20+ Cattle Gestation Facts: Essential Guide For Farmers

Introduction to Cattle Gestation
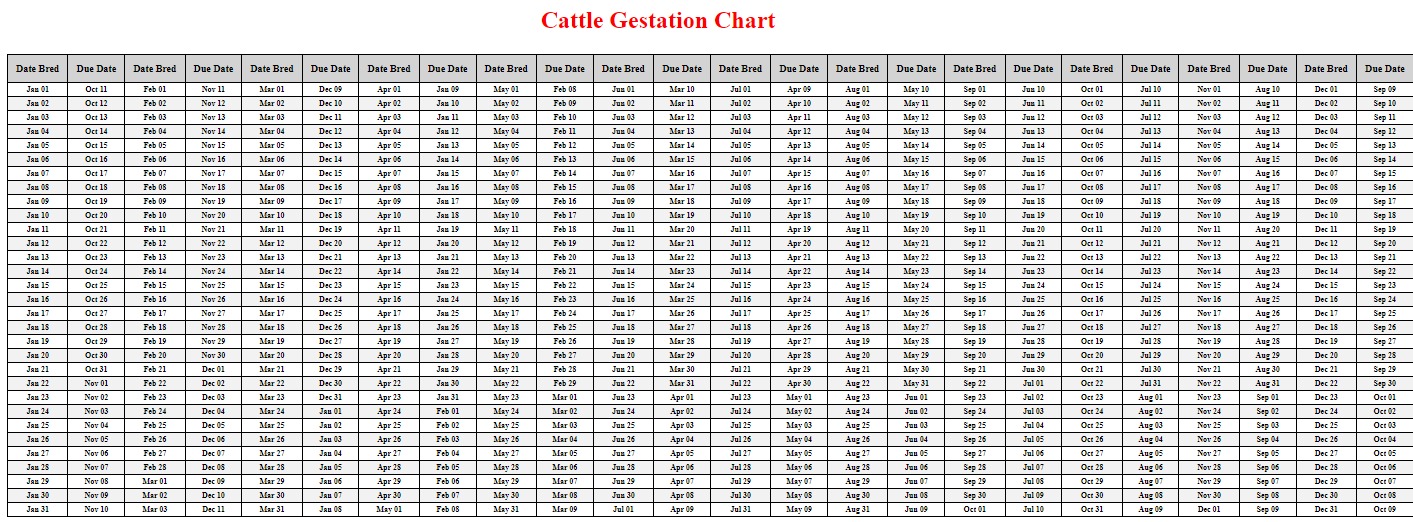
Understanding cattle gestation is crucial for farmers and ranchers as it directly impacts the success and profitability of their operations. Gestation, the period of pregnancy in cattle, requires careful management to ensure healthy calves and optimal herd productivity. This comprehensive guide will delve into the fascinating world of cattle gestation, providing farmers with essential insights and practical tips. From the unique reproductive cycle of cattle to the various factors influencing gestation, we will explore it all. So, let’s dive in and uncover the secrets of cattle gestation!
The Cattle Reproductive Cycle
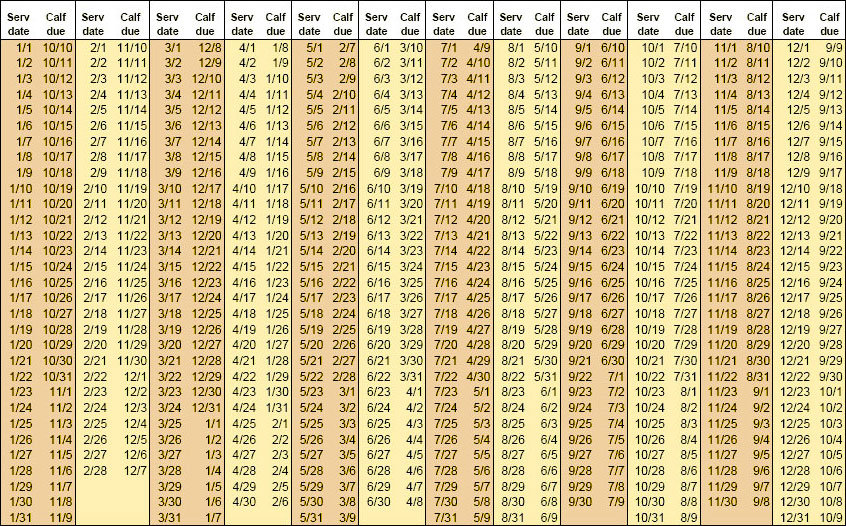
Cattle, like other mammals, have a well-defined reproductive cycle that consists of several distinct phases. Understanding this cycle is fundamental to managing cattle reproduction effectively. Here’s an overview of the key stages:
Estrus or Heat
- Definition: Estrus, commonly known as “heat,” is the period when a cow is receptive to breeding and can become pregnant. During this phase, the cow exhibits behavioral and physical changes, indicating her readiness for mating.
- Duration: Estrus typically lasts for 16 to 20 hours, but it can vary among individuals and breeds.
- Signs of Estrus: Look out for these signs to identify cows in heat:
- Mounting or being mounted by other cows.
- Standing to be mounted, a behavior known as “standing heat.”
- Mucous discharge from the vulva.
- Increased tail movement and restlessness.
Ovulation
- Timing: Ovulation, the release of an egg from the ovary, occurs near the end of the estrus cycle. It is crucial for successful fertilization.
- Significance: Proper timing of insemination relative to ovulation is essential for achieving pregnancy. Bulls or artificial insemination (AI) should be introduced or performed during this critical window.
Gestation Period
- Definition: Gestation is the time between conception and birth, during which the fetus develops and grows inside the cow’s uterus.
- Duration: The average gestation period in cattle is approximately 283 days, but it can range from 279 to 290 days.
- Factors Affecting Gestation: Several factors can influence the length of gestation, including breed, nutrition, and the health of the cow.
Parturition or Calving
- Definition: Parturition, commonly referred to as “calving,” is the process of giving birth to a calf.
- Signs of Impending Calving: As calving approaches, cows may display the following signs:
- A relaxed pelvic ligament.
- Enlargement and softening of the vulva.
- Waxing, the secretion of a waxy substance from the teats.
- Nesting behavior, where the cow seeks a secluded place to give birth.
Factors Influencing Cattle Gestation
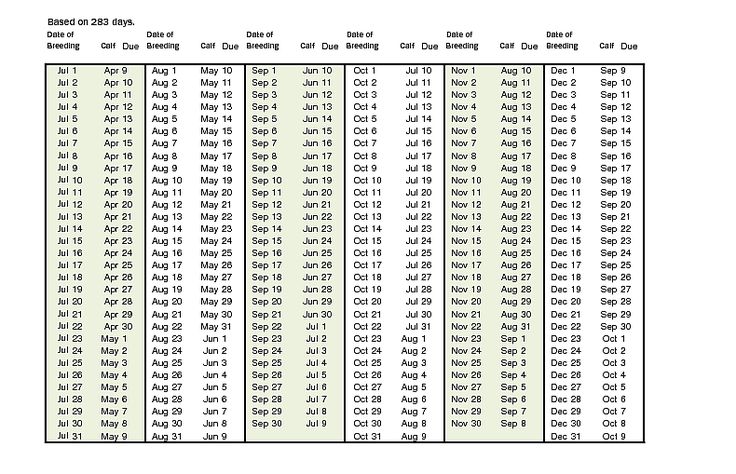
Numerous factors can impact the duration and success of cattle gestation. Being aware of these factors allows farmers to optimize reproductive management and ensure healthy pregnancies. Here are some key considerations:
Breed and Genetics
- Breed Variations: Different cattle breeds have varying gestation periods. For instance, dairy breeds like Holsteins tend to have slightly longer gestation periods compared to beef breeds like Angus.
- Genetic Influence: Genetic factors can affect the length of gestation and the overall reproductive performance of cattle. Selective breeding can help improve these traits over time.
Nutrition and Body Condition
- Nutrition: Proper nutrition is vital for maintaining a healthy reproductive cycle. Cows with adequate nutrition are more likely to conceive and carry pregnancies to term.
- Body Condition Scoring: Monitoring body condition through scoring systems helps farmers assess the nutritional status of their cattle. Aim for a moderate body condition score (BCS) of around 5 to ensure optimal reproductive health.
Health and Disease
- Health Status: The overall health of the cow plays a significant role in gestation. Cows with underlying health issues or diseases may experience complications during pregnancy.
- Disease Prevention: Implementing good biosecurity practices and regular veterinary care can help prevent diseases that could impact gestation, such as brucellosis or leptospirosis.
Environmental Factors
- Climate and Season: Environmental conditions can influence gestation. Extreme temperatures or stressful environments may affect reproductive performance.
- Comfort and Stress: Providing a comfortable and stress-free environment for cows during gestation is essential. Overcrowding or inadequate housing can lead to increased stress levels, potentially impacting pregnancy outcomes.
Management Practices
- Timing of Insemination: Proper timing of insemination or breeding is crucial for successful conception. Farmers should work closely with their veterinarians or AI technicians to determine the optimal time for breeding based on the cow’s reproductive cycle.
- Heat Detection: Accurate heat detection is essential for timely insemination. Visual observation, along with the use of heat detection aids like tail paint or electronic heat detection devices, can improve detection accuracy.
Managing Cattle Gestation
Effective management of cattle gestation involves a combination of careful planning, monitoring, and timely interventions. Here are some key strategies for farmers to consider:
Breeding and Insemination
- Breed Selection: Choose bulls or semen with desirable traits, such as fertility, milk production, or growth rate, to improve the genetic potential of the herd.
- Artificial Insemination (AI): AI offers several advantages, including the ability to select high-quality genetics, reduce the risk of disease transmission, and improve conception rates. Consult with a veterinarian or AI technician for guidance.
Pregnancy Diagnosis
- Palpation: Experienced veterinarians can perform rectal palpation to detect pregnancy as early as 30 to 40 days after breeding. This method is useful for confirming pregnancy and estimating the expected calving date.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound technology provides a non-invasive and accurate way to diagnose pregnancy and assess fetal development. It can be performed as early as 28 to 35 days after breeding.
Gestation Monitoring
- Body Condition Scoring: Regularly monitor the body condition of pregnant cows to ensure they maintain an optimal BCS throughout gestation. Adjust feeding programs as needed.
- Health Monitoring: Keep a close eye on the overall health of pregnant cows. Promptly address any health issues or diseases that may arise during gestation.
Calving Management
- Calving Assistance: Be prepared for calving emergencies by having the necessary equipment and knowledge to assist cows during difficult births. Consult with a veterinarian for guidance on calving management.
- Colostrum Management: Ensure that newborn calves receive adequate colostrum, the first milk produced by the cow, within the first few hours of life. Colostrum provides essential antibodies and nutrients for the calf’s health and immunity.
Common Gestation Challenges and Solutions
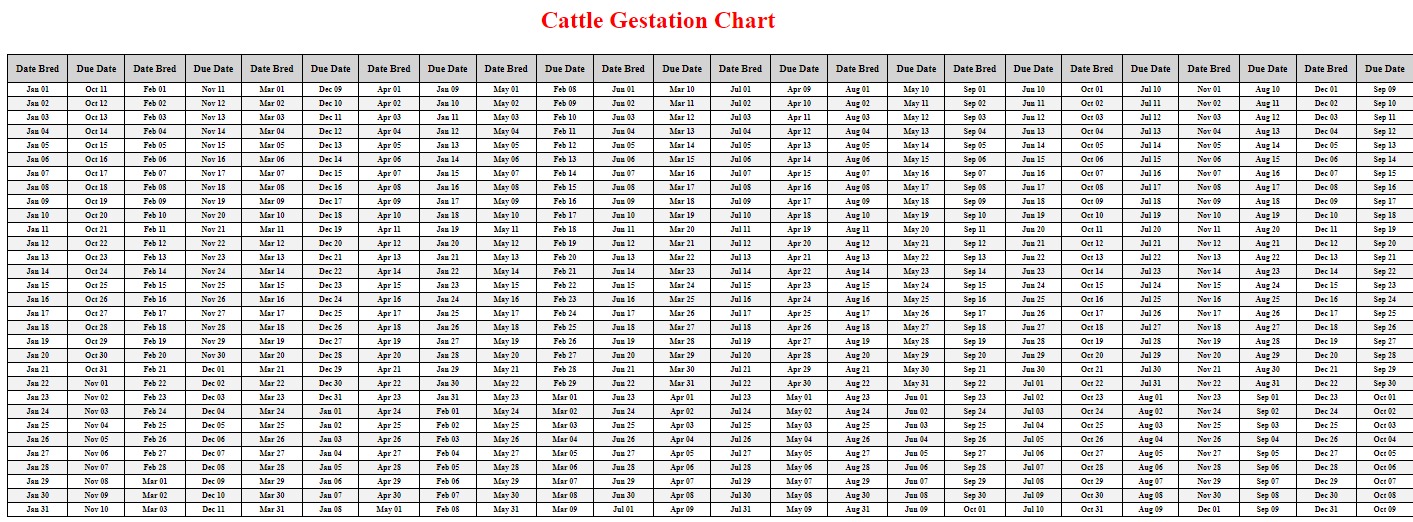
Cattle gestation is not without its challenges. Farmers may encounter various issues during the reproductive cycle. Here are some common challenges and practical solutions:
Anestrus or Prolonged Intervals Between Estruses
- Definition: Anestrus is the absence of estrus or heat cycles. It can occur due to nutritional deficiencies, disease, or stress.
- Solution:
- Improve nutrition and provide a balanced diet.
- Address any underlying health issues.
- Consider using hormonal treatments under veterinary guidance to induce estrus.
Abortion or Embryonic Loss
- Causes: Abortion can be caused by various factors, including disease, nutritional deficiencies, or trauma.
- Prevention:
- Implement biosecurity measures to prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
- Provide a balanced diet and ensure adequate mineral supplementation.
- Minimize stress and provide a calm environment during gestation.
Dystocia or Difficult Calving
- Definition: Dystocia refers to difficult or prolonged calving, often requiring assistance.
- Management:
- Be prepared with calving equipment and have a veterinarian’s contact information readily available.
- Learn proper calving assistance techniques, such as pulling calves or using calving aids.
- Monitor cows closely during the calving season and intervene promptly if needed.
Advanced Gestation Techniques
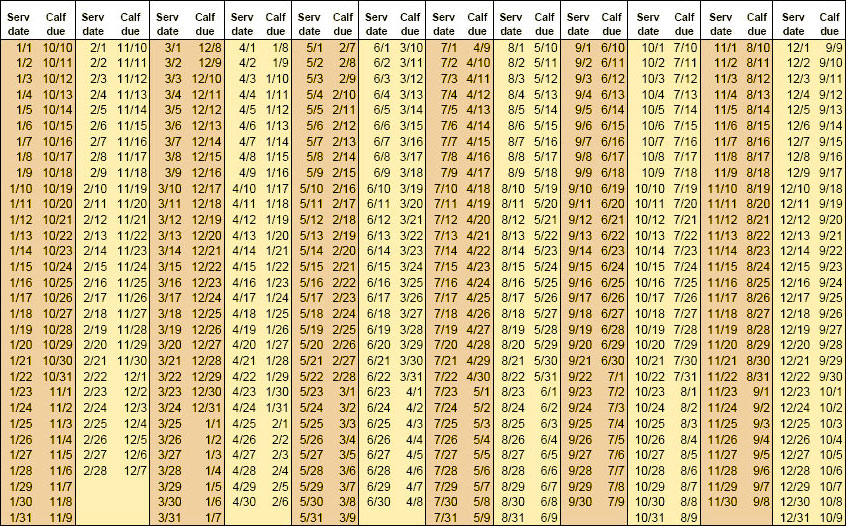
For farmers seeking to optimize their reproductive management, several advanced techniques can be employed:
Embryo Transfer
- Process: Embryo transfer involves the collection of high-quality embryos from donor cows and transferring them to recipient cows for gestation.
- Advantages: This technique allows for the propagation of superior genetics and can increase the number of calves born from a single breeding season.
Synchronization of Estrus
- Definition: Estrus synchronization involves the use of hormonal treatments to control and synchronize the estrus cycles of a group of cows.
- Benefits: Synchronization simplifies breeding management, allowing farmers to inseminate a larger number of cows within a shorter time frame.
Sexed Semen
- Technology: Sexed semen is a technology that allows for the selection of sperm with a specific gender, either male or female.
- Application: Farmers can use sexed semen to selectively produce male or female calves, depending on their breeding goals.
Conclusion
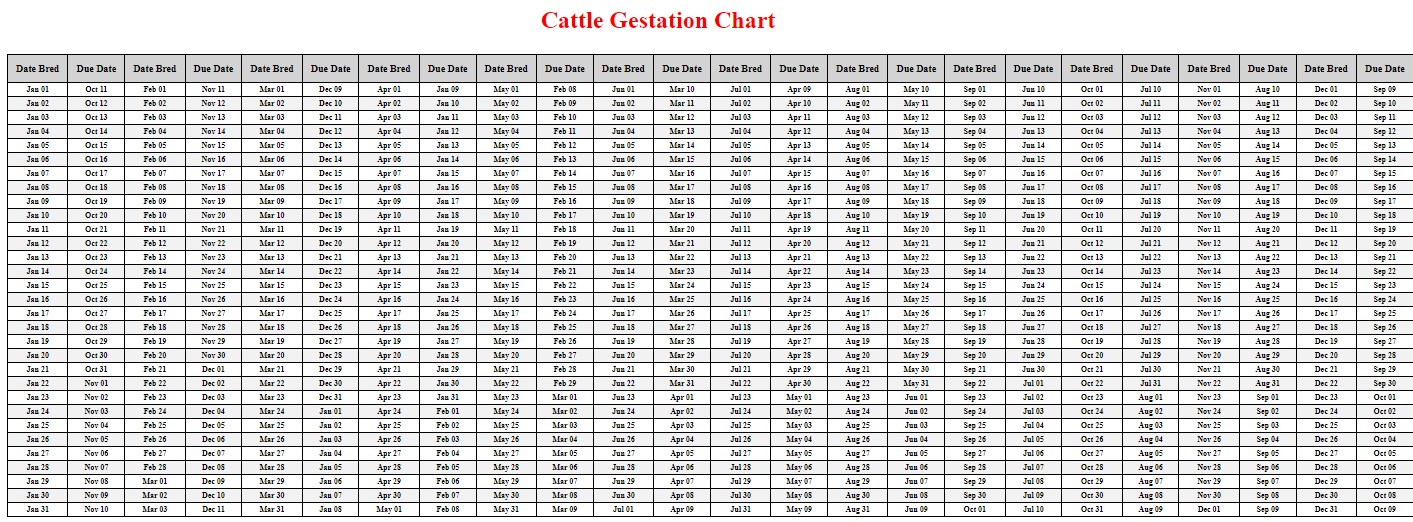
Cattle gestation is a complex and fascinating process that requires careful management and attention to detail. By understanding the cattle reproductive cycle, factors influencing gestation, and effective management strategies, farmers can optimize reproductive performance and ensure healthy pregnancies. From proper breeding techniques to advanced technologies like embryo transfer and estrus synchronization, there are numerous tools available to enhance cattle reproduction. With the right knowledge and proactive management, farmers can achieve successful cattle gestation and contribute to the sustainability and profitability of their operations.
FAQ
How long is the average gestation period in cattle?
+The average gestation period in cattle is approximately 283 days, but it can range from 279 to 290 days.
What are the signs of a cow in heat (estrus)?
+Cows in heat may exhibit mounting behavior, stand to be mounted, have a mucous discharge from the vulva, and show increased tail movement and restlessness.
How can I improve the reproductive performance of my cattle herd?
+To improve reproductive performance, focus on proper nutrition, maintain a moderate body condition score, implement good biosecurity practices, and consider advanced techniques like embryo transfer or estrus synchronization.
What should I do if I suspect a cow is experiencing a difficult calving (dystocia)?
+If you suspect dystocia, contact a veterinarian immediately. They can provide guidance and assistance during difficult calving situations.
Can I use sexed semen to selectively produce male or female calves?
+Yes, sexed semen technology allows farmers to choose the gender of their calves. This can be useful for specific breeding goals, such as producing dairy heifers or beef steers.