Essential Guide To Static Noise Margin: Mastering The Basics

Introduction to Static Noise Margin

Static Noise Margin (SNM) is a crucial parameter in the world of electronics, particularly in the design and analysis of analog circuits. It plays a vital role in ensuring the integrity and reliability of signal transmission, especially in the presence of noise and interference. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the fundamentals of Static Noise Margin, exploring its definition, significance, and practical applications. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of SNM and its importance in various electronic systems.
Understanding Static Noise Margin

Definition
Static Noise Margin refers to the maximum voltage swing that a circuit can tolerate before the output signal is corrupted or distorted due to noise. It is a measure of the circuit’s resilience against noise and its ability to maintain accurate signal transmission. SNM is typically expressed in volts (V) or as a percentage of the circuit’s supply voltage.
Significance
The significance of Static Noise Margin lies in its role as a critical factor in the performance and stability of analog circuits. Here’s why SNM is essential:
- Noise Immunity: SNM provides a buffer against noise, ensuring that the circuit can withstand a certain level of noise without compromising the integrity of the output signal.
- Signal Integrity: A higher SNM indicates better signal integrity, as it allows the circuit to handle larger voltage swings without distortion.
- Reliability: Circuits with adequate SNM are more reliable, as they can maintain accurate signal transmission even in noisy environments.
- Design Optimization: Understanding SNM helps engineers optimize circuit designs, ensuring that the desired signal levels are maintained while minimizing the impact of noise.
Factors Affecting Static Noise Margin

Several factors influence the Static Noise Margin of a circuit. By considering these factors, engineers can make informed decisions to improve SNM and enhance circuit performance. Here are the key factors:
- Supply Voltage: The supply voltage directly affects SNM. Higher supply voltages generally result in larger voltage swings, which can improve SNM.
- Input Signal Level: The amplitude of the input signal impacts SNM. Circuits with higher input signal levels often have better SNM.
- Noise Sources: The presence and intensity of noise sources, such as thermal noise, shot noise, and flicker noise, can significantly affect SNM.
- Circuit Components: The choice of components, such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors, plays a role in determining SNM. Different components have varying noise characteristics.
- Circuit Topology: The arrangement and configuration of circuit elements can impact SNM. Some topologies are more noise-resistant than others.
Calculating Static Noise Margin

Calculating Static Noise Margin involves analyzing the circuit’s input and output characteristics and determining the maximum allowable noise margin. Here’s a simplified step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Identify Input and Output Levels
- Input Level: Determine the minimum and maximum voltage levels at the circuit’s input.
- Output Level: Identify the voltage levels at the circuit’s output for the given input levels.
Step 2: Calculate Voltage Swing
- Subtract the minimum input voltage from the maximum input voltage to find the input voltage swing.
- Subtract the minimum output voltage from the maximum output voltage to find the output voltage swing.
Step 3: Determine Static Noise Margin
- Compare the input and output voltage swings.
- SNM is the difference between the input and output voltage swings, expressed as a percentage of the supply voltage or in volts.
Improving Static Noise Margin

Engineers employ various techniques to enhance Static Noise Margin and improve the performance of analog circuits. Here are some common strategies:
- Noise Reduction: Implementing noise reduction techniques, such as shielding and filtering, can minimize the impact of noise on the circuit.
- Component Selection: Choosing components with low noise characteristics, such as low-noise amplifiers and resistors, can improve SNM.
- Circuit Optimization: Optimizing the circuit’s topology and component values can enhance SNM. This involves careful analysis and simulation.
- Power Supply Regulation: Stable and well-regulated power supplies contribute to better SNM by reducing voltage fluctuations.
- Feedback Techniques: Feedback loops can be used to improve SNM by providing negative feedback, which helps suppress noise.
Applications of Static Noise Margin
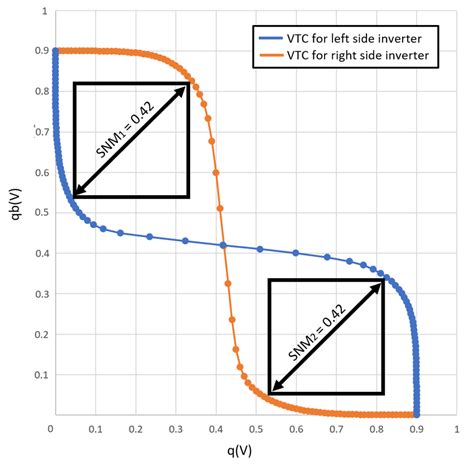
Static Noise Margin finds applications in various electronic systems where signal integrity and noise immunity are crucial. Here are some notable examples:
- Communication Systems: SNM is vital in communication circuits, ensuring reliable transmission of data and minimizing errors caused by noise.
- Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs): ADCs rely on SNM to accurately convert analog signals into digital form without distortion.
- Audio and Video Systems: Maintaining a high SNM is essential in audio and video circuits to deliver clear and noise-free signals.
- Power Management: SNM plays a role in power management circuits, ensuring stable and noise-free power distribution.
- Sensors and Instrumentation: Sensors and measurement systems benefit from high SNM to provide accurate and reliable data.
Table: Common Noise Sources and Their Impact
| Noise Source | Description | Impact on SNM |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Noise | Random noise caused by temperature variations | Can reduce SNM, especially in high-temperature environments. |
| Shot Noise | Noise due to random fluctuations in current flow | Affects SNM by introducing random voltage variations. |
| Flicker Noise (1/f Noise) | Low-frequency noise that increases with decreasing frequency | Reduces SNM, particularly in circuits with low-frequency signals. |
| Intermodulation Noise | Noise generated by the interaction of multiple signals | Can degrade SNM, especially in circuits with complex signal processing. |
| Crosstalk | Noise coupling between adjacent signal lines | May decrease SNM by introducing interference between signals. |
| Power Supply Noise | Noise from the power supply | Affects SNM by introducing voltage fluctuations, impacting circuit performance. |

Conclusion
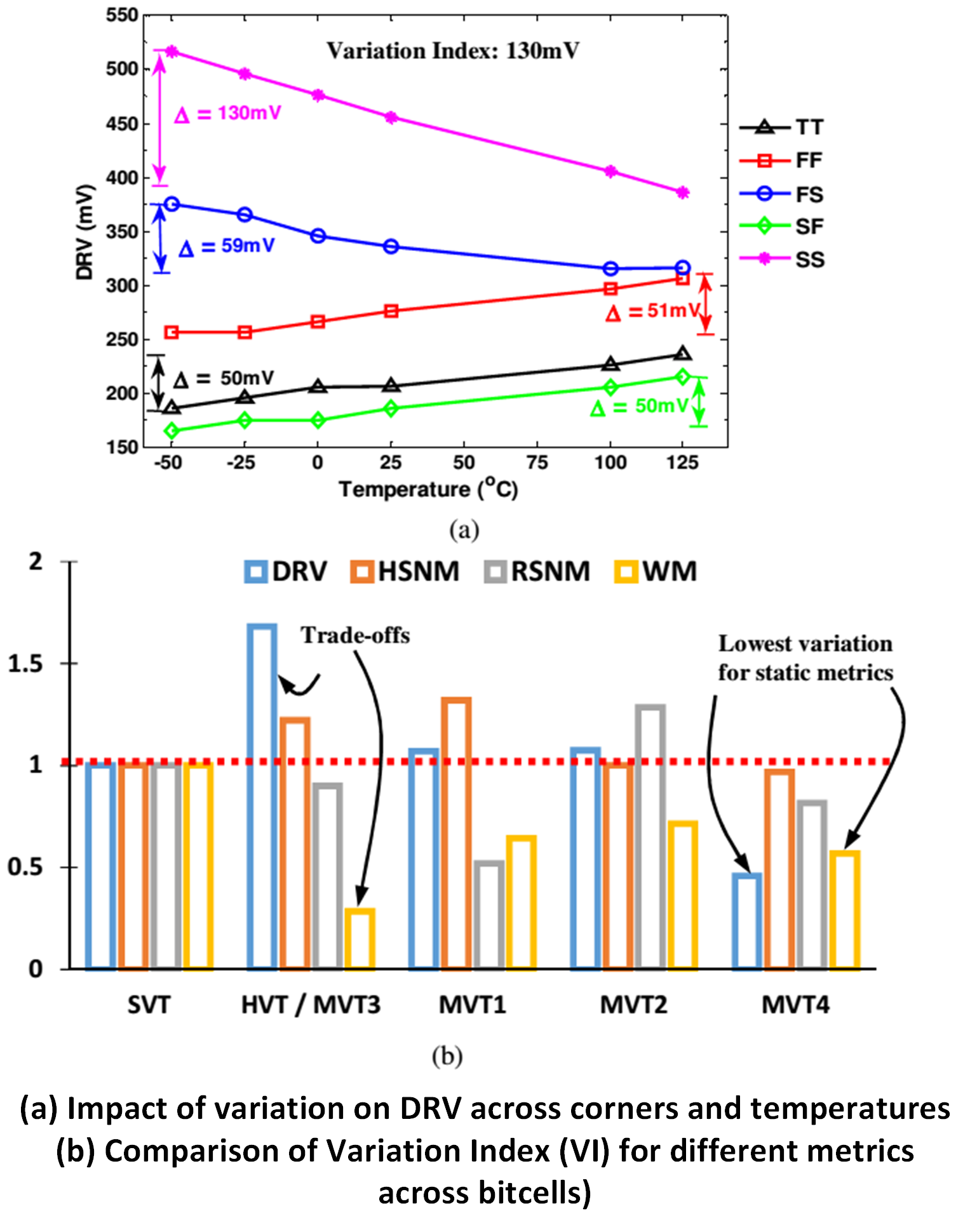
Static Noise Margin is a fundamental concept in analog circuit design, providing a measure of a circuit’s resilience against noise. By understanding the factors that influence SNM and implementing strategies to improve it, engineers can ensure the reliability and performance of electronic systems. From communication systems to audio and video applications, Static Noise Margin plays a crucial role in maintaining signal integrity and minimizing the impact of noise. With a solid grasp of SNM, engineers can design robust and high-performance circuits that meet the demands of modern electronic devices.
FAQ

What is the ideal Static Noise Margin for a circuit?
+The ideal SNM depends on the specific application and circuit requirements. In general, a higher SNM is desirable, as it indicates better noise immunity and signal integrity. However, achieving an excessively high SNM may not always be practical or necessary.
How does SNM impact power consumption?
+SNM and power consumption are interconnected. Higher SNM often requires larger voltage swings, which can increase power consumption. Engineers must strike a balance between SNM and power efficiency to optimize circuit performance.
Can SNM be improved through software or digital techniques?
+While software and digital techniques can enhance overall system performance, they may not directly impact SNM. SNM is primarily an analog concept, and improvements are achieved through circuit design and component selection.