Inverted T Wave In V2

Inverted T waves in V2 are a common electrocardiogram (ECG) finding that can have various causes and interpretations. This blog post aims to delve into the significance of inverted T waves in lead V2, exploring their potential implications and providing insights into their clinical relevance.
Understanding Inverted T Waves in V2
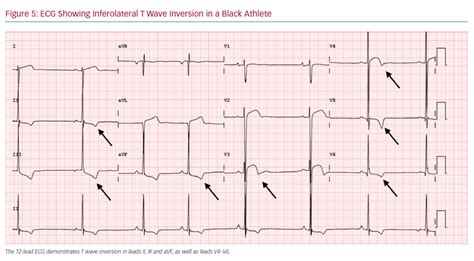
An inverted T wave in lead V2 refers to a specific pattern observed on an ECG, where the T wave is flipped upside down, appearing as a negative deflection following the QRS complex. Normally, T waves are typically upright and represent the repolarization of the ventricles.
The presence of inverted T waves in lead V2 can indicate underlying cardiac conditions or physiological variations. It is essential to consider the clinical context and correlate the ECG findings with the patient's symptoms, medical history, and other diagnostic tests to make an accurate diagnosis.
Causes of Inverted T Waves in V2

Inverted T waves in V2 can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Physiological Variations: Inverted T waves may be observed in healthy individuals, particularly in young adults and athletes. These variations are often benign and do not indicate any underlying pathology.
- Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS): Inverted T waves in V2 can be a sign of ACS, which includes conditions such as unstable angina and myocardial infarction (heart attack). ACS is characterized by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to ischemia and potential damage.
- Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH): LVH is an enlargement of the left ventricle, often due to conditions like hypertension or aortic stenosis. Inverted T waves in V2 can be associated with LVH, as the enlarged ventricle may cause electrical changes on the ECG.
- Myocardial Contusion: Traumatic events, such as chest injuries, can result in myocardial contusion, causing temporary damage to the heart muscle. Inverted T waves in V2 may be observed in cases of myocardial contusion.
- Valvular Heart Disease: Certain valvular heart diseases, such as aortic stenosis or regurgitation, can lead to changes in ventricular function and electrical conduction, potentially resulting in inverted T waves in V2.
- Pericarditis: Inflammation of the pericardium, known as pericarditis, can cause electrical changes on the ECG, including inverted T waves in V2.
Clinical Significance and Interpretation
The interpretation of inverted T waves in V2 depends on various factors, including the presence of other ECG abnormalities, the patient's symptoms, and the overall clinical picture.
In cases of ACS, inverted T waves in V2, especially when accompanied by other ECG changes such as ST-segment elevation or depression, can indicate ongoing myocardial ischemia or injury. Prompt evaluation and management are crucial to prevent further complications.
For patients with LVH, inverted T waves in V2 may reflect the presence of hypertrophy and the associated electrical changes. Further evaluation, such as echocardiography, can help confirm the diagnosis and guide management.
In the context of myocardial contusion, inverted T waves in V2 may resolve over time as the heart muscle heals. Close monitoring and repeat ECGs may be necessary to assess the resolution of the abnormality.
Valvular heart disease and pericarditis can also present with inverted T waves in V2. A comprehensive clinical assessment, including a thorough medical history and physical examination, is essential to differentiate between these conditions and other potential causes.
Differential Diagnosis
When encountering inverted T waves in V2, it is important to consider the differential diagnosis to rule out other conditions that may present with similar ECG findings. Some conditions to consider include:
- Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB): LBBB can cause changes in the QRS complex and T waves, including inverted T waves in V2. However, the presence of other ECG findings, such as a wide QRS complex and a leftward shift of the frontal plane axis, can help differentiate LBBB from other causes.
- Early Repolarization: Early repolarization is a benign condition characterized by J-point elevation and may result in inverted T waves in V2. However, early repolarization typically occurs in young, healthy individuals and is often associated with a specific ECG pattern, including a gradual slope of the ST segment and symmetrical T wave inversion.
- Hyperkalemia: Elevated potassium levels can cause ECG changes, including flattened or inverted T waves. In addition to inverted T waves in V2, hyperkalemia may present with other ECG abnormalities, such as peaked T waves and widened QRS complexes.
- Right Ventricular Hypertrophy (RVH): RVH can cause electrical changes on the ECG, including inverted T waves in V2. However, other leads, such as V1 and V4, may also demonstrate T wave inversions in RVH.
Management and Further Evaluation

The management of inverted T waves in V2 depends on the underlying cause and the patient's clinical presentation. Here are some general approaches:
- ACS Management: In cases of suspected ACS, prompt evaluation and treatment are essential. This may include administration of oxygen, pain relief, antiplatelet therapy, and early invasive strategies such as coronary angiography and potential revascularization.
- LVH Management: For patients with LVH, the primary goal is to manage the underlying condition, such as hypertension or aortic stenosis. This may involve lifestyle modifications, medication management, and close monitoring.
- Myocardial Contusion Management: Management of myocardial contusion primarily focuses on supportive care and pain management. Close observation and repeat ECGs may be necessary to monitor the resolution of ECG abnormalities.
- Valvular Heart Disease Management: Treatment of valvular heart disease depends on the specific condition and its severity. Medical management, surgical intervention, or a combination of both may be required.
- Pericarditis Management: Pericarditis management typically involves anti-inflammatory medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids, to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
In addition to these initial management steps, further evaluation may be warranted to confirm the diagnosis and guide long-term management. This may include additional imaging studies, such as echocardiography or cardiac MRI, as well as laboratory tests to assess cardiac enzymes and other relevant markers.
Precautions and Limitations
While inverted T waves in V2 can provide valuable information, it is important to consider the following precautions and limitations:
- Clinical Correlation: ECG findings should always be interpreted in the context of the patient's clinical presentation, medical history, and other diagnostic tests. Inverted T waves in V2 may have different implications depending on the overall clinical picture.
- Lead Placement: Proper lead placement is crucial for accurate interpretation of ECG findings. Inverted T waves in V2 may be more pronounced or less apparent depending on the lead placement and patient's body habitus.
- Artifact and Noise: ECG artifacts and noise can sometimes mimic inverted T waves. It is important to ensure proper ECG recording and minimize external interference to obtain accurate readings.
- Normal Variants: Inverted T waves in V2 may be observed in healthy individuals as normal variants. Differentiating between benign variations and pathological changes requires careful clinical assessment and consideration of the patient's overall health status.
Conclusion
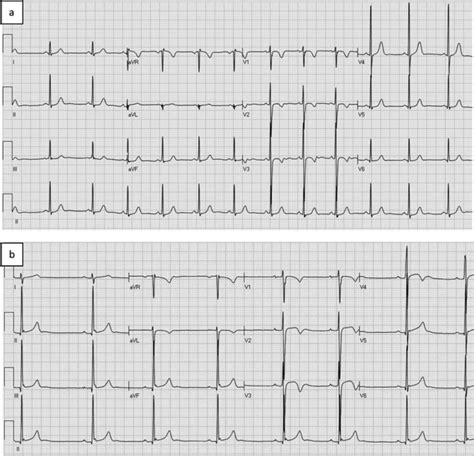
Inverted T waves in V2 can have various causes and interpretations, ranging from benign physiological variations to acute cardiac conditions. Accurate diagnosis and management require a comprehensive clinical evaluation, including consideration of the patient's symptoms, medical history, and other diagnostic tests. By understanding the potential causes and clinical significance of inverted T waves in V2, healthcare professionals can provide appropriate care and optimize patient outcomes.
What are the common causes of inverted T waves in V2?
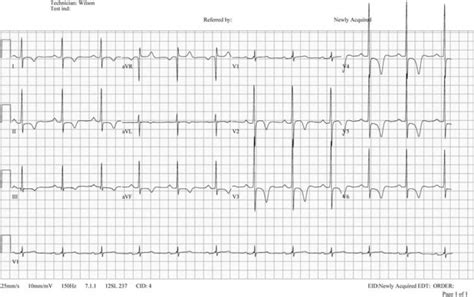
+
Inverted T waves in V2 can be caused by physiological variations, acute coronary syndrome, left ventricular hypertrophy, myocardial contusion, valvular heart disease, and pericarditis.
How can I differentiate between benign variations and pathological changes in inverted T waves in V2?

+
Differentiating between benign variations and pathological changes requires a comprehensive clinical assessment, including consideration of the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and other diagnostic tests. Inverted T waves in V2 as a benign variation are often observed in healthy individuals, particularly in young adults and athletes, and do not indicate any underlying pathology.
What are the management strategies for inverted T waves in V2 due to acute coronary syndrome (ACS)?
+
Management of ACS typically involves prompt evaluation and treatment. This may include administration of oxygen, pain relief, antiplatelet therapy, and early invasive strategies such as coronary angiography and potential revascularization.
Can inverted T waves in V2 be a sign of left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH)?
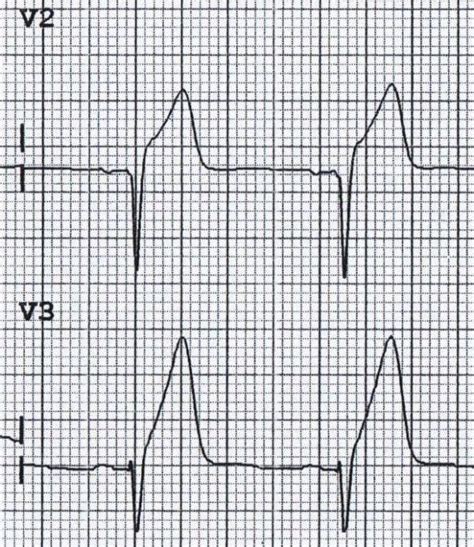
+
Yes, inverted T waves in V2 can be associated with LVH. LVH is an enlargement of the left ventricle, often due to conditions like hypertension or aortic stenosis. Further evaluation, such as echocardiography, can help confirm the diagnosis and guide management.
What are the key considerations when interpreting inverted T waves in V2 on an ECG?
+
When interpreting inverted T waves in V2, it is important to consider the presence of other ECG abnormalities, the patient’s symptoms, and the overall clinical picture. Clinical correlation and a comprehensive evaluation are essential to differentiate between various potential causes and make an accurate diagnosis.