18 Tutorials: Understand Standard Deviation Units And Their Impact
What is Standard Deviation?

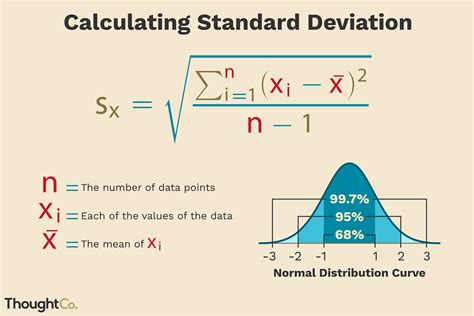
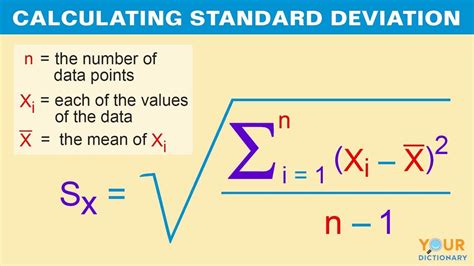
Standard deviation is a statistical measure that quantifies the amount of variation or dispersion in a set of data. It provides valuable insights into the spread of values within a dataset, helping us understand how tightly or loosely the data is clustered around the mean. In simple terms, it tells us how much individual data points deviate from the average. By calculating standard deviation, we can assess the consistency or variability of the data and make informed decisions based on its distribution.
Why is Standard Deviation Important?

Understanding standard deviation is crucial in various fields, including finance, economics, psychology, and data science. It allows us to:
- Assess Risk: Standard deviation is often used to measure the volatility or risk associated with investments or financial instruments. Higher standard deviation indicates greater variability and potential risk.
- Compare Datasets: By comparing the standard deviations of different datasets, we can evaluate their relative variability and make meaningful comparisons.
- Set Benchmarks: Standard deviation helps establish benchmarks or reference points for evaluating the performance of individuals, businesses, or processes.
- Identify Outliers: It enables us to identify extreme values or outliers that significantly deviate from the rest of the data, which can be useful for data cleaning and analysis.
- Analyze Patterns: Standard deviation assists in identifying patterns, trends, and anomalies within a dataset, aiding in decision-making and forecasting.
Calculating Standard Deviation

To calculate standard deviation, we follow these steps:
- Calculate the Mean: Determine the average value of the dataset by summing up all the values and dividing by the total number of data points.
- Find the Deviation: For each data point, calculate the difference between its value and the mean.
- Square the Deviations: Square each deviation to ensure positive values and avoid cancellation when summing.
- Sum the Squared Deviations: Add up all the squared deviations.
- Divide by the Number of Data Points: Divide the sum of squared deviations by the total number of data points to obtain the variance.
- Take the Square Root: Finally, take the square root of the variance to get the standard deviation.
Let’s illustrate this with an example:
Suppose we have a dataset with the following values: [2, 4, 6, 8, 10].
- Calculate the Mean: (2 + 4 + 6 + 8 + 10) / 5 = 4.
- Find the Deviations: [2 - 4, 4 - 4, 6 - 4, 8 - 4, 10 - 4] = [-2, 0, 2, 4, 6].
- Square the Deviations: [(-2)^2, (0)^2, (2)^2, (4)^2, (6)^2] = [4, 0, 4, 16, 36].
- Sum the Squared Deviations: 4 + 0 + 4 + 16 + 36 = 60.
- Divide by the Number of Data Points: 60 / 5 = 12.
- Take the Square Root: √12 ≈ 3.46.
So, the standard deviation for this dataset is approximately 3.46.
Interpreting Standard Deviation

Standard deviation helps us understand the spread of data and its implications:
- Low Standard Deviation: A small standard deviation indicates that the data points are closely clustered around the mean, suggesting a high degree of consistency or reliability.
- High Standard Deviation: A large standard deviation suggests that the data points are widely spread out, indicating greater variability or uncertainty.
- Comparing Standard Deviations: When comparing two datasets with different means, a larger standard deviation implies a wider spread of values, even if the means are similar.
Visualizing Standard Deviation

Visual representations, such as histograms or box plots, can help us interpret standard deviation more effectively. Histograms display the frequency of data points within specific ranges, while box plots provide a summary of the data’s distribution, including the median, quartiles, and outliers.
Standard Deviation in Real-World Applications

Standard deviation finds applications in various fields:
- Finance: It is used to measure the volatility of stock prices, interest rates, or investment portfolios, helping investors assess risk and make informed decisions.
- Economics: Standard deviation helps analyze economic indicators, such as GDP growth rates or inflation rates, to understand the stability or variability of an economy.
- Psychology: In psychological research, standard deviation is employed to assess the consistency of test scores or behavioral patterns.
- Quality Control: Manufacturers utilize standard deviation to monitor and control the quality of their products, ensuring consistency and meeting industry standards.
- Weather Forecasting: Meteorologists use standard deviation to measure the variability of weather patterns, aiding in predicting extreme weather events.
Normal Distribution and Standard Deviation

The normal distribution, also known as the Gaussian distribution, is a continuous probability distribution that follows a bell-shaped curve. Standard deviation plays a crucial role in understanding normal distributions:
- Mean and Standard Deviation: In a normal distribution, approximately 68% of the data falls within one standard deviation of the mean, 95% within two standard deviations, and 99.7% within three standard deviations.
- Symmetry and Central Tendency: The normal distribution is symmetric, with the mean, median, and mode coinciding at the center of the distribution.
- Standardizing Data: Standard deviation allows us to standardize data by converting it into a standard normal distribution, making it easier to compare and analyze different datasets.
Standard Deviation and Outliers

Outliers are data points that significantly deviate from the rest of the dataset and can heavily influence the standard deviation. It is essential to identify and handle outliers appropriately:
- Detecting Outliers: Outliers can be detected by comparing individual data points to the overall distribution or by using statistical methods like the Z-score or the interquartile range (IQR).
- Handling Outliers: Depending on the context, outliers may be removed, transformed, or treated as separate cases. It is crucial to carefully consider the impact of outliers on the analysis and make informed decisions.
Standard Deviation in Hypothesis Testing

Standard deviation is an essential component in hypothesis testing, a statistical method used to make inferences about a population based on sample data. It helps determine the significance of observed differences or relationships:
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses: Hypothesis testing involves setting up a null hypothesis (H0) and an alternative hypothesis (H1). The null hypothesis assumes no significant difference or relationship, while the alternative hypothesis suggests otherwise.
- Test Statistics: Standard deviation is used to calculate test statistics, such as the t-statistic or the F-statistic, which measure the magnitude of observed differences or relationships.
- Significance Level: The significance level, often denoted as α, determines the threshold for rejecting the null hypothesis. Common significance levels include 0.05 and 0.01.
- P-value: The p-value represents the probability of obtaining the observed data or more extreme results under the null hypothesis. If the p-value is less than the significance level, the null hypothesis is rejected.
Standard Deviation and Confidence Intervals
Confidence intervals provide a range of values within which we expect the true population parameter to lie with a certain level of confidence. Standard deviation is used to calculate confidence intervals:
- Confidence Level: The confidence level, often denoted as 1 - α, represents the probability that the true population parameter falls within the confidence interval. Common confidence levels include 95% and 99%.
- Margin of Error: The margin of error is half the width of the confidence interval and is calculated using the standard deviation and the critical value from the t-distribution (for small sample sizes) or the z-distribution (for large sample sizes).
- Calculating Confidence Intervals: Confidence intervals are constructed by adding and subtracting the margin of error from the sample mean. For example, a 95% confidence interval for the mean would be calculated as: mean ± (critical value * standard deviation / √n), where n is the sample size.
Standard Deviation and Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical technique used to model the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. Standard deviation plays a crucial role in regression analysis:
- Residuals: In regression analysis, residuals represent the differences between the observed values of the dependent variable and the predicted values based on the regression model. Standard deviation is used to measure the variability of these residuals.
- Standard Error of the Estimate: The standard error of the estimate is a measure of the average distance between the observed values and the predicted values. It is calculated as the square root of the mean squared error, which is the average of the squared residuals.
- R-squared: R-squared is a statistical measure that indicates the proportion of the variance in the dependent variable that can be explained by the independent variables in the regression model. It ranges from 0 to 1, with higher values indicating a better fit.
Standard Deviation and Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis involves analyzing and forecasting data that is collected sequentially over time. Standard deviation is an important tool in time series analysis:
- Autocorrelation: Autocorrelation measures the correlation between a time series and a lagged version of itself. Standard deviation is used to assess the significance of autocorrelation, as it helps determine whether the correlation is statistically significant or simply due to random fluctuations.
- Moving Averages: Moving averages are a common technique used in time series analysis to smooth out short-term fluctuations and identify long-term trends. Standard deviation is used to determine the optimal window size for moving averages, as it helps balance the trade-off between smoothing and preserving important trends.
- Forecasting: Standard deviation is also used in forecasting time series data. By calculating the standard deviation of the residuals from a forecasting model, we can assess the accuracy and reliability of the forecasts.
Standard Deviation and Risk Management
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks to achieve organizational goals. Standard deviation is a valuable tool in risk management:
- Risk Assessment: Standard deviation is used to quantify the volatility or uncertainty associated with different types of risks, such as market risk, credit risk, or operational risk. By calculating the standard deviation of historical data or simulating scenarios, risk managers can estimate the potential impact of risks on financial or operational outcomes.
- Risk Mitigation: Once risks have been identified and assessed, standard deviation helps in determining the appropriate risk mitigation strategies. For example, in portfolio management, risk managers may use standard deviation to measure the diversification benefits of different asset classes or to assess the effectiveness of hedging strategies.
- Risk Monitoring: Standard deviation is also used for ongoing risk monitoring. By regularly calculating and comparing standard deviations, risk managers can identify changes in risk levels and take proactive measures to manage them.
Conclusion
Standard deviation is a powerful statistical tool that provides valuable insights into the variability and distribution of data. It helps us assess risk, compare datasets, set benchmarks, identify outliers, and analyze patterns. By understanding standard deviation, we can make informed decisions and draw meaningful conclusions from our data. Whether it’s in finance, economics, psychology, or other fields, standard deviation plays a crucial role in quantifying uncertainty and guiding decision-making processes.
What is the formula for calculating standard deviation?
+The formula for calculating standard deviation is: √(∑(x - μ)^2 / n), where x represents each data point, μ is the mean, and n is the total number of data points.
How is standard deviation used in finance?
+In finance, standard deviation is used to measure the volatility of investment returns, helping investors assess risk and make informed decisions.
Can standard deviation be negative?
+No, standard deviation cannot be negative. It is always a positive value, representing the spread of data around the mean.
What is the relationship between standard deviation and variance?
+Variance is the square of the standard deviation. Standard deviation is the square root of the variance, providing a more intuitive measure of dispersion.
How does standard deviation affect the normal distribution?
+In a normal distribution, standard deviation determines the width of the bell-shaped curve. A larger standard deviation indicates a wider spread of values, while a smaller standard deviation indicates a narrower spread.