F 35 Cruise Speed
The F-35 Lightning II, a highly advanced fighter aircraft, has garnered significant attention for its capabilities and performance. Among the various aspects that contribute to its prowess is its cruise speed, which plays a crucial role in its overall efficiency and effectiveness. In this article, we will delve into the cruise speed of the F-35, exploring its significance, performance, and how it compares to other aircraft in its class.
Understanding Cruise Speed

Before we dive into the specifics of the F-35's cruise speed, let's first understand what cruise speed entails. In aviation, cruise speed refers to the optimal speed at which an aircraft can travel for an extended period while maintaining efficiency and fuel economy. It is typically chosen to balance the aircraft's performance, range, and payload capacity.
For fighter jets like the F-35, cruise speed becomes even more critical due to their primary role in combat and rapid response missions. A higher cruise speed allows these aircraft to cover greater distances quickly, reach their targets faster, and potentially gain a tactical advantage over adversaries.
F-35 Cruise Speed Performance

The F-35 Lightning II, developed by Lockheed Martin, is a fifth-generation fighter jet designed for a range of missions, including air-to-air combat, ground attack, and reconnaissance. Its cruise speed is an essential factor in its overall performance and mission effectiveness.
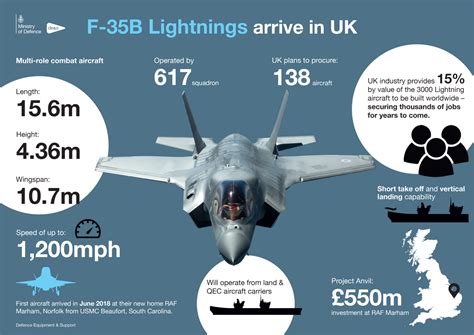
The F-35 boasts an impressive cruise speed of approximately Mach 1.6 (around 1,200 miles per hour or 1,931 kilometers per hour). This high-subsonic speed places it among the fastest fighter jets in service today. Achieving such a speed is made possible by the aircraft's advanced aerodynamic design, powerful engines, and sophisticated propulsion systems.
The F-35's cruise speed is particularly advantageous in long-range missions, where its ability to maintain a high subsonic speed for extended periods becomes a significant asset. This enables the aircraft to cover vast distances quickly, reducing the time required to reach distant targets or potential threat areas.
Additionally, the F-35's cruise speed contributes to its overall stealth capabilities. By operating at high subsonic speeds, the aircraft generates less noise and radar signature, making it more difficult for enemy radar systems to detect and track. This stealth advantage is crucial in modern warfare, where advanced radar and sensor technologies are prevalent.
Comparison with Other Aircraft

To understand the F-35's cruise speed in context, let's compare it to other notable fighter jets:
| Aircraft | Cruise Speed |
|---|---|
| F-35 Lightning II | Mach 1.6 (1,200 mph / 1,931 km/h) |
| F-22 Raptor | Mach 1.8 (1,300 mph / 2,092 km/h) |
| F-16 Fighting Falcon | Mach 0.9 (600 mph / 965 km/h) |
| Su-35 Flanker-E | Mach 1.5 (1,000 mph / 1,609 km/h) |

As seen in the table above, the F-35's cruise speed is impressive, placing it among the fastest fighter jets. While the F-22 Raptor has a slightly higher cruise speed, the F-35's capabilities are still remarkable and well-suited for its multi-role mission profile.
Factors Affecting Cruise Speed

Several factors influence an aircraft's cruise speed, and understanding these factors can provide insight into the F-35's performance:
- Aerodynamic Design: The F-35's sleek and streamlined design reduces drag, allowing it to achieve higher speeds with less power.
- Engine Performance: The aircraft's powerful engines, such as the Pratt & Whitney F135, deliver the necessary thrust to maintain high cruise speeds.
- Propulsion Systems: Advanced propulsion technologies, including variable cycle engines, enable the F-35 to optimize its performance across different flight regimes.
- Weight and Payload: The F-35's ability to carry a significant payload while maintaining high cruise speeds is a testament to its efficient design and powerful engines.
Operational Advantages

The F-35's cruise speed offers several operational advantages, including:
- Rapid Deployment: The aircraft's high cruise speed allows it to reach distant locations quickly, making it an invaluable asset for rapid response missions.
- Enhanced Surveillance: The F-35's ability to cover vast areas at high speeds makes it an effective platform for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) missions.
- Tactical Advantage: In combat scenarios, the F-35's cruise speed can provide a strategic edge, allowing it to engage targets quickly and potentially outmaneuver adversaries.
- Efficient Mission Profile: By maintaining a high cruise speed, the F-35 can complete missions with reduced fuel consumption, increasing its overall range and endurance.
Notes

⚠️ Note: The F-35's cruise speed is a crucial aspect of its overall performance and mission effectiveness. Its high-subsonic speed allows it to excel in long-range missions, rapid response scenarios, and stealth operations. While the F-22 Raptor has a slightly higher cruise speed, the F-35's capabilities are well-suited for its multi-role mission profile.
Conclusion

The F-35 Lightning II's cruise speed is a testament to its advanced design and engineering. With a top cruise speed of Mach 1.6, it ranks among the fastest fighter jets in service today. This high-subsonic speed provides the aircraft with operational advantages, including rapid deployment, enhanced surveillance capabilities, and a tactical edge in combat. As the F-35 continues to serve in various air forces around the world, its cruise speed will remain a key factor in its success and mission effectiveness.
What is the maximum speed of the F-35?

+
The F-35 can reach a top speed of approximately Mach 1.6, making it a highly capable and fast fighter jet.
How does the F-35’s cruise speed compare to other fighter jets?

+
While the F-22 Raptor has a slightly higher cruise speed, the F-35’s capabilities are impressive and well-suited for its multi-role mission profile.
What factors contribute to the F-35’s high cruise speed?

+
The F-35’s cruise speed is influenced by its aerodynamic design, powerful engines, advanced propulsion systems, and efficient weight distribution.