Design The Ultimate British Army Brigade Guide Now

Welcome to the ultimate guide on designing and understanding the British Army Brigade, a fundamental building block of the military's land forces. In this comprehensive overview, we'll delve into the intricacies of brigade composition, organization, and the critical role they play in modern warfare.
Understanding the Brigade Structure
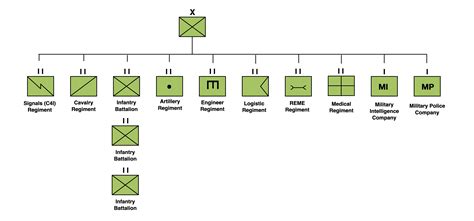
The British Army Brigade is a versatile and powerful unit, designed to be highly adaptable to various mission requirements. At its core, a brigade consists of a headquarters, combat units, and support elements, forming a balanced and self-sufficient force.
Brigade Headquarters

The brigade headquarters serves as the command and control center, responsible for strategic decision-making and overall mission coordination. It includes key personnel such as the brigade commander, staff officers, and communication specialists.
Combat Units

The combat units are the brigade's primary offensive and defensive elements. They are typically comprised of infantry battalions, armored regiments, and artillery batteries, each specializing in specific combat roles and equipped with the necessary weaponry and vehicles.
Infantry Battalions
Infantry battalions are the backbone of the brigade, providing ground troops with exceptional mobility and firepower. They are trained to operate in various environments, from urban settings to rugged terrain, and are equipped with a range of weapons, including small arms, machine guns, and anti-tank missiles.
Armored Regiments
Armored regiments bring heavy firepower and protection to the brigade. They are equipped with main battle tanks, armored personnel carriers, and other armored vehicles, offering superior mobility and offensive capabilities. Armored regiments are crucial for breaking through enemy defenses and securing key objectives.
Artillery Batteries
Artillery batteries provide long-range fire support, offering precision strikes and area denial capabilities. They are equipped with a variety of artillery systems, including howitzers, multiple-launch rocket systems, and mortar teams. Artillery batteries play a vital role in suppressing enemy positions, destroying targets, and providing cover for advancing troops.
Support Elements
The support elements of a brigade are essential for sustaining combat operations and ensuring the overall effectiveness of the unit. These elements include logistics, engineering, medical, and signal units, each playing a critical role in maintaining the brigade's operational readiness.
Logistics Units
Logistics units are responsible for the supply and distribution of essential resources, such as fuel, ammunition, food, and equipment. They ensure that combat units have the necessary support to carry out their missions effectively. Logistics units also manage transportation and maintenance, keeping the brigade operationally ready.
Engineering Units
Engineering units provide critical engineering capabilities, including construction, demolition, and the repair of infrastructure. They are skilled in building defensive positions, bridging rivers, and clearing obstacles, ensuring the brigade can maneuver effectively in any terrain.
Medical Units
Medical units are responsible for providing medical care and evacuation services to injured personnel. They operate field hospitals, aid stations, and medical evacuation teams, ensuring the brigade's combat effectiveness is maintained even in the face of casualties. Medical units also provide preventive healthcare and sanitation services.
Signal Units
Signal units are the communication experts, responsible for establishing and maintaining the brigade's communication networks. They provide secure and reliable communication channels, allowing for effective command and control. Signal units also support the integration of various communication systems, ensuring seamless information sharing between units.
Brigade Deployment and Missions

The British Army Brigade is designed to be highly flexible, capable of deploying and conducting a wide range of missions, from conventional warfare to peacekeeping operations. Here's an overview of the brigade's deployment and mission capabilities:
Conventional Warfare

In conventional warfare scenarios, the brigade serves as a powerful offensive and defensive force. It can rapidly deploy and engage in large-scale operations, utilizing its combat units to break through enemy defenses, secure key objectives, and maintain territorial control. The brigade's balanced composition allows it to adapt to changing battlefield dynamics, ensuring a swift and effective response.
Peacekeeping Operations

The brigade also plays a crucial role in peacekeeping and stability operations. It can deploy to conflict zones, providing a robust and impartial presence to monitor and enforce peace agreements. The brigade's infantry battalions are well-equipped to conduct patrols, provide security, and engage in confidence-building measures, fostering a stable environment for civilian populations.
Counter-Insurgency and Counter-Terrorism
In counter-insurgency and counter-terrorism operations, the brigade employs a combination of offensive and defensive tactics. Its infantry battalions, supported by specialized units, conduct targeted raids, surveillance missions, and intelligence-gathering operations. The brigade's ability to adapt and operate in diverse environments makes it an effective force against asymmetric threats.
Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief

The brigade's support elements are vital in providing humanitarian assistance and disaster relief. Medical units can set up field hospitals and provide medical aid to affected populations, while engineering units can assist in rebuilding infrastructure and providing essential services. The brigade's logistics units ensure the efficient distribution of aid and supplies, making it a valuable asset in times of crisis.
Brigade Training and Exercises

To maintain its combat readiness and effectiveness, the brigade undergoes rigorous training and participates in various exercises. These training activities ensure that soldiers are proficient in their roles and can operate as a cohesive unit.
Individual and Unit Training
Individual soldiers within the brigade receive comprehensive training in their respective specialties. This includes weapons handling, combat tactics, physical fitness, and specialized skills relevant to their roles. Regular training exercises also focus on unit-level proficiency, ensuring that combat units can operate effectively as a team.
Combined Arms Training
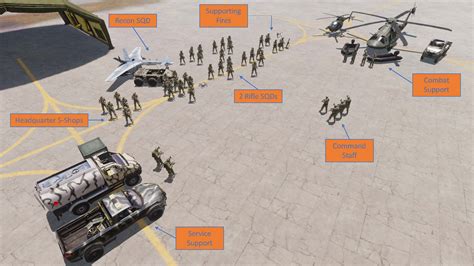
Combined arms training brings together different combat units to simulate realistic combat scenarios. Infantry, armor, and artillery units train together, practicing coordinated maneuvers, fire and movement techniques, and integrated combat operations. This training enhances the brigade's ability to function as a cohesive and effective force.
Live-Fire Exercises

Live-fire exercises provide soldiers with the opportunity to engage in realistic combat simulations, utilizing live ammunition. These exercises are conducted in controlled environments, allowing soldiers to experience the intensity of combat and refine their marksmanship, targeting, and tactical skills. Live-fire exercises are crucial for maintaining the brigade's combat proficiency.
Joint Training with Allied Forces
The brigade often conducts joint training exercises with allied forces, fostering interoperability and enhancing cooperation. These exercises simulate complex scenarios, allowing soldiers to work alongside their international counterparts, sharing best practices and strengthening international military partnerships.
Brigade Leadership and Command
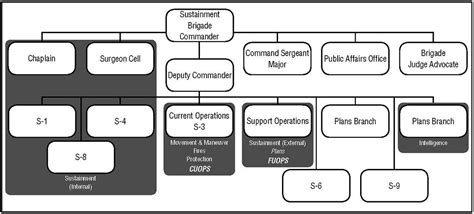
Effective leadership and command are crucial to the success of any military unit, and the brigade is no exception. The brigade commander, typically a highly experienced and respected officer, leads the brigade with a clear vision and strategic mindset.
Brigade Commander
The brigade commander is responsible for the overall performance and mission success of the brigade. They provide strategic direction, make critical decisions, and ensure the effective coordination of all brigade elements. The commander's leadership style and decision-making abilities are key factors in the brigade's operational effectiveness.
Staff Officers
Staff officers support the brigade commander, providing specialized expertise in various functional areas. These officers include operations, intelligence, logistics, and communications specialists. They assist in planning, coordinating, and executing missions, ensuring that the brigade's operations are well-organized and executed efficiently.
Command and Control
Command and control are essential aspects of brigade operations. The brigade headquarters maintains constant communication with combat units and support elements, ensuring real-time situational awareness and effective decision-making. Advanced communication systems and secure networks enable the brigade commander to maintain control and adapt to changing circumstances.
Brigade Logistics and Sustainment

Logistics and sustainment are critical aspects of brigade operations, ensuring that combat units have the necessary resources and support to carry out their missions effectively.
Supply and Distribution
Logistics units are responsible for the supply and distribution of essential resources. They manage the procurement, storage, and distribution of fuel, ammunition, food, and equipment. Efficient supply chain management ensures that combat units have the necessary resources to maintain their operational readiness and combat effectiveness.
Transportation and Mobility
Transportation and mobility are vital for the brigade's deployment and maneuverability. Logistics units manage the movement of personnel and equipment, utilizing a range of vehicles, including trucks, armored vehicles, and helicopters. Efficient transportation capabilities enable the brigade to rapidly deploy and reposition its forces, adapting to changing mission requirements.
Maintenance and Repair
Maintenance and repair teams are responsible for keeping the brigade's equipment and vehicles in optimal condition. They conduct routine maintenance, diagnose and repair mechanical issues, and ensure that all assets are ready for deployment. Regular maintenance reduces the risk of equipment failure and enhances the brigade's overall operational readiness.
Brigade in Action: Case Studies

To illustrate the brigade's capabilities and effectiveness, let's explore a few case studies showcasing its role in various military operations.
Operation X: Conventional Warfare
In a hypothetical scenario, the British Army Brigade is deployed to a conflict zone to engage in conventional warfare operations. The brigade's combat units, including infantry, armor, and artillery, work in close coordination to break through enemy defenses and secure key objectives. The brigade's ability to rapidly deploy and adapt to changing battlefield conditions proves crucial in achieving mission success.
Operation Y: Peacekeeping
The brigade is deployed to a volatile region as part of a peacekeeping mission. Its infantry battalions conduct patrols, monitor ceasefires, and engage in confidence-building measures with local communities. The brigade's impartial presence helps to de-escalate tensions, prevent outbreaks of violence, and promote long-term stability in the region.
Operation Z: Counter-Terrorism
In a counter-terrorism operation, the brigade employs a combination of offensive and defensive tactics. Its specialized units, including intelligence and surveillance teams, work alongside infantry battalions to gather intelligence, track terrorist cells, and conduct targeted raids. The brigade's ability to operate in diverse environments and adapt to dynamic threats proves critical in disrupting terrorist networks.
The Future of the British Army Brigade
As military technology and tactics evolve, the British Army Brigade is continually adapting to meet new challenges. Here's a glimpse into the future of brigade operations:
Enhanced Intelligence and Surveillance
The brigade of the future will leverage advanced intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance capabilities. Drones, satellite imagery, and sophisticated sensors will provide real-time situational awareness, enabling the brigade to make more informed decisions and adapt its tactics accordingly.
Robotics and Autonomous Systems
Robotics and autonomous systems will play an increasingly significant role in brigade operations. Unmanned vehicles and robots will assist in a variety of tasks, from logistics and transportation to combat support. These technologies will enhance the brigade's efficiency, reduce the risk to soldiers, and improve overall mission effectiveness.
Network-Centric Warfare
Network-centric warfare will continue to shape the brigade's operational approach. Advanced communication networks and data-sharing capabilities will enable real-time information sharing between units, enhancing coordination and decision-making. The brigade will leverage the power of big data and artificial intelligence to optimize its operations and gain a strategic advantage.
Integration of Emerging Technologies
The British Army Brigade will continue to integrate emerging technologies, such as advanced materials, 3D printing, and augmented reality. These technologies will enhance the brigade's combat capabilities, improve soldier protection, and enable more efficient logistics and maintenance processes.
Conclusion
The British Army Brigade is a versatile and powerful military unit, designed to meet a wide range of mission requirements. Its balanced composition, effective leadership, and adaptable training make it a formidable force on the battlefield. From conventional warfare to peacekeeping and counter-terrorism, the brigade plays a crucial role in maintaining national security and promoting stability around the world. As technology advances, the brigade will continue to evolve, leveraging cutting-edge capabilities to stay at the forefront of modern warfare.
What is the typical size of a British Army Brigade?
+A British Army Brigade typically consists of around 3,000 to 5,000 soldiers, depending on its composition and mission requirements.
How are brigades organized within the British Army structure?
+Brigades are organized within the British Army as part of the land forces command structure. They are subordinate to divisions and are further divided into subordinate units such as battalions and regiments.
What are the key advantages of the brigade structure in modern warfare?
+The brigade structure offers several advantages, including flexibility, adaptability, and self-sufficiency. Brigades can be tailored to specific mission requirements, allowing for a balanced and effective force. They can rapidly deploy and respond to changing circumstances, making them highly versatile in modern warfare.
How does the British Army Brigade collaborate with other military branches?
+The British Army Brigade often collaborates with other military branches, such as the Royal Air Force and Royal Navy, to achieve joint military objectives. This collaboration involves coordinated planning, combined operations, and the integration of air and naval assets to support ground forces.

