Household Level Heterogeneity
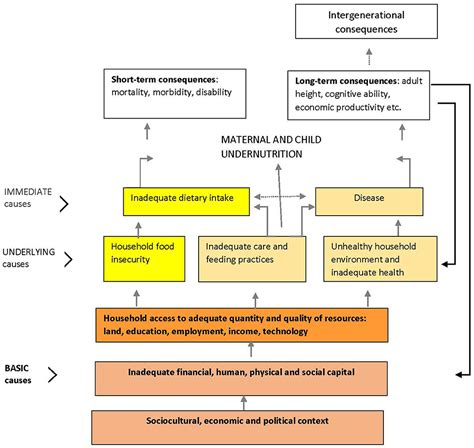
Understanding household level heterogeneity is crucial for a comprehensive analysis of various economic and social phenomena. This concept delves into the diverse characteristics and behaviors within households, which can significantly impact policy decisions and research outcomes. By examining these variations, we can gain deeper insights into how households function and make decisions, ultimately leading to more effective strategies and interventions.
The Significance of Household Level Heterogeneity

Household level heterogeneity is a multifaceted concept that encompasses a wide range of factors, including demographic, socioeconomic, and behavioral variations. These differences can manifest in income levels, educational backgrounds, health status, consumption patterns, and many other aspects of household life.
Recognizing and analyzing these variations is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it allows for a more nuanced understanding of the population, especially when considering that households are the fundamental units of consumption and production. Secondly, it helps in identifying specific groups or segments within the population that may require targeted interventions or policies. Lastly, it enables researchers and policymakers to design more effective strategies by taking into account the unique needs and circumstances of different households.
Exploring Key Dimensions of Household Level Heterogeneity

To grasp the concept of household level heterogeneity fully, it's essential to explore its key dimensions. These dimensions provide a comprehensive view of the variations within households and offer valuable insights for policy formulation and research.
Demographic Factors
Demographic factors play a significant role in shaping household characteristics. These include the age, gender, and composition of household members. For instance, a household with elderly members may have different healthcare needs and financial considerations compared to a household with young, working-age individuals. Similarly, households with children may have distinct educational and recreational preferences.
Socioeconomic Status
Socioeconomic status is another critical dimension of household level heterogeneity. This encompasses factors such as income, occupation, and educational attainment. Households with higher socioeconomic status may have better access to resources and opportunities, while those with lower status may face challenges such as limited access to healthcare, education, and financial stability.
Health and Well-being
The health and well-being of household members is yet another important aspect. This dimension includes physical and mental health, as well as overall life satisfaction. Households with members facing health challenges may require specific support and resources, such as access to healthcare services or disability support.
Consumption Patterns
Consumption patterns also contribute to household level heterogeneity. These patterns include the types and amounts of goods and services consumed by households. For example, households with young children may have higher expenditure on education and childcare, while retired households may have different consumption needs and preferences.
Other Dimensions
Apart from the aforementioned dimensions, there are several other factors that contribute to household level heterogeneity. These include geographical location, cultural background, household size, and the presence of special needs or disabilities among household members.
Implications for Policy and Research
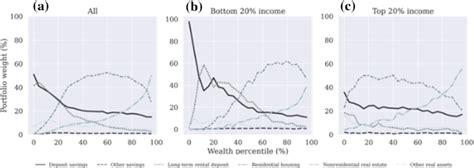
The recognition and analysis of household level heterogeneity have significant implications for policy formulation and research. By understanding the diverse characteristics and needs of households, policymakers can design more effective and targeted interventions. For instance, policies aimed at improving access to healthcare or education can be tailored to specific household groups based on their unique circumstances.
Similarly, researchers can benefit from studying household level heterogeneity by gaining deeper insights into the factors that influence household decisions and behaviors. This knowledge can enhance the validity and applicability of research findings, leading to more accurate predictions and recommendations.
Methods for Analyzing Household Level Heterogeneity
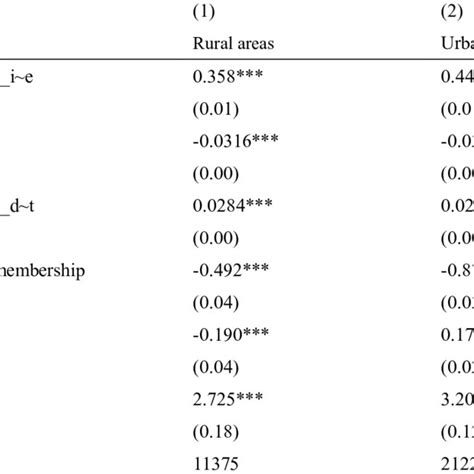
Analyzing household level heterogeneity requires the use of appropriate research methods and tools. These methods can vary depending on the specific research question or policy objective. Some common approaches include:
- Surveys and Interviews: Collecting data through surveys and interviews allows researchers to gather information directly from households. This method provides valuable insights into household characteristics, behaviors, and preferences.
- Administrative Data: Analyzing administrative data, such as tax records or social welfare databases, can provide a wealth of information on household income, employment status, and other socioeconomic factors.
- Focus Groups and Participatory Research: Engaging with households through focus groups or participatory research methods can offer qualitative insights into household decision-making processes and experiences.
- Secondary Data Analysis: Analyzing existing datasets, such as census data or household expenditure surveys, can provide a broad overview of household level heterogeneity across different populations.
It's important to note that the choice of research method should be guided by the specific research question and the availability of resources. Additionally, combining different methods can provide a more comprehensive understanding of household level heterogeneity.
Addressing Challenges in Household Level Heterogeneity Research

While studying household level heterogeneity offers valuable insights, it also presents certain challenges. These challenges include:
- Data Availability: Obtaining comprehensive and reliable data on household characteristics can be challenging, especially in regions with limited infrastructure or resources.
- Privacy and Ethics: Research involving sensitive household information requires careful consideration of privacy and ethical guidelines to ensure the protection of participants' rights.
- Sample Size and Representation: Achieving a representative sample of households, especially when studying specific subgroups, can be difficult due to limited population size or geographical dispersion.
- Methodological Complexity: Analyzing household level heterogeneity often requires advanced statistical techniques and expertise, which may pose challenges for researchers without specialized training.
Addressing these challenges requires a thoughtful approach, including careful planning, collaboration with experts, and the use of appropriate research methods and tools.
Conclusion

Household level heterogeneity is a critical concept for understanding the diverse characteristics and behaviors of households. By recognizing and analyzing these variations, policymakers and researchers can design more effective strategies and interventions. This blog post has explored the key dimensions of household level heterogeneity, its implications for policy and research, and the methods and challenges associated with its analysis. By embracing a holistic approach to household-level research, we can contribute to more informed decision-making and improve the well-being of households across diverse contexts.
What is household level heterogeneity, and why is it important to study it?
+Household level heterogeneity refers to the diverse characteristics and behaviors within households, which can significantly impact policy decisions and research outcomes. Studying this concept is crucial for understanding the population’s nuanced needs and designing effective strategies and interventions.
What are the key dimensions of household level heterogeneity?
+Key dimensions include demographic factors (age, gender, composition), socioeconomic status (income, occupation, education), health and well-being (physical and mental health), consumption patterns (goods and services consumed), and other factors such as geographical location and cultural background.
How does understanding household level heterogeneity benefit policymakers and researchers?
+By understanding household level heterogeneity, policymakers can design more effective and targeted interventions, while researchers can gain deeper insights into household decision-making processes and behaviors, leading to more accurate predictions and recommendations.
What are some common methods for analyzing household level heterogeneity?
+Common methods include surveys and interviews, administrative data analysis, focus groups and participatory research, and secondary data analysis. The choice of method depends on the research question and available resources.
What challenges are associated with studying household level heterogeneity?
+Challenges include data availability, privacy and ethical considerations, achieving representative samples, and the complexity of advanced statistical techniques.

