15 Volcano Facts: A Comprehensive Guide To Eruptions

Introduction
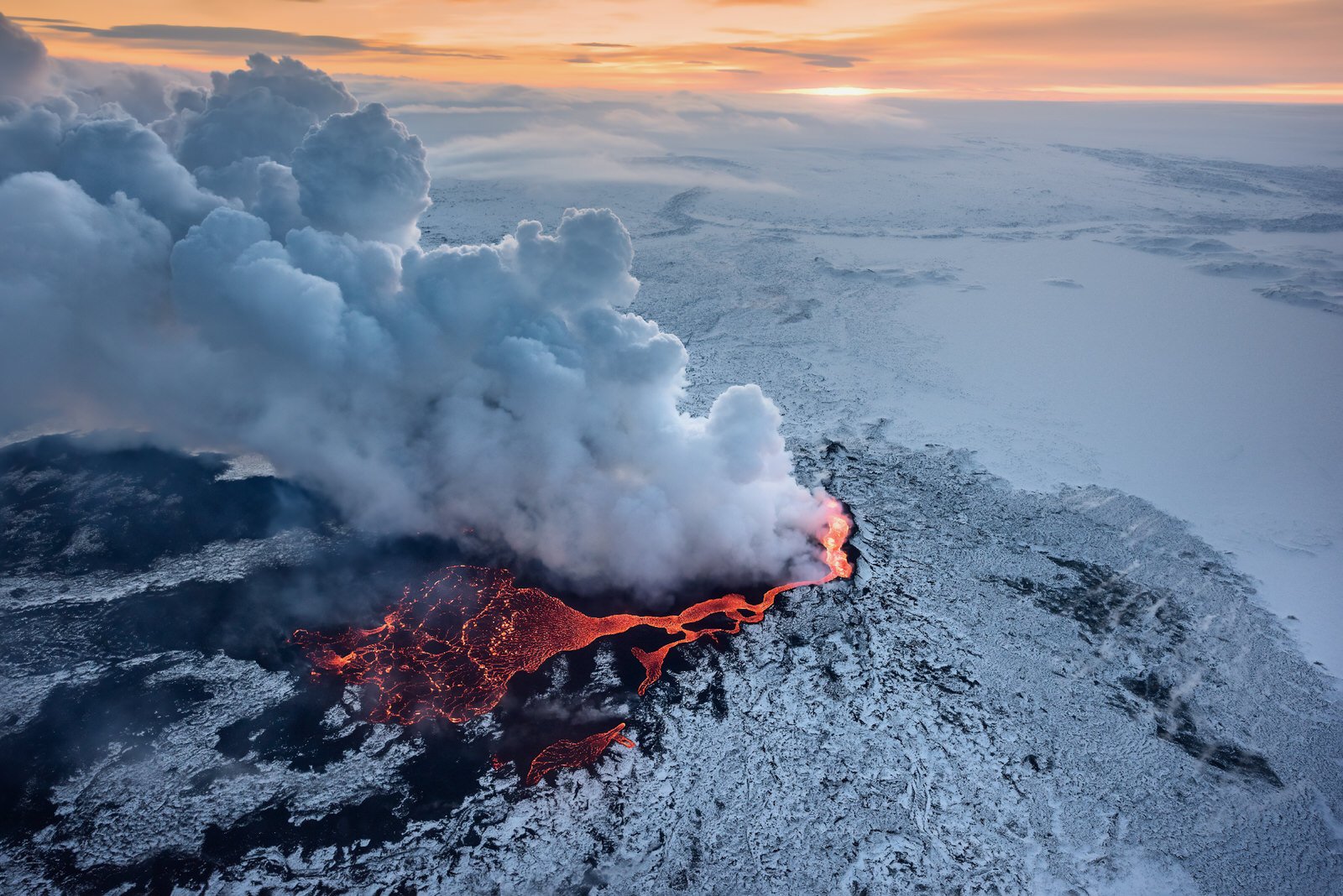

Volcanoes are awe-inspiring natural phenomena that have captivated humans for centuries. From their majestic eruptions to the rich ecosystems they support, volcanoes are a fascinating subject of study. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into 15 intriguing facts about volcanoes, exploring their formation, behavior, and impact on our planet. Get ready to embark on a volcanic journey!
Formation and Types

1. Volcanic Birth
Volcanoes are born from the intense heat and pressure deep within the Earth’s crust. They form when molten rock, known as magma, rises from the mantle and erupts onto the surface, creating a volcanic cone. This process is a result of tectonic plate movement and the Earth’s internal heat.
2. Volcano Classification
Volcanoes are classified based on their shape, size, and eruptive behavior. The three main types are:
Shield Volcanoes: Characterized by their gentle slopes and broad, low-profile shapes, shield volcanoes are formed by the eruption of fluid basaltic lava. They are often associated with hot spots, such as the Hawaiian Islands.
Stratovolcanoes (Composite Volcanoes): These volcanoes have a more conical shape and are composed of alternating layers of lava, ash, and pyroclastic material. They are known for their explosive eruptions and can be found along subduction zones, like Mount Fuji in Japan.
Cinder Cone Volcanoes: Cinder cones are smaller volcanoes with steep slopes formed by the accumulation of volcanic cinders and ash. They are often found on the flanks of larger volcanoes and can produce spectacular lava fountains during eruptions.
Eruptive Behavior
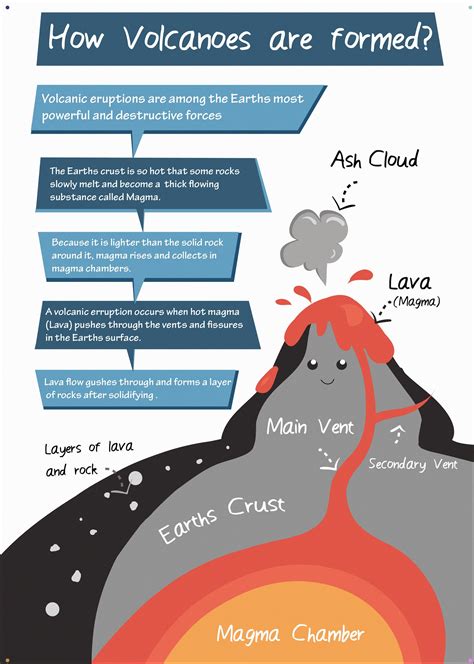
3. Eruption Styles
Volcanoes exhibit a wide range of eruptive behaviors, which can be broadly categorized into two main styles:
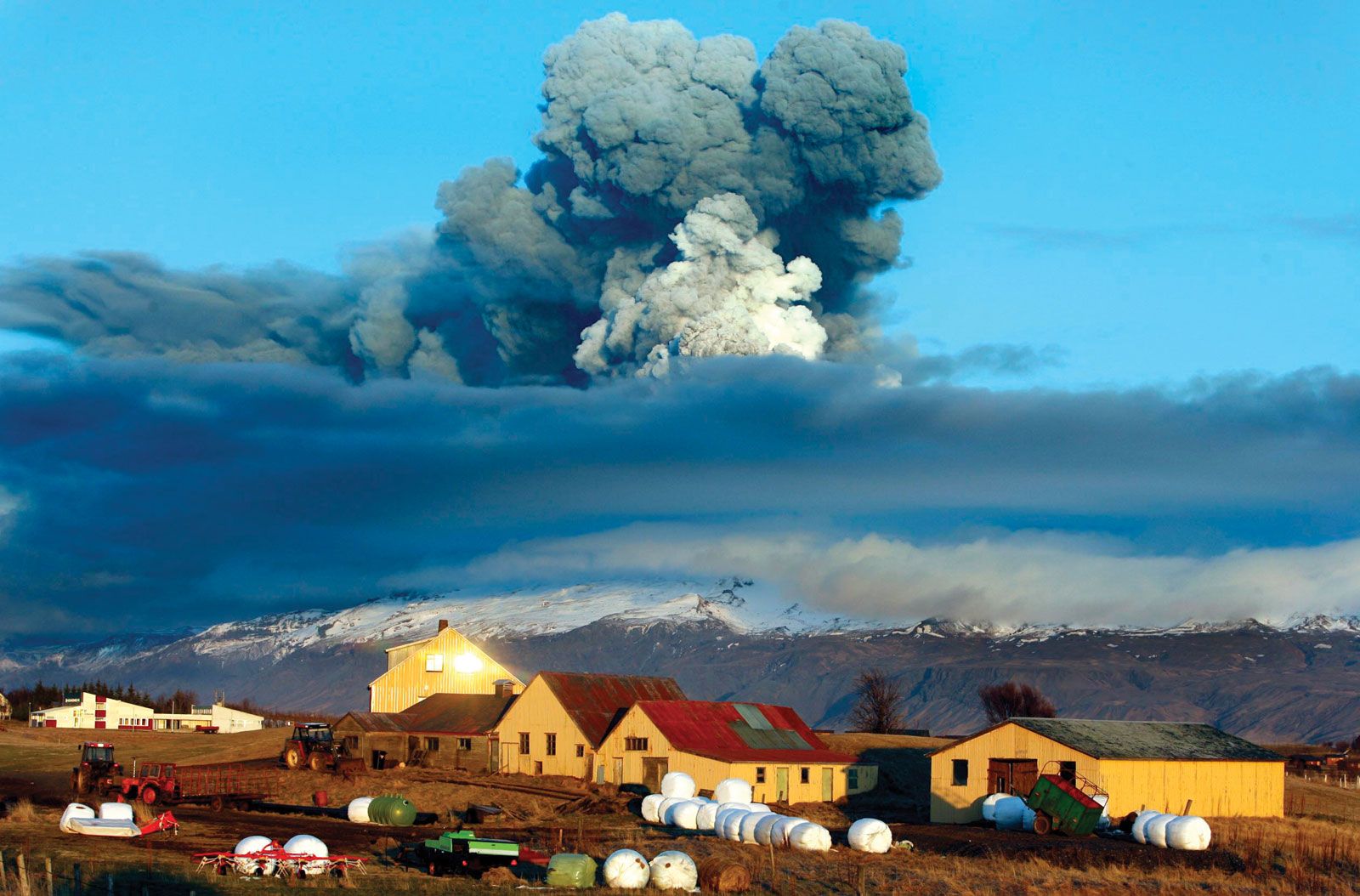
Explosive Eruptions: These eruptions are characterized by the rapid release of gas-rich magma, resulting in powerful explosions and the ejection of volcanic material. Explosive eruptions can be extremely hazardous and often produce ash clouds that can affect aviation and local populations.
Effusive Eruptions: In contrast, effusive eruptions involve the slow and steady flow of lava, creating rivers of molten rock. Effusive eruptions are generally less violent and can result in the formation of lava tubes and lava lakes.
4. Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI)
The Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) is a scale used to measure the magnitude of volcanic eruptions. It ranges from 0 to 8, with higher numbers indicating more explosive and destructive eruptions. The VEI takes into account factors such as the volume of ejected material, the height of the eruption column, and the duration of the eruption.
Volcanic Hazards

5. Pyroclastic Flows
One of the most dangerous volcanic hazards is the pyroclastic flow. These fast-moving currents of hot gas, ash, and volcanic material can reach speeds of up to 100 km/h (62 mph) and temperatures exceeding 1,000°C (1,832°F). Pyroclastic flows are extremely destructive and can devastate everything in their path.
6. Lahars
Lahars, also known as volcanic mudflows, are another significant hazard associated with volcanoes. They occur when volcanic material mixes with water, forming a dense and destructive flow. Lahars can travel long distances, burying and destroying anything in their path, including infrastructure and communities.
Impact on Environment

7. Volcanic Soils
Volcanic eruptions can have a positive impact on the environment by enriching soils with essential nutrients. Volcanic ash and lava deposits provide valuable minerals and nutrients, making volcanic soils highly fertile. These fertile soils support diverse ecosystems and contribute to the growth of lush vegetation.
8. Volcanic Gases
While volcanic gases can be harmful to humans and the environment, they also play a crucial role in the Earth’s climate. Gases such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and water vapor are released during eruptions and can have both short-term and long-term effects on the atmosphere. Volcanic gases can contribute to the formation of aerosols, which can influence global temperatures and climate patterns.
Volcanic Activity Around the World

9. Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire, also known as the Circum-Pacific Belt, is a region that encircles the Pacific Ocean and is home to a large number of active volcanoes. This volcanic hotspot is a result of the subduction of tectonic plates, leading to frequent volcanic activity and earthquakes.
10. Volcanic Hot Spots
Volcanic hot spots are areas where volcanic activity is concentrated, often far from plate boundaries. These hot spots are believed to be caused by mantle plumes, which are columns of hot, buoyant material rising from deep within the Earth. Famous volcanic hot spots include the Hawaiian Islands and the Yellowstone Caldera.
Volcano Monitoring and Prediction

11. Volcano Monitoring Techniques
Volcano monitoring is crucial for predicting and mitigating volcanic hazards. Scientists use various techniques to study volcanic activity, including:
Seismic Monitoring: Detecting and analyzing seismic activity to identify earthquake swarms and ground deformation.
Gas Emissions: Measuring the composition and quantity of gases emitted by volcanoes to detect changes that may indicate an impending eruption.
Ground Deformation: Monitoring the movement of the Earth’s surface using GPS and satellite technology to detect subtle changes that could signal magma movement.
Thermal Imaging: Using thermal cameras to detect heat signatures and identify areas of volcanic activity.
12. Eruption Prediction
While predicting volcanic eruptions is challenging, scientists have made significant progress in recent years. By combining data from various monitoring techniques and analyzing historical patterns, volcanologists can provide early warnings and evacuation notices to at-risk communities.
Volcanic Tourism

13. Volcanoes as Tourist Attractions
Volcanoes have become popular tourist destinations, attracting adventure seekers and nature enthusiasts from around the world. Some of the most visited volcanoes include:
Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania: This iconic volcano is a popular destination for hikers and climbers, offering breathtaking views and a chance to explore the diverse ecosystems of the mountain.
Mount Fuji, Japan: As one of the most recognizable volcanoes globally, Mount Fuji is a symbol of Japan’s culture and nature. It attracts thousands of visitors each year, many of whom aim to reach the summit.
Mount Etna, Italy: Mount Etna, the tallest active volcano in Europe, offers a unique experience with its frequent eruptions and stunning lava flows. Visitors can explore the volcanic landscape and witness the power of nature up close.
Volcanic Eruptions and Human History

14. Ancient Eruptions
Volcanic eruptions have left their mark on human history, often with devastating consequences. Some notable ancient eruptions include:
Thera Eruption (Santorini): The eruption of the Thera volcano around 1600 BCE is believed to have caused the decline of the Minoan civilization on the island of Santorini. The eruption triggered a massive tsunami and left a significant impact on the ancient world.
Mount Vesuvius (Pompeii): The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 CE buried the Roman cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum under ash and pyroclastic flows. The well-preserved remains of these cities provide a unique glimpse into ancient Roman life.
15. Modern Eruptions and Responses
In modern times, volcanic eruptions continue to pose challenges and threats to communities. However, with advanced monitoring and evacuation plans, the impact of eruptions can be minimized. Some recent notable eruptions include:
Eyjafjallajökull, Iceland (2010): The eruption of Eyjafjallajökull disrupted air travel across Europe due to the vast ash cloud it produced. The eruption highlighted the need for improved volcanic ash monitoring and aviation safety measures.
Mount St. Helens, USA (1980): The explosive eruption of Mount St. Helens was one of the most significant volcanic events in recent history. It resulted in the loss of lives and extensive damage to the surrounding area. The eruption led to advancements in volcanic research and emergency response protocols.
Notes:

🌋 Note: Always stay informed about volcanic activity and follow official guidelines if you plan to visit active volcanoes.
🌋 Note: Volcanic eruptions can be unpredictable, so it’s essential to respect the power of nature and prioritize safety.
Final Thoughts
Volcanoes are fascinating natural wonders that continue to captivate and inspire us. From their majestic eruptions to the rich ecosystems they support, volcanoes play a significant role in shaping our planet. By understanding their formation, behavior, and impact, we can appreciate the beauty and power of these geological marvels while also being aware of the potential hazards they pose.
Remember to stay informed, follow safety guidelines, and explore the wonders of volcanoes responsibly. Whether you’re an adventurer seeking volcanic landscapes or a researcher studying volcanic processes, volcanoes offer a wealth of knowledge and an unforgettable experience.
FAQ
What is the most active volcano in the world?
+The most active volcano in the world is Kīlauea in Hawaii. It has been erupting continuously since 1983, producing lava flows and volcanic gases.
Can volcanic eruptions be predicted accurately?
+While volcanic eruptions can be challenging to predict accurately, advancements in monitoring techniques and scientific understanding have improved prediction capabilities. However, some eruptions may still occur without prior warning.
What are the different stages of a volcanic eruption?
+A volcanic eruption typically goes through several stages, including pre-eruptive unrest, explosive eruption (if applicable), lava flow, and post-eruptive settling. Each stage can vary in duration and intensity.
How do volcanoes impact climate change?
+Volcanic eruptions can have both short-term and long-term effects on the climate. Short-term effects include the cooling of the atmosphere due to the presence of volcanic ash and aerosols. Long-term effects can include the release of greenhouse gases, which contribute to global warming.
Are volcanic eruptions always dangerous?
+Volcanic eruptions can range from relatively benign to extremely dangerous. The level of danger depends on various factors, including the type of eruption, the proximity of populated areas, and the availability of evacuation plans and resources.