Bell Shaped Histogram

A bell-shaped histogram, also known as a normal distribution, is a fundamental concept in statistics and data analysis. It is characterized by a symmetrical, bell-like curve that represents the distribution of data points around a central value. Understanding and interpreting bell-shaped histograms is crucial for various fields, including science, engineering, and social sciences, as it provides valuable insights into the underlying patterns and trends in the data.
Understanding Bell-Shaped Histograms
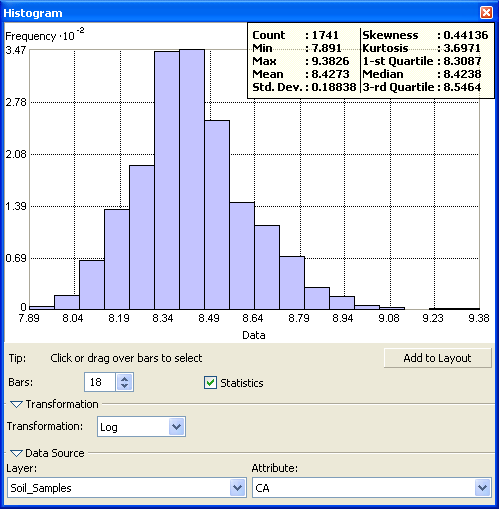
A bell-shaped histogram is a graphical representation of data that follows a normal distribution. It is a visual display of the frequency or count of data points falling within specific intervals or bins. The histogram takes the shape of a symmetrical bell curve, with the highest point, or peak, representing the mode or most frequent value.
The normal distribution is defined by two key parameters: the mean and the standard deviation. The mean represents the central tendency of the data, while the standard deviation measures the dispersion or spread of the data points around the mean. In a bell-shaped histogram, the mean and median coincide, indicating a balanced distribution.
Characteristics of Bell-Shaped Histograms

Bell-shaped histograms exhibit several distinctive characteristics:
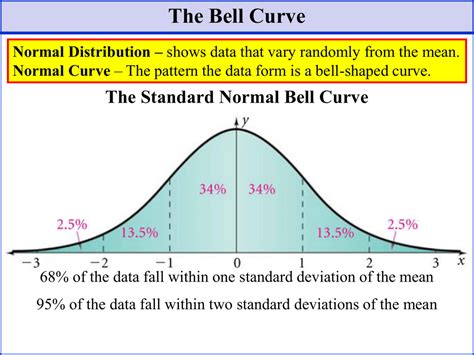
- Symmetry: The histogram is symmetric about the mean, meaning that the left and right sides of the curve are mirror images of each other.
- Mode: The mode, or the most frequent value, is located at the peak of the curve.
- Skewness: Bell-shaped histograms are typically not skewed, as the mean, median, and mode are approximately equal.
- Kurtosis: The kurtosis, or the measure of peakedness, is close to zero, indicating a distribution that is neither too peaked nor too flat.
Creating a Bell-Shaped Histogram

To create a bell-shaped histogram, follow these steps:
- Collect Data: Gather a dataset that you believe follows a normal distribution. Ensure that the data is quantitative and continuous.
- Calculate Mean and Standard Deviation: Compute the mean and standard deviation of the dataset. These values will be crucial for constructing the histogram.
- Determine Bin Width: Choose an appropriate bin width for your histogram. The bin width determines the number of intervals or bins in which the data will be divided. A smaller bin width provides more detail, while a larger bin width smooths out the distribution.
- Create Bins: Divide the range of data values into equal-width bins based on the chosen bin width. Ensure that the bins cover the entire range of data.
- Count Data Points: Count the number of data points that fall within each bin. This will give you the frequency or count for each bin.
- Plot the Histogram: Create a bar chart with the bins on the x-axis and the frequency on the y-axis. Adjust the bar heights according to the frequency of data points in each bin.
- Fit a Normal Curve: Superimpose a normal probability distribution curve onto the histogram. This curve will have the same mean and standard deviation as your data.
- Interpret the Histogram: Analyze the shape of the histogram and compare it to the normal curve. A close alignment between the histogram and the normal curve indicates that your data follows a normal distribution.
Interpreting Bell-Shaped Histograms

Bell-shaped histograms provide valuable insights into the distribution of data. Here are some key interpretations:
- Central Tendency: The mean, median, and mode of a bell-shaped histogram are located at the center of the distribution. This indicates that the data is symmetrically distributed around the central value.
- Spread and Variability: The standard deviation measures the spread of data points around the mean. A smaller standard deviation indicates a narrow distribution, while a larger standard deviation suggests a wider spread of data.
- Outliers: Bell-shaped histograms are sensitive to outliers, which are extreme values that deviate significantly from the rest of the data. Outliers can distort the shape of the histogram and affect the accuracy of statistical analyses.
- Skewness and Kurtosis: Although bell-shaped histograms are typically not skewed, it is important to assess the skewness and kurtosis of your data. Skewness measures the asymmetry of the distribution, while kurtosis assesses the peakedness. Deviations from the normal distribution can provide insights into the underlying data patterns.
Applications of Bell-Shaped Histograms

Bell-shaped histograms have numerous applications across various fields:
- Quality Control: In manufacturing and quality assurance, bell-shaped histograms are used to monitor and control production processes. By analyzing the distribution of product characteristics, companies can identify deviations and take corrective actions.
- Social Sciences: Bell-shaped histograms are commonly used in social sciences, such as psychology and sociology, to analyze and interpret data related to human behavior, attitudes, and demographics.
- Financial Analysis: In finance, bell-shaped histograms are employed to assess the risk and return of investment portfolios. By examining the distribution of returns, investors can make informed decisions and manage their portfolios effectively.
- Medical Research: Bell-shaped histograms play a crucial role in medical research, particularly in analyzing clinical trial data and understanding the distribution of patient characteristics or treatment outcomes.
- Environmental Studies: In environmental science, bell-shaped histograms are used to study the distribution of various environmental parameters, such as temperature, precipitation, or air quality.
Notes
📈 Note: Bell-shaped histograms are a powerful tool for visualizing and interpreting data. However, it is important to note that not all datasets follow a normal distribution. In such cases, other types of distributions, such as skewed or bimodal distributions, may be more appropriate.
Conclusion

Bell-shaped histograms are a fundamental tool in statistics and data analysis, providing a visual representation of normal distributions. By understanding the characteristics and interpretations of bell-shaped histograms, researchers and analysts can gain valuable insights into the underlying patterns and trends in their data. Whether it is in quality control, social sciences, finance, or environmental studies, bell-shaped histograms play a crucial role in making informed decisions and drawing meaningful conclusions from data.
What is a bell-shaped histogram?
+A bell-shaped histogram, also known as a normal distribution, is a graphical representation of data that follows a symmetrical bell-like curve. It is characterized by a central tendency and a balanced distribution of data points around the mean.
How is a bell-shaped histogram created?
+To create a bell-shaped histogram, you need to collect data, calculate the mean and standard deviation, determine bin width, create bins, count data points in each bin, and plot the histogram. Finally, you can fit a normal curve onto the histogram for comparison.
What are the key characteristics of a bell-shaped histogram?
+Bell-shaped histograms exhibit symmetry, with the mean, median, and mode located at the center of the distribution. They have a narrow spread of data points around the mean and are not skewed or peaked.
What are the applications of bell-shaped histograms?
+Bell-shaped histograms are used in various fields, including quality control, social sciences, financial analysis, medical research, and environmental studies. They provide insights into the distribution of data and help make informed decisions.
Can all datasets be represented by a bell-shaped histogram?
+No, not all datasets follow a normal distribution. Some datasets may exhibit skewed or bimodal distributions, which require different types of histograms or statistical analyses.


