Acid Reflux And Coughing

Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a common digestive issue that can lead to various uncomfortable symptoms, including coughing. When acid from the stomach flows back into the esophagus, it can irritate the throat and trigger a persistent cough. Understanding the connection between acid reflux and coughing is crucial for managing this condition effectively. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for acid reflux-related coughing, providing valuable insights for those seeking relief.
Understanding Acid Reflux and Its Impact on Coughing

Acid reflux occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a muscle that acts as a valve between the stomach and esophagus, weakens or relaxes inappropriately. This allows stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus, causing a burning sensation known as heartburn. However, the impact of acid reflux extends beyond heartburn, as it can also irritate the throat and vocal cords, leading to a persistent cough.
The connection between acid reflux and coughing is often overlooked, as many individuals associate coughing with respiratory conditions. However, when coughing persists without any signs of a respiratory infection, it could be a symptom of underlying acid reflux. Recognizing this link is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
Causes of Acid Reflux-Related Coughing

Acid reflux-related coughing can be triggered by various factors. Here are some common causes:
- Weakened Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES): A weakened LES is a primary cause of acid reflux. When the LES fails to close tightly, it allows stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus, leading to irritation and coughing.
- Hiatal Hernia: A hiatal hernia occurs when a portion of the stomach pushes up through the diaphragm, causing the LES to malfunction. This can result in acid reflux and subsequent coughing.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts pressure on the abdomen, pushing stomach acid upwards and causing reflux. Obesity is a significant risk factor for acid reflux and related coughing.
- Dietary Factors: Certain foods and beverages can trigger acid reflux. Spicy foods, citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate, caffeine, and alcohol are common culprits. Consuming these triggers can lead to acid reflux and coughing.
- Lying Down or Bending Over: Gravity plays a role in acid reflux. When you lie down or bend over, it becomes easier for stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus, especially after eating. This can result in nighttime coughing episodes.
- Smoking: Smoking irritates the throat and weakens the LES, making it more susceptible to acid reflux. Smoking is a significant risk factor for acid reflux-related coughing.
Symptoms of Acid Reflux-Related Coughing
Coughing due to acid reflux can present with various symptoms. Here are some common indicators:
- Persistent Cough: A dry, non-productive cough that lasts for an extended period is a classic symptom of acid reflux-related coughing. It may worsen at night or after meals.
- Sore Throat: Acid reflux can irritate the throat, leading to a sore or scratchy throat. This sensation may be more prominent in the morning or after eating.
- Hoarseness: The irritation caused by stomach acid can affect the vocal cords, resulting in hoarseness or a change in voice quality.
- Postnasal Drip: Acid reflux can stimulate the production of excess mucus, leading to postnasal drip. This can further irritate the throat and trigger coughing.
- Chronic Throat Clearing: Individuals with acid reflux-related coughing may find themselves frequently clearing their throat due to the irritation caused by stomach acid.
Diagnosing Acid Reflux-Related Coughing

Diagnosing acid reflux-related coughing involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. Here are some steps that may be taken during the diagnostic process:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Your doctor will review your medical history, including any existing health conditions and medications. They will also perform a physical examination to assess your overall health.
- Endoscopy: An endoscopy is a procedure where a thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted into your esophagus to visualize the area. This allows the doctor to examine the esophagus for signs of irritation or damage caused by acid reflux.
- pH Monitoring: pH monitoring involves placing a small tube through your nose into the esophagus to measure the acidity levels. This test helps determine if stomach acid is reaching the esophagus and causing reflux.
- Manometry: Manometry is used to measure the pressure and function of the LES. It helps evaluate the strength and coordination of the LES, providing insights into the cause of acid reflux.
- Barium Swallow Study: This imaging test involves swallowing a liquid containing barium, which coats the esophagus and makes it visible on X-rays. It helps identify any structural abnormalities or reflux episodes.
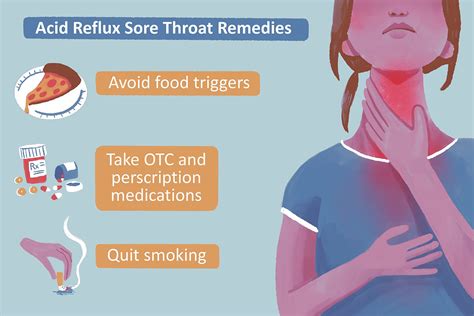
Treatment Options for Acid Reflux-Related Coughing
Treating acid reflux-related coughing involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and, in severe cases, surgical interventions. Here are some effective treatment approaches:
Lifestyle Modifications
- Dietary Changes: Avoiding trigger foods and adopting a healthy, balanced diet can significantly reduce acid reflux symptoms. Limiting spicy foods, citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate, caffeine, and alcohol is often recommended.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can alleviate pressure on the abdomen, reducing the likelihood of acid reflux. Losing excess weight through a combination of diet and exercise is beneficial.
- Elevating the Head of the Bed: Raising the head of your bed by 6-8 inches can help prevent acid reflux by using gravity to keep stomach acid down. This simple adjustment can provide relief during sleep.
- Avoiding Late-Night Meals: Eating close to bedtime can trigger acid reflux. It is advisable to finish your last meal at least 2-3 hours before lying down to allow sufficient time for digestion.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking cessation is crucial for managing acid reflux-related coughing. Quitting smoking can improve LES function and reduce throat irritation.
Medications
- Antacids: Over-the-counter antacids can provide quick relief by neutralizing stomach acid. However, they are a temporary solution and may not address the underlying cause of acid reflux.
- H2 Receptor Blockers: These medications reduce acid production in the stomach and are available over-the-counter or by prescription. They provide long-lasting relief for acid reflux symptoms.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): PPIs are prescription medications that block acid production and are highly effective in managing acid reflux. They are often recommended for long-term management.
- Promotility Agents: In some cases, promotility agents may be prescribed to improve the movement of food through the digestive tract, reducing the risk of acid reflux.
Surgical Interventions
In severe cases of acid reflux that do not respond to lifestyle modifications and medications, surgical interventions may be considered. Here are some surgical options:
- Nissen Fundoplication: This surgical procedure involves wrapping the upper part of the stomach around the LES to strengthen it and prevent acid reflux. It is typically performed laparoscopically.
- LINX Device: The LINX device is a small, flexible band of magnets placed around the LES. It helps reinforce the LES, preventing acid reflux while allowing food to pass through.
Managing Acid Reflux-Related Coughing at Home

In addition to medical treatments, there are several home remedies and self-care measures that can help manage acid reflux-related coughing. Here are some effective strategies:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help dilute stomach acid and soothe the throat. Aim for 8-10 glasses of water per day.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Identify and avoid foods that trigger your acid reflux. Keep a food diary to track your symptoms and make informed dietary choices.
- Chew Gum: Chewing sugar-free gum can stimulate saliva production, which helps neutralize stomach acid and provide relief from coughing.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Stress and anxiety can worsen acid reflux symptoms. Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help manage stress and reduce coughing episodes.
- Use a Humidifier: Dry air can irritate the throat and exacerbate coughing. Using a humidifier in your bedroom can add moisture to the air, providing relief and soothing the throat.
When to Seek Medical Attention

While acid reflux-related coughing can often be managed with lifestyle modifications and over-the-counter medications, there are situations where medical attention is necessary. Here are some red flags that indicate you should consult a healthcare professional:
- Coughing that persists for an extended period without improvement.
- Severe or persistent chest pain.
- Difficulty swallowing or a feeling of food getting stuck in the throat.
- Unintentional weight loss.
- Chronic hoarseness or voice changes.
- Recurring pneumonia or respiratory infections.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical advice to rule out more serious conditions and receive appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
Acid reflux-related coughing can significantly impact your quality of life, but with proper management, relief is possible. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take control of your condition and find effective solutions. Remember, seeking medical guidance is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. With the right approach, you can bid farewell to acid reflux-related coughing and enjoy a healthier, more comfortable life.
Can acid reflux cause a persistent cough without heartburn symptoms?
+Yes, it is possible to experience acid reflux-related coughing without noticeable heartburn symptoms. Coughing can be the primary or only symptom of acid reflux, especially when it persists for an extended period.
Are there any natural remedies for acid reflux-related coughing?
+While natural remedies can provide temporary relief, they may not address the underlying cause of acid reflux. It is best to consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive treatment plan. However, some natural remedies like ginger, aloe vera, and slippery elm have shown potential in soothing throat irritation.
Can acid reflux-related coughing be a sign of a more serious condition?
+In some cases, persistent coughing can be a symptom of a more serious condition, such as asthma, pneumonia, or even lung cancer. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if your cough persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
How long does it take for acid reflux-related coughing to improve with treatment?
+The time it takes for acid reflux-related coughing to improve varies depending on the individual and the treatment approach. With lifestyle modifications and medications, you may notice improvement within a few weeks. However, it is essential to be patient and consistent with your treatment plan for long-term relief.
Can children experience acid reflux-related coughing?
+Yes, children can also experience acid reflux-related coughing. In infants and young children, it may present as frequent spitting up, vomiting, or irritability after feeding. It is important to consult a pediatrician for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.


