20+ Ways To Calculate A1c: The Ultimate Guide To Mastering Your Diabetes Care
Introduction

A1c, or glycated hemoglobin, is a crucial measure for individuals with diabetes as it provides an overview of their average blood sugar levels over the past 2–3 months. Understanding and managing A1c levels is essential for effective diabetes care and preventing complications. This comprehensive guide aims to explore various methods and tools available for calculating A1c, empowering individuals to take control of their health and make informed decisions.
Understanding A1c

Before delving into the calculation methods, it’s important to grasp the concept of A1c and its significance. A1c is a measure of the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that has glucose attached to it. Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen. When glucose binds to hemoglobin, it forms glycated hemoglobin, which remains in the bloodstream for the life of the red blood cell, approximately 120 days.
By analyzing the A1c level, healthcare professionals can assess an individual’s average blood sugar control over an extended period. This long-term view helps identify trends and make adjustments to diabetes management plans. A1c is typically measured through a simple blood test, offering valuable insights into overall diabetes control.
Calculating A1c: Methods and Tools
1. Laboratory Testing

The most common and accurate method for determining A1c is through laboratory testing. This involves a small blood sample being drawn and sent to a laboratory for analysis. The result is usually available within a few days. Laboratory testing is considered the gold standard for A1c measurement, providing precise and reliable data.
2. Point-of-Care Testing

Point-of-care (POC) testing offers a convenient alternative to laboratory testing. These tests can be performed in a healthcare provider’s office or even at home using a POC A1c test kit. The process involves a finger-stick blood sample, which is then analyzed by a portable device. Results are typically available within minutes, allowing for quick assessment and decision-making.
3. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)

Continuous glucose monitoring systems provide real-time glucose data and can also estimate A1c levels. CGM devices use a small sensor inserted under the skin to continuously measure glucose levels. Over time, these devices can calculate an estimated A1c value, offering a more comprehensive view of glucose control.
4. A1c Calculators

Numerous online A1c calculators are available, offering a convenient way to estimate A1c levels. These calculators typically require inputting average blood sugar readings and the duration of diabetes. While not as accurate as laboratory tests, they can provide a rough estimate and help track progress over time.
5. A1c Conversion Formulas
For those with access to their average blood sugar levels, conversion formulas can be used to estimate A1c. These formulas consider factors such as the average blood sugar level and the duration of diabetes. While not as precise as laboratory tests, they can give a general idea of A1c levels.
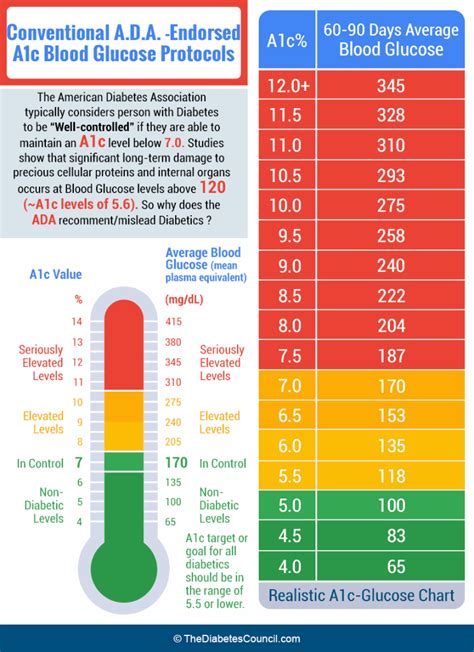
6. Average Blood Sugar to A1c Conversion Table

An average blood sugar to A1c conversion table can be a useful tool for estimating A1c levels. This table provides a quick reference to convert average blood sugar readings into A1c percentages. It is important to note that this method assumes a constant blood sugar level, which may not always be the case.
7. Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG)
Self-monitoring of blood glucose involves regularly testing blood sugar levels at home using a glucose meter. While SMBG does not directly measure A1c, it provides valuable data for estimating A1c levels. By tracking blood sugar trends and averages, individuals can gain insights into their overall glucose control.
8. Glucose Logs and Trends
Maintaining detailed glucose logs and analyzing trends can be an effective way to estimate A1c levels. By tracking blood sugar readings over time, individuals can identify patterns and calculate average blood sugar levels. This information can then be used to estimate A1c, providing a snapshot of glucose control.
9. A1c Self-Testing Kits

A1c self-testing kits are available for home use, offering a convenient and accessible way to measure A1c levels. These kits typically involve a finger-stick blood sample, which is then analyzed using a test strip and a portable device. Results are usually available within minutes, allowing individuals to monitor their A1c levels regularly.
10. Healthcare Provider Assessment

Healthcare providers, such as endocrinologists or diabetes specialists, play a crucial role in A1c management. They can assess an individual’s overall diabetes control, review glucose logs, and interpret A1c test results. Their expertise and guidance are invaluable in optimizing diabetes management plans.
11. Regular A1c Testing
Regular A1c testing is essential for effective diabetes management. The frequency of testing may vary depending on individual needs and recommendations from healthcare providers. Generally, it is recommended to have an A1c test at least twice a year, or more frequently if necessary.
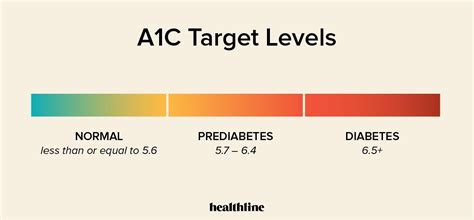
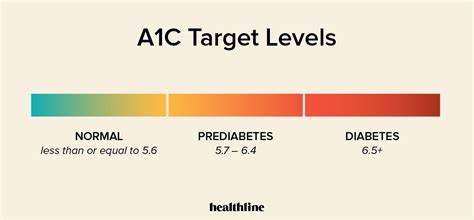
12. Understanding A1c Targets
Setting and understanding A1c targets is crucial for diabetes management. The American Diabetes Association recommends an A1c target of % for most non-pregnant adults with diabetes. However, individual targets may vary based on factors such as age, overall health, and the presence of diabetes complications.
13. Interpreting A1c Results
Interpreting A1c results requires understanding the context and trends. A single A1c measurement may not provide a complete picture, as glucose levels can fluctuate. It is important to consider the overall trend and discuss any concerns or questions with a healthcare provider.
14. Tracking A1c Over Time
Tracking A1c levels over time is essential for monitoring progress and making adjustments to diabetes management plans. By comparing A1c results over several months or years, individuals can identify patterns, assess the effectiveness of their current approach, and make necessary changes.
15. A1c and Diabetes Complications
A1c levels are closely linked to the risk of diabetes complications. High A1c levels over an extended period can increase the likelihood of developing complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Maintaining optimal A1c levels is crucial for reducing these risks.
16. Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a significant role in managing A1c levels. Adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress can all positively impact A1c. Making sustainable lifestyle changes is key to long-term diabetes management.
17. Medication Adjustments
For individuals with diabetes, medication adjustments may be necessary to achieve optimal A1c levels. Working closely with a healthcare provider to find the right medication regimen and dosage is essential. Regular monitoring and adjustments can help ensure effective glucose control.
18. Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is often a crucial component of diabetes management, especially for individuals with type 1 diabetes or those with advanced type 2 diabetes. Insulin helps regulate blood sugar levels and can significantly impact A1c. Working with a healthcare provider to optimize insulin therapy is vital for achieving target A1c levels.
19. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Integration
Integrating CGM data with A1c measurements can provide a more comprehensive view of glucose control. CGM devices offer real-time glucose readings, allowing individuals to identify patterns, detect trends, and make timely adjustments to their diabetes management plan.
20. Self-Management Education
Self-management education is essential for individuals with diabetes to understand their condition and make informed decisions. Learning about diabetes, its impact on the body, and effective management strategies can empower individuals to take control of their health. Seeking support from diabetes educators or support groups can be beneficial.
21. Technology and Apps
Technology and mobile apps can be valuable tools for managing diabetes and tracking A1c levels. There are numerous apps available that allow individuals to log blood sugar readings, track trends, and estimate A1c. These apps can provide convenient and accessible ways to monitor diabetes and make informed decisions.
Conclusion

Calculating and managing A1c levels is a crucial aspect of diabetes care. By utilizing the various methods and tools outlined in this guide, individuals can take an active role in their diabetes management. Regular A1c testing, combined with lifestyle modifications, medication adjustments, and self-management education, can help achieve optimal A1c levels and reduce the risk of diabetes complications. Remember, effective diabetes management is a journey, and with the right tools and support, individuals can thrive and lead healthy lives.
FAQ

What is the difference between A1c and average blood sugar levels?
+A1c represents the average blood sugar levels over a period of 2-3 months, while average blood sugar levels refer to the average of individual glucose readings taken at different times.
How often should I get my A1c tested?
+The frequency of A1c testing may vary depending on individual needs and recommendations from healthcare providers. Generally, it is recommended to have an A1c test at least twice a year.
Can I estimate my A1c at home without a test kit or laboratory testing?
+Yes, there are several methods to estimate A1c at home, such as using A1c calculators, conversion formulas, or average blood sugar to A1c conversion tables. However, these methods may not be as accurate as laboratory tests.
What are the benefits of using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) for A1c estimation?
+CGM provides real-time glucose data and can estimate A1c levels. It offers a more comprehensive view of glucose control, allowing individuals to identify patterns and make timely adjustments to their diabetes management plan.
How can I optimize my diabetes management plan based on my A1c results?
+Discuss your A1c results with your healthcare provider, who can assess your overall diabetes control and provide guidance on lifestyle modifications, medication adjustments, and insulin therapy if necessary.
