Convert Per Hour Wages To Salary: The Ultimate Guide

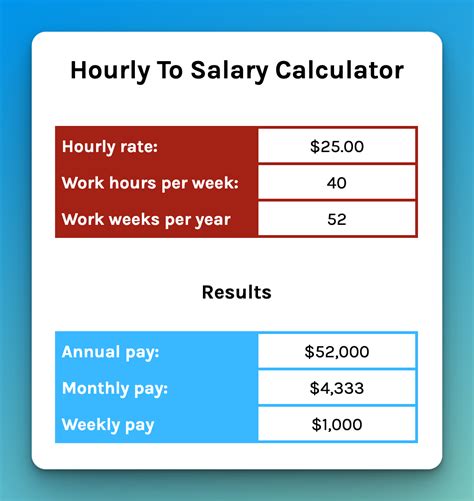
Understanding how to convert per hour wages to a yearly salary is a crucial skill for both employees and employers. This guide will provide a comprehensive step-by-step process to ensure an accurate and fair conversion, benefiting all parties involved.
Step 1: Gather Essential Information
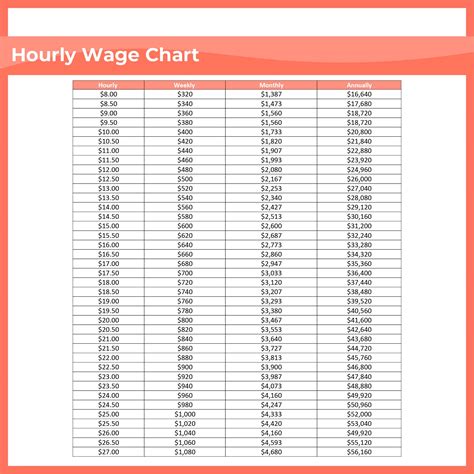
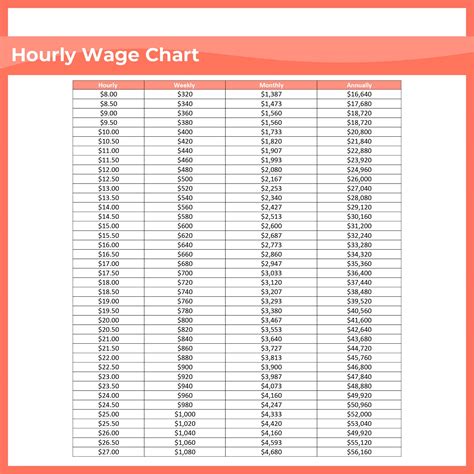
Before you begin the conversion process, it's essential to gather the necessary details. You'll need to know the following:
- The hourly wage rate
- The number of hours worked per week
- The number of weeks worked per year (typically 52)
For instance, let's consider an employee earning an hourly wage of $20 and working 40 hours per week.
Step 2: Calculate Weekly Earnings

The first step is to determine the weekly earnings. Multiply the hourly wage by the number of hours worked per week.
In our example:
$20 (hourly wage) x 40 (hours/week) = $800 (weekly earnings)
Step 3: Determine Annual Salary

Now, calculate the annual salary by multiplying the weekly earnings by the number of weeks worked per year.
Using our example:
$800 (weekly earnings) x 52 (weeks/year) = $41,600 (annual salary)
So, an employee earning $20 per hour and working 40 hours per week would have an annual salary of $41,600.
Step 4: Consider Overtime and Benefits

In some cases, employees may work overtime, which should be factored into the salary calculation. Additionally, consider any benefits or additional compensation, such as healthcare, retirement plans, or bonuses.
For instance, if an employee works 10 hours of overtime per week at time-and-a-half (1.5x) their regular rate, their weekly earnings would increase.
Overtime rate: $20 x 1.5 = $30
Overtime earnings: $30 x 10 hours = $300
Total weekly earnings (including overtime): $800 + $300 = $1,100
This employee's annual salary, including overtime, would be $1,100 x 52 weeks = $57,200.
Step 5: Adjust for Part-Time Work
If an employee works part-time, the calculation will be slightly different. In this case, you'll need to determine the number of hours worked per week and the total weeks worked per year.
For example, a part-time employee working 20 hours per week for 48 weeks would have an annual salary of $20 x 20 hours x 48 weeks = $19,200.
Step 6: Tax and Deduction Considerations
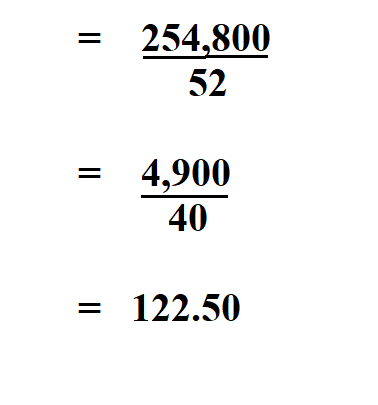
It's important to note that the annual salary calculated above is the gross salary before taxes and deductions. Employers and employees must consider the applicable taxes and deductions, such as income tax, social security, and Medicare, which will reduce the take-home pay.
Employers should consult with tax professionals or use tax calculators to ensure accurate deductions.
Step 7: Review and Confirm

Once you've calculated the annual salary, review the figures and confirm with the employee or employer. Ensure that all the information used in the calculation is accurate and up-to-date.
It's essential to have open communication to address any concerns or queries regarding the salary conversion.
Step 8: Adjustments and Negotiations

In some cases, the calculated annual salary may not align with the desired or expected earnings. This could be due to various factors, such as market rates, experience, or negotiation power.
Employees and employers can engage in negotiations to reach a mutually beneficial agreement. This may involve discussing additional benefits, performance-based incentives, or adjustments to the hourly wage or working hours.
Step 9: Document and Communicate
After finalizing the annual salary, it's crucial to document the agreement. Create a written record, such as an employment contract or offer letter, that outlines the terms, including the hourly wage, working hours, and annual salary.
Effective communication is key. Ensure that both parties understand the terms and conditions, including any benefits, overtime policies, and performance expectations.
Conclusion

Converting per hour wages to an annual salary is a straightforward process when you have the right information and follow a systematic approach. By breaking down the steps and considering various factors, such as overtime, benefits, and taxes, you can ensure an accurate and fair salary calculation.
Remember, open communication and a willingness to negotiate can lead to a mutually beneficial employment relationship. This guide provides a foundation for understanding the conversion process, but it's always recommended to seek professional advice for complex scenarios or specific industry requirements.
How often should I review and adjust my salary?
+
It’s recommended to review your salary annually or when significant changes occur, such as a promotion or a substantial increase in responsibilities. Regular reviews ensure that your earnings remain competitive and aligned with your skills and experience.
Are there any legal requirements for minimum wages or overtime pay?
+
Yes, most countries have legal minimum wage requirements and overtime pay regulations. It’s crucial to stay informed about these laws to ensure compliance and fair treatment of employees. Consult with legal professionals or government resources for specific information.
How can I negotiate a higher salary or better benefits?

+
Effective negotiation requires research and preparation. Understand your market value, highlight your skills and achievements, and be prepared to discuss your contributions to the organization. Be open to discussing various aspects of compensation, such as base salary, bonuses, and benefits.


