15 Roman Soldier Ranks: The Ultimate Guide To Ancient Rome's Military Hierarchy

Dive into the intricate world of the Roman military hierarchy, where power and prestige were carefully organized into distinct ranks. This comprehensive guide will take you through the 15 Roman soldier ranks, offering an in-depth look at the roles, responsibilities, and privileges of each position. From the lowly private to the revered commander-in-chief, every rank played a crucial part in the mighty Roman army's success.
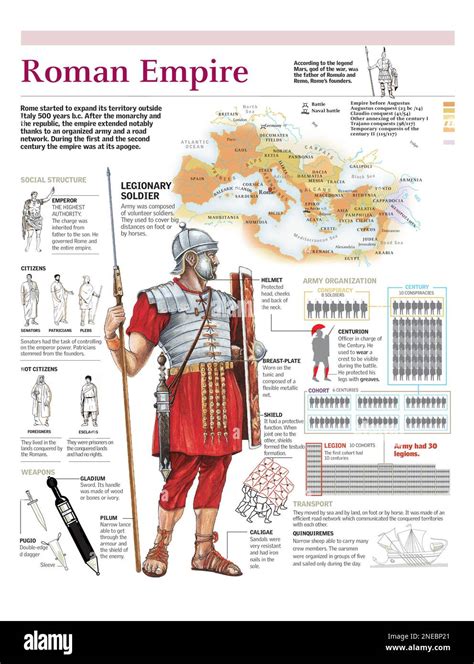
The Legionary: The Backbone of the Roman Army

At the heart of the Roman military machine stood the legionary, a soldier who embodied the very essence of Roman military might. These brave men formed the core of the Roman legions, the elite fighting force that struck fear into the hearts of Rome's enemies.
Legionaries were renowned for their discipline, training, and unwavering loyalty to the Roman state. They were the ultimate warriors, trained to fight with ferocity and precision, and their skills were honed through rigorous drills and exercises.
Here's a closer look at the legionary's role and responsibilities:
- Role: Legionaries were the infantry soldiers, forming the backbone of the Roman army. They were trained to fight in close combat, using a variety of weapons, including swords, spears, and shields.
- Responsibilities: Legionaries were responsible for engaging in combat, defending Roman territory, and participating in military campaigns. They were also trained in engineering and construction, often building roads, fortifications, and other infrastructure during their campaigns.
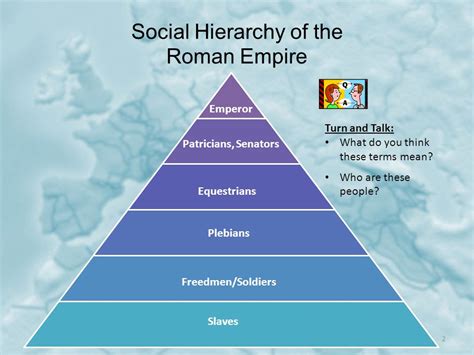
The Rank Structure: A Pyramid of Power

The Roman military hierarchy was organized in a hierarchical manner, with each rank building upon the other. This structure ensured a clear chain of command and efficient coordination during battles. Here's a breakdown of the 15 Roman soldier ranks, from the lowest to the highest:
- Privatus (Private): The lowest rank in the Roman army, privates were typically new recruits undergoing basic training. They had limited rights and privileges and were often assigned to menial tasks.
- Tiuper (Trumpeter): Trumpeters were responsible for conveying orders and signals on the battlefield. Their role was crucial in maintaining communication and coordination among the troops.
- Caligatus (Caligati): These were the ordinary soldiers, also known as "common soldiers." They formed the bulk of the Roman army and were responsible for the day-to-day operations and combat.
- Sursum (Surplus): Surplus soldiers were a special category of soldiers who had completed their service but chose to continue serving. They were often assigned to support roles or as instructors.
- Signifer (Standard-Bearer): Standard-bearers were an integral part of the Roman army. They carried the legion's standard, a flag or emblem that represented the unit's identity and served as a rallying point during battles.
- Immunes (Immunes): Immunes were specialized soldiers who were exempt from certain duties due to their specific skills. They included engineers, surgeons, and other specialists.
- Duplicarius (Double Pay): This rank denoted soldiers who received double pay for their exceptional skills or bravery. They were often veterans or experienced soldiers.
- Sesquiplicarius (One-and-a-Half Pay): Similar to the Duplicarius, these soldiers received one-and-a-half times the regular pay for their expertise or distinguished service.
- Decurio (Decurion): Decurions were cavalry officers who commanded a squadron of 30 to 40 cavalrymen. They were highly skilled riders and played a crucial role in Roman cavalry tactics.
- Centurio (Centurion): Centurions were the backbone of the Roman army's leadership. They commanded a century, a unit of 80 to 100 soldiers, and were known for their bravery and tactical prowess.
- Tribunus Militum (Military Tribune): Military Tribunes were young officers, often from noble families, who served as senior commanders. They were responsible for leading and training the legionaries.
- Praefectus Castrorum (Camp Prefect): The Camp Prefect was the legion's third-in-command, responsible for overseeing the camp's administration, logistics, and defense.
- Legatus Legionis (Legate of the Legion): The Legate was the second-in-command of the legion, acting as the legion commander's deputy. They were often experienced and highly skilled officers.
- Legatus Augusti Pro Praetore (Governor): This rank denoted the governor of a province, who also served as the commander-in-chief of the province's legions. They were typically former consuls or praetors.
- Imperator (Commander-in-Chief): The highest military rank in Rome, the Imperator was the commander-in-chief of all Roman forces. This rank was typically held by the Emperor himself or a designated general.
- Princeps Senatus (First Man of the Senate): Although not a military rank per se, the Princeps Senatus held immense power and influence. They were the leader of the Roman Senate and often played a crucial role in military decision-making.
The Rise Through the Ranks: A Journey of Merit and Service

Advancement through the Roman military ranks was not solely based on time served but also on merit, skill, and bravery. Soldiers could rise through the ranks by displaying exceptional leadership, tactical prowess, or acts of valor on the battlefield.
Here's a closer look at the path to promotion:
- Merit: Soldiers who demonstrated exceptional skills, courage, or strategic thinking were often promoted to higher ranks. This could include acts of bravery in battle, successful completion of missions, or innovative tactics.
- Experience: While not a guarantee, experience played a significant role in advancement. Veterans who had served for many years and gained valuable battlefield experience were often considered for higher positions.
- Recommendations: Commanders and senior officers played a crucial role in recommending soldiers for promotion. Their assessments and endorsements carried significant weight in the promotion process.
- Training and Education: The Roman army placed a high value on education and training. Soldiers who invested in their own development, such as learning new skills or studying military tactics, were often favored for advancement.
The Roman Military: A Force to Be Reckoned With

The Roman military's success was not solely due to its disciplined soldiers and hierarchical structure but also to its innovative tactics, advanced weaponry, and strategic thinking. The Romans were masters of siege warfare, road building, and engineering, which gave them a significant advantage over their enemies.
The Roman army's strength lay in its ability to adapt and evolve. It embraced new technologies, such as the gladius sword and the pilum spear, and developed advanced tactics like the famous "Testudo" formation, which provided protection against enemy projectiles.
The Legacy of the Roman Soldier Ranks

The Roman soldier ranks left an indelible mark on military history, influencing the organization and structure of armies for centuries to come. The hierarchical system, with its clear chain of command and defined roles, set a standard for military efficiency and effectiveness.
Even today, many modern militaries still echo the Roman model, with ranks and roles that bear a striking resemblance to their ancient counterparts. The legacy of the Roman soldier ranks serves as a testament to the enduring impact of Rome's military might.
 Note: The information provided in this guide is based on historical records and scholarly research. However, it's important to note that the Roman military hierarchy was not static and could vary slightly depending on the period and specific legion.
Note: The information provided in this guide is based on historical records and scholarly research. However, it's important to note that the Roman military hierarchy was not static and could vary slightly depending on the period and specific legion.
Conclusion

Exploring the Roman soldier ranks provides a fascinating insight into the inner workings of one of history's most formidable military forces. From the humble private to the revered commander-in-chief, each rank played a vital role in the Roman army's success. The Roman military's hierarchical structure, combined with its disciplined soldiers and innovative tactics, solidified its place as a dominant force in the ancient world.
FAQ

What was the role of a Roman legionary?
+
Roman legionaries were the infantry soldiers who formed the backbone of the Roman army. They were trained to fight in close combat, using a variety of weapons, and were known for their discipline and loyalty.
How did soldiers advance through the ranks in the Roman army?

+
Advancement in the Roman army was based on merit, skill, and bravery. Soldiers could rise through the ranks by displaying exceptional leadership, tactical prowess, or acts of valor on the battlefield.
What was the highest military rank in Rome?

+
The highest military rank in Rome was the Imperator, which was typically held by the Emperor himself or a designated general. They were the commander-in-chief of all Roman forces.
How did the Roman military influence modern military structures?
+
The Roman military’s hierarchical structure and defined roles set a standard for military efficiency and effectiveness. Many modern militaries still echo the Roman model, with ranks and roles that bear a striking resemblance to their ancient counterparts.
What were some of the Roman army’s innovative tactics and technologies?

+
The Roman army was known for its innovative tactics, such as the “Testudo” formation, which provided protection against enemy projectiles. They also embraced new technologies like the gladius sword and the pilum spear.

