Calculating Line Of Best Fit

Introduction
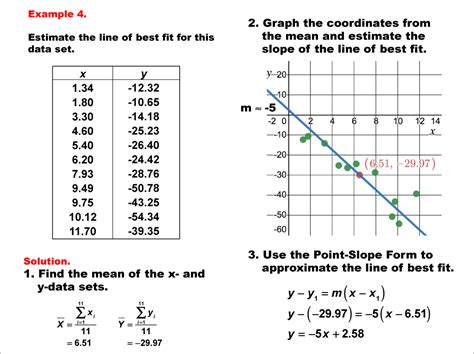
Determining the line of best fit is a fundamental concept in statistics and data analysis. It allows us to establish a relationship between two variables and make predictions based on that relationship. In this blog post, we will explore the process of calculating the line of best fit, also known as the regression line, and delve into the different methods and techniques involved. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to find the line of best fit and its applications in various fields.
Understanding the Line of Best Fit

The line of best fit, or regression line, is a straight line that represents the average relationship between two variables in a dataset. It is a visual representation of the trend or pattern observed in the data. This line serves as a predictive tool, enabling us to estimate the value of one variable based on the value of the other.
When dealing with a scatter plot, which displays the relationship between two variables, the line of best fit helps us identify the overall trend and make generalizations about the data. It provides a simplified representation of the complex relationships between variables, making it easier to understand and analyze the data.
Methods for Calculating the Line of Best Fit

There are several methods to calculate the line of best fit, each with its own advantages and applications. Let’s explore some of the most commonly used techniques:
Method 1: Least Squares Method

The least squares method is one of the most popular and widely used techniques for finding the line of best fit. It aims to minimize the sum of the squares of the vertical distances between the data points and the line. By doing so, it ensures that the line closely follows the pattern of the data.
To calculate the line of best fit using the least squares method, we need to find the values of the slope (m) and y-intercept (b) that minimize the sum of squared residuals. The formula for the slope is:
\[ \begin{equation*} m = \frac{\sum_{i=1}^{n}(x_i - \bar{x})(y_i - \bar{y})}{\sum_{i=1}^{n}(x_i - \bar{x})^2} \end{equation*} \]
Where: - m is the slope of the line. - x_i and y_i are the i-th values of the x and y variables, respectively. - \bar{x} and \bar{y} are the means of the x and y variables, respectively.
The formula for the y-intercept is:
\[ \begin{equation*} b = \bar{y} - m\bar{x} \end{equation*} \]
Once we have the values of m and b, we can write the equation of the line of best fit as:
\[ \begin{equation*} y = mx + b \end{equation*} \]
Method 2: Linear Regression

Linear regression is another powerful technique for finding the line of best fit. It involves fitting a linear model to the data and estimating the coefficients that best describe the relationship between the variables. Linear regression can be performed using statistical software or programming languages, making it a convenient choice for data analysis.
The linear regression model can be represented as:
\[ \begin{equation*} y = \beta_0 + \beta_1x + \epsilon \end{equation*} \]
Where: - y is the dependent variable. - x is the independent variable. - \beta_0 and \beta_1 are the coefficients to be estimated. - \epsilon is the error term.
By minimizing the sum of squared residuals, we can estimate the values of \beta_0 and \beta_1, which represent the y-intercept and slope of the line of best fit, respectively.
Method 3: Moving Average

The moving average method is a simple yet effective approach to calculate the line of best fit. It involves calculating the average of a certain number of data points and connecting these averages with a straight line. This method is particularly useful when dealing with time series data or when the relationship between variables is not linear.
To apply the moving average method, we need to choose a window size, which determines the number of data points to be averaged. By sliding this window across the data and calculating the average for each window, we can obtain a smoothed line that represents the overall trend.
Applications of the Line of Best Fit

The line of best fit has a wide range of applications across various fields. Some notable applications include:
Prediction and Forecasting: The line of best fit allows us to make predictions about future values based on the relationship between variables. It is commonly used in fields such as economics, finance, and meteorology to forecast trends and make informed decisions.
Trend Analysis: By examining the line of best fit, we can identify patterns and trends in the data. This is valuable in fields like market research, where understanding consumer behavior and preferences is crucial.
Modeling and Simulation: The line of best fit serves as a foundation for building mathematical models and simulations. It helps in understanding the underlying relationships between variables and allows for the creation of realistic representations of real-world phenomena.
Quality Control: In manufacturing and quality control processes, the line of best fit can be used to monitor and control product quality. By comparing the actual data with the predicted values from the line of best fit, deviations can be detected, and corrective actions can be taken.
Advantages and Limitations

The line of best fit offers several advantages, including its simplicity, ease of interpretation, and ability to provide a visual representation of the data. It allows for quick and efficient analysis, especially when dealing with large datasets.
However, it is important to note that the line of best fit has certain limitations. It assumes a linear relationship between variables, which may not always be the case. Non-linear relationships or complex patterns may require more advanced techniques, such as polynomial regression or non-linear regression, to accurately model the data.
Conclusion

In this blog post, we explored the concept of the line of best fit and the various methods used to calculate it. We learned about the least squares method, linear regression, and the moving average method, each with its own strengths and applications. Understanding how to find the line of best fit is essential for data analysis and interpretation, as it enables us to uncover patterns, make predictions, and gain insights from our data. By applying these techniques, we can leverage the power of statistics to solve real-world problems and make informed decisions.
FAQ
What is the line of best fit used for?

+
The line of best fit is used to establish a relationship between two variables and make predictions based on that relationship. It is commonly used in fields such as statistics, economics, and data analysis.
How do I choose the appropriate method for calculating the line of best fit?

+
The choice of method depends on the nature of your data and the specific requirements of your analysis. The least squares method is suitable for linear relationships, while linear regression can handle more complex models. The moving average method is often used for time series data or when the relationship is non-linear.
Can I use the line of best fit for non-linear relationships?

+
While the line of best fit assumes a linear relationship, it can still provide useful insights for non-linear relationships. However, for more accurate modeling of non-linear data, techniques like polynomial regression or non-linear regression should be considered.


