- Year-Round Harvest: Controlled environments allow for continuous crop growth, providing a steady supply of fresh produce.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Vertical farms use less water and land, minimizing the carbon footprint of food production.
- Urban Food Security: Bringing food production closer to consumers reduces transportation needs and enhances food security.
4. Affordable and Innovative Housing Solutions

Addressing the global housing crisis requires innovative and affordable housing solutions. Here are some approaches that are making a difference:
- Prefabricated and Modular Construction: Factory-built components reduce construction time and costs, allowing for faster and more efficient housing development.
- Tiny Houses and Micro-Apartments: Compact living spaces maximize efficiency and minimize environmental impact, offering affordable housing options.
- Co-Living and Shared Housing: Shared amenities and common spaces reduce individual costs, promoting a sense of community and social interaction.
- Adaptive Reuse of Buildings: Converting existing structures into housing, such as repurposing old warehouses or industrial spaces, provides unique and affordable living options.
5. Smart Transportation and Mobility
Efficient transportation systems are vital for the functionality of urban areas. Smart mobility solutions aim to reduce congestion, improve accessibility, and enhance the overall commuting experience.
- Electric and Autonomous Vehicles: The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving technologies is transforming urban transportation, reducing emissions and improving safety.
- Shared Mobility Services: Ride-sharing, bike-sharing, and scooter-sharing platforms offer convenient and affordable transportation options, reducing the need for private car ownership.
- Intelligent Traffic Signal Systems: Advanced algorithms optimize traffic signal timings based on real-time data, improving traffic flow and reducing delays.
- Last-Mile Delivery Solutions: Innovative approaches, such as drone deliveries and cargo bikes, address the challenge of last-mile logistics, reducing congestion and emissions.
6. Resilient and Adaptive Infrastructure

Climate change and extreme weather events pose significant challenges to urban infrastructure. Building resilient and adaptive systems is crucial for ensuring the long-term sustainability of cities.
- Green Infrastructure: Implementing natural solutions like rain gardens, bioswales, and green infrastructure helps manage stormwater runoff and reduce the risk of flooding.
- Seismic-Resistant Buildings: Advanced engineering techniques and materials enhance the resilience of buildings in earthquake-prone areas, protecting lives and property.
- Resilient Power Grids: Microgrids and distributed energy systems improve the reliability of electricity supply, ensuring critical infrastructure can function during outages.
- Flood-Resistant Design: Elevating critical infrastructure, implementing flood barriers, and utilizing flood-resistant materials protect essential services during extreme weather events.
7. Digital Twin Technology

Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical assets and systems, allowing for real-time monitoring, analysis, and optimization. This innovation is transforming the way we manage and maintain urban infrastructure.
- Infrastructure Monitoring: Digital twins provide valuable insights into the performance and condition of buildings, bridges, and other critical infrastructure, enabling proactive maintenance.
- Urban Planning and Simulation: Digital twins help urban planners test different scenarios and evaluate the impact of proposed developments before implementation.
- Energy Efficiency Optimization: By simulating energy consumption patterns, digital twins assist in identifying areas for improvement and implementing energy-saving measures.
8. Circular Economy in Construction

The construction industry is embracing the principles of the circular economy, aiming to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency. Here are some key practices:
- Material Reuse and Recycling: Salvaging and reusing building materials reduces the demand for new resources and diverts waste from landfills.
- Design for Deconstruction: Buildings are designed with ease of disassembly in mind, allowing for the recovery and reuse of components at the end of their lifespan.
- Green Demolition: Implementing techniques like deconstruction and selective demolition minimizes waste generation and maximizes material recovery.
- Waste-to-Energy Solutions: Converting construction and demolition waste into energy through processes like gasification or incineration reduces waste and generates renewable energy.
9. Mixed-Use Development and Walkability

Mixed-use development combines residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within a single area, promoting walkability and reducing the need for long commutes. This approach offers numerous benefits:
- Reduced Traffic Congestion: Having amenities and services within walking distance decreases the reliance on private vehicles, easing traffic congestion.
- Enhanced Social Interaction: Mixed-use developments foster a sense of community and encourage social connections, improving overall well-being.
- Sustainable Land Use: Optimizing land use and reducing urban sprawl, mixed-use development minimizes the environmental impact of urban expansion.
10. Public Space Revitalization

Revitalizing public spaces, such as parks, plazas, and streetscapes, can transform urban areas into vibrant and inclusive hubs. Here are some strategies for successful public space revitalization:
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in the design and programming of public spaces ensures that they meet the needs and desires of residents.
- Activating Underutilized Spaces: Transforming vacant lots, alleys, or underpasses into vibrant public spaces adds value to the surrounding area and enhances urban vitality.
- Green Infrastructure Integration: Incorporating green elements like gardens, trees, and water features improves the aesthetics and environmental quality of public spaces.
- Art and Cultural Initiatives: Incorporating public art, performances, and cultural events adds a unique character to public spaces, attracting visitors and promoting social interaction.
As we continue to innovate and push the boundaries of what is possible in the built environment, we unlock the full potential of our urban spaces. These innovations not only enhance the livability and sustainability of our cities but also contribute to a more resilient and equitable future. By embracing these cutting-edge solutions, we can create thriving and vibrant urban ecosystems that meet the needs of current and future generations.
FAQ
What are the key benefits of smart city initiatives?
+Smart city initiatives offer numerous benefits, including improved efficiency, enhanced citizen services, reduced environmental impact, and better data-driven decision-making.
How can green architecture benefit the environment?
+Green architecture reduces the environmental impact of buildings by minimizing energy consumption, promoting sustainable materials, and enhancing biodiversity through green roofs and walls.
What are the advantages of vertical farming in urban areas?
+Vertical farming offers increased food production, year-round harvest, reduced environmental impact, and improved urban food security by bringing fresh produce closer to consumers.
How do shared mobility services contribute to sustainable transportation?
+Shared mobility services, such as ride-sharing and bike-sharing, reduce the need for private car ownership, decrease congestion, and provide affordable and convenient transportation options.
What is the role of digital twin technology in infrastructure management?
+Digital twin technology allows for real-time monitoring, analysis, and optimization of urban infrastructure, enabling proactive maintenance and enhancing the overall efficiency of city systems.

