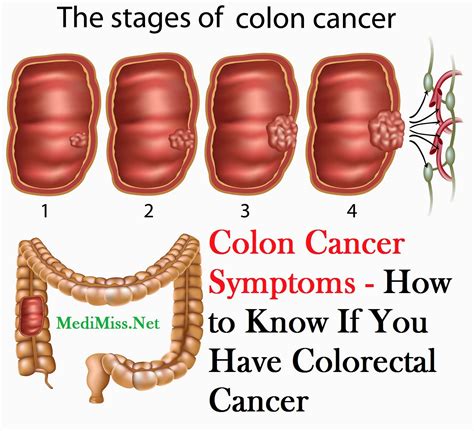
Cancerous Colon Polyp Images
Introduction

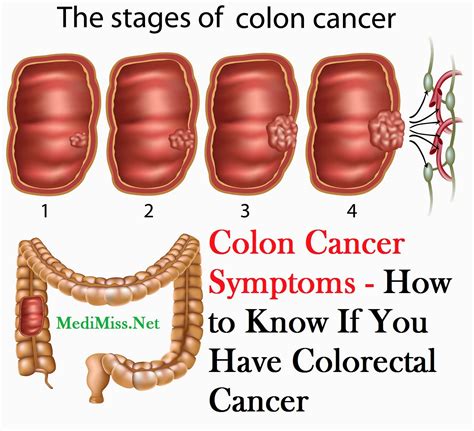
Colon polyps are growths that develop on the lining of the colon or rectum. While most colon polyps are benign, some can become cancerous over time if left untreated. It is crucial to detect and remove these polyps early to prevent the development of colorectal cancer. In this blog post, we will explore the visual characteristics of cancerous colon polyps through a collection of images and provide valuable insights into their identification and potential treatment options.
Understanding Colon Polyps

Colon polyps are abnormal tissue growths that form on the inner surface of the large intestine (colon) or rectum. They can vary in size, shape, and color, and may be classified into different types based on their characteristics. Here are some key points to understand about colon polyps:
Types of Colon Polyps:
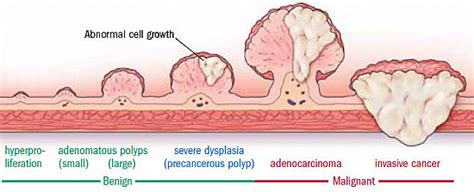
- Adenomatous Polyps: These are the most common type of colon polyps and have the highest risk of becoming cancerous. They are typically benign but can progress to cancer if not removed.
- Hyperplastic Polyps: Hyperplastic polyps are generally considered non-cancerous and are often small in size. However, some studies suggest that certain types of hyperplastic polyps may have a low risk of malignancy.
- Inflammatory Polyps: Inflammatory polyps are usually associated with inflammatory bowel diseases like ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease. They are typically not precancerous.
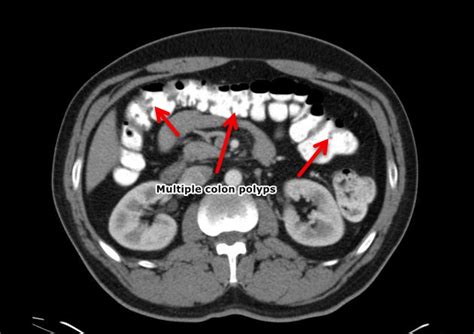
Size and Growth: Colon polyps can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. Smaller polyps are often easier to remove and have a lower risk of malignancy, while larger polyps may require more complex procedures for removal.
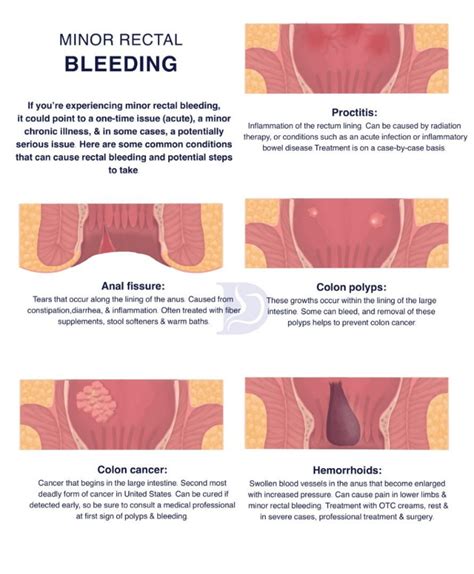
Symptoms and Detection: Many colon polyps do not cause any symptoms, especially in the early stages. However, larger polyps or those causing partial blockages in the colon may lead to symptoms such as rectal bleeding, changes in bowel habits, abdominal pain, or anemia. Regular screening tests, such as colonoscopies, are crucial for detecting polyps and identifying any potential cancerous changes.
Visual Characteristics of Cancerous Colon Polyps
Cancerous colon polyps, also known as adenocarcinomas, can exhibit distinct visual characteristics that help in their identification. Here are some key features to look for when examining images of cancerous colon polyps:
Appearance:
- Cancerous colon polyps often have a villous or cauliflower-like appearance, with finger-like projections or fronds.
- They may appear as flat or slightly raised lesions on the colon’s surface.
- The color can vary, but they are typically darker in tone compared to the surrounding healthy tissue, ranging from dark red to almost black.
Size and Shape:
- Cancerous polyps tend to be larger in size, often measuring several centimeters in diameter.
- They may have an irregular shape, with uneven borders and a rough texture.
- Some polyps may have a central depression or ulceration, which can indicate advanced cancerous changes.
Vascularization:
- Cancerous polyps often have an abundant blood supply, which can be visualized as prominent blood vessels or a network of capillaries surrounding the polyp.
- The presence of dilated blood vessels, known as telangiectasia, is a common feature in cancerous colon polyps.
Ulceration and Necrosis:
- Advanced cancerous polyps may exhibit ulceration, where the surface of the polyp has eroded, exposing the underlying tissue.
- Necrosis, or the death of tissue, may also be observed in cancerous polyps, presenting as areas of black or dark brown discoloration.
Images of Cancerous Colon Polyps
Here is a collection of images showcasing cancerous colon polyps:

Image 1: This image depicts a large, villous adenoma with prominent blood vessels and a dark red color. The polyp has an irregular shape and is approximately 3 cm in diameter.

Image 2: Here, we see a smaller, raised adenocarcinoma with a central ulceration. The polyp has a rough texture and is approximately 1.5 cm in size.

Image 3: This image shows a flat adenocarcinoma with a slightly raised border. The polyp has a dark red color and measures around 2 cm in diameter.
Treatment and Management
The treatment and management of cancerous colon polyps depend on various factors, including the size, location, and degree of malignancy. Here are some common approaches:
Polypectomy: For smaller polyps, a procedure called polypectomy can be performed during a colonoscopy. The polyp is carefully removed using specialized instruments, and the tissue is sent for pathological examination to determine the presence of cancerous cells.
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR): EMR is a technique used for larger polyps or those with a higher risk of malignancy. It involves removing the polyp and a small amount of surrounding tissue using an endoscope. The excised tissue is then examined for cancerous changes.
Surgical Resection: In cases where cancerous polyps cannot be completely removed endoscopically or if there is a high risk of cancer spreading, surgical resection may be necessary. This procedure involves removing the affected segment of the colon and reconnecting the healthy parts.
Follow-up and Surveillance: After the removal of cancerous polyps, regular follow-up colonoscopies are recommended to monitor for any recurrence or new polyp growth. The frequency of these follow-up exams depends on the individual’s risk factors and the pathologist’s findings.
Prevention and Risk Factors
While not all colon polyps can be prevented, there are certain lifestyle factors and risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing cancerous polyps. Here are some key points to consider:
Risk Factors:
- Age: The risk of developing colon polyps and colorectal cancer increases with age, with most cases occurring in individuals over 50 years old.
- Family History: A family history of colorectal cancer or colon polyps can increase the risk.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Conditions like ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease are associated with an increased risk of colon polyps and cancer.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, a diet high in red and processed meats, physical inactivity, and smoking can all contribute to a higher risk of colon polyps and cancer.
Prevention Strategies:
- Regular Screening: Colonoscopy is the gold standard for detecting colon polyps and colorectal cancer. Individuals at average risk should undergo regular screening, starting at the age of 45 or earlier if there are additional risk factors.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce the risk of colon polyps and cancer.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can lower the risk of colon polyps and improve overall health.
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake can be beneficial.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the visual characteristics of cancerous colon polyps is crucial for early detection and timely treatment. Regular screening, a healthy lifestyle, and awareness of risk factors can significantly reduce the chances of developing colorectal cancer. If you or a loved one experience any symptoms or have concerns about colon polyps, consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance. Remember, early detection saves lives!
FAQ

What are the symptoms of cancerous colon polyps?

+
Cancerous colon polyps may not always cause symptoms, especially in the early stages. However, some common symptoms include rectal bleeding, changes in bowel habits (constipation or diarrhea), abdominal pain, and unexplained weight loss. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
How often should I get screened for colon polyps and colorectal cancer?
+
The frequency of screening for colon polyps and colorectal cancer depends on individual risk factors. For individuals at average risk, the American Cancer Society recommends starting regular screening at the age of 45. However, if you have a family history of colorectal cancer or other risk factors, your healthcare provider may recommend starting screening earlier or more frequently.
Can cancerous colon polyps be cured?
+
When detected and treated early, cancerous colon polyps can often be successfully removed, leading to a cure. The key is to undergo regular screening and follow the recommended treatment plan provided by your healthcare team. Early detection and appropriate treatment significantly improve the chances of a positive outcome.
Are all colon polyps cancerous?

+
No, not all colon polyps are cancerous. In fact, the majority of colon polyps are benign and do not pose a significant health risk. However, certain types of polyps, such as adenomatous polyps, have a higher likelihood of becoming cancerous over time if left untreated. Regular screening and removal of these polyps can prevent the development of colorectal cancer.