Iran Gdp Per Capita
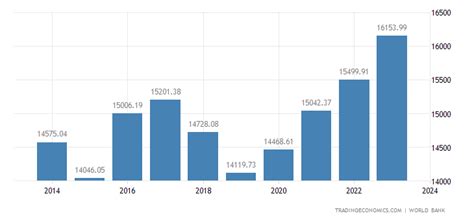
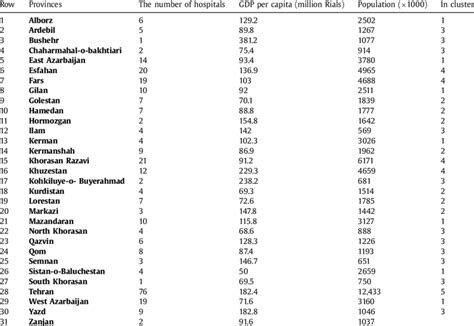
The GDP per capita of Iran is an important economic indicator that provides insights into the country's economic performance and the standard of living of its citizens. It represents the total value of goods and services produced within Iran, divided by its population. In this blog post, we will delve into the factors influencing Iran's GDP per capita, its historical trends, and its significance in understanding the country's economic landscape.
Understanding GDP Per Capita
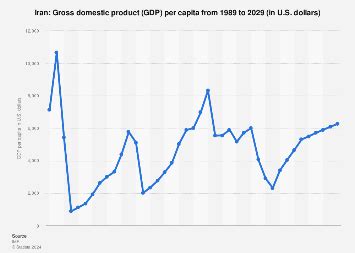
GDP per capita is a crucial metric for assessing a country's economic development and the well-being of its people. It measures the average income or economic output of each individual in a country, providing a snapshot of their purchasing power and overall economic prosperity.
When analyzing GDP per capita, it is essential to consider various factors such as population growth, economic policies, international trade, and the distribution of wealth within a country. These elements collectively shape the trajectory of a nation's economic growth and the living standards of its citizens.
Historical Trends in Iran's GDP Per Capita
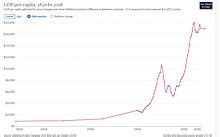
Iran's GDP per capita has experienced fluctuations over the years, influenced by a range of internal and external factors. Let's take a look at some key periods in Iran's economic history and their impact on GDP per capita:
Pre-Revolutionary Era (1960s-1970s)
During the 1960s and 1970s, Iran witnessed significant economic growth, primarily driven by the oil industry. The country's GDP per capita surged as a result of increased oil production and exports. This period of prosperity led to improvements in infrastructure, education, and healthcare, raising the standard of living for many Iranians.
Post-Revolutionary Challenges (1980s)
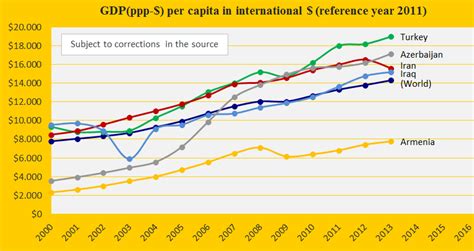
The Iranian Revolution in 1979 brought about political and economic instability, impacting the country's GDP per capita. The subsequent Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988) further strained the economy, leading to a decline in GDP per capita as resources were diverted towards military efforts. The war's impact on Iran's economy was significant, affecting various sectors and slowing down economic growth.
Recovery and Growth (1990s-2000s)

In the 1990s and 2000s, Iran began to recover from the post-revolutionary challenges. The government implemented economic reforms, focusing on diversification and reducing reliance on oil. This period saw a gradual increase in GDP per capita as the country's non-oil sectors, such as agriculture, manufacturing, and services, gained momentum. Iran's economy started to stabilize, and living standards improved for many Iranians.
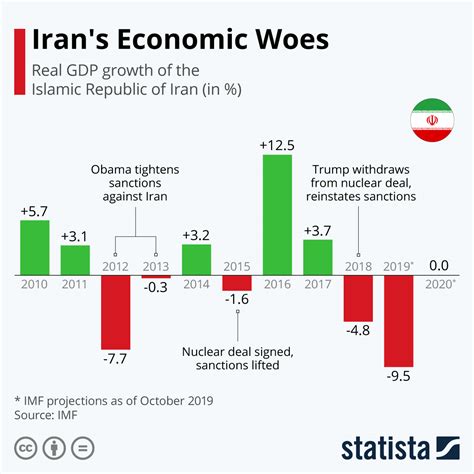
Sanctions and Economic Downturn (2010s)
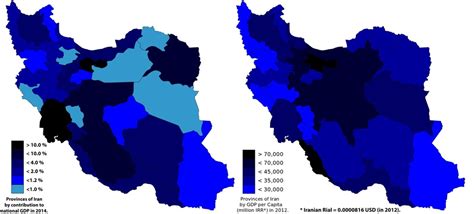
The 2010s presented new challenges for Iran's economy as international sanctions were imposed due to concerns over its nuclear program. These sanctions restricted Iran's access to global markets and financial systems, impacting its ability to export oil and conduct international trade. As a result, Iran's GDP per capita experienced a downturn, with the country facing economic difficulties and a decline in living standards for its citizens.
JCPOA and Economic Relief (2015-2018)

In 2015, the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), also known as the Iran nuclear deal, was signed between Iran and major world powers. This agreement provided economic relief for Iran by lifting certain sanctions and allowing for increased international trade. As a result, Iran's GDP per capita showed signs of improvement during this period, with the country experiencing a boost in economic activity and a rise in living standards.
Recent Developments (2019-Present)
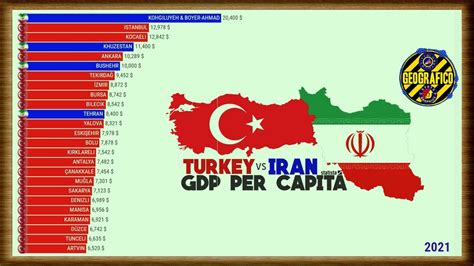
Since 2019, Iran has faced renewed economic challenges, including the re-imposition of sanctions by the United States and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. These factors have led to a decline in Iran's GDP per capita, as the country grapples with reduced oil exports, inflation, and economic instability. The ongoing geopolitical tensions and global health crisis have further complicated Iran's economic recovery efforts.
Factors Influencing Iran's GDP Per Capita

Several key factors play a significant role in shaping Iran's GDP per capita:
- Oil Dependency: Iran's economy is heavily reliant on oil exports, making it vulnerable to fluctuations in global oil prices and international sanctions. The country's GDP per capita is closely tied to the performance of the oil industry.
- Geopolitical Factors: Iran's geopolitical position and its relations with other countries, particularly the United States, have a substantial impact on its economy. Sanctions and political tensions can directly affect Iran's ability to engage in international trade and attract foreign investment.
- Economic Policies: The government's economic policies, including monetary and fiscal measures, play a crucial role in shaping Iran's economic growth and GDP per capita. Effective policies can promote investment, stimulate economic activity, and improve living standards.
- Population Growth: Iran's population growth rate can influence its GDP per capita. A growing population can lead to increased demand for goods and services, potentially boosting economic activity. However, it also poses challenges in terms of providing adequate employment opportunities and social services.
- International Trade: Iran's participation in global trade networks is essential for its economic development. Access to international markets and the ability to export non-oil products can enhance Iran's GDP per capita by increasing revenue and creating job opportunities.
Impact on Standard of Living
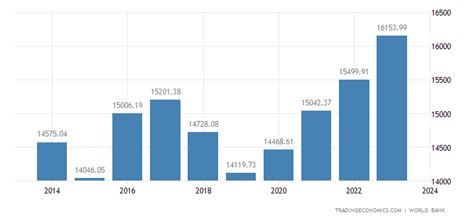
Iran's GDP per capita directly affects the standard of living of its citizens. A higher GDP per capita generally indicates a higher level of economic prosperity, which can lead to improved access to healthcare, education, and other essential services. It can also result in increased purchasing power, allowing individuals to afford better housing, transportation, and a higher quality of life.
On the other hand, a declining GDP per capita can have adverse effects on the standard of living. It may lead to reduced access to basic necessities, higher unemployment rates, and a decrease in overall well-being. The impact of a declining GDP per capita is often felt most acutely by vulnerable populations, such as low-income households and those in rural areas.
Comparative Analysis
To better understand Iran's GDP per capita, it is beneficial to compare it with other countries in the region and globally. Here's a table comparing Iran's GDP per capita with select countries:
| Country | GDP Per Capita (USD) |
|---|---|
| Iran | 5,760 |
| Saudi Arabia | 24,017 |
| United Arab Emirates | 39,739 |
| Turkey | 9,310 |
| India | 2,170 |
| United States | 62,791 |

As seen in the table, Iran's GDP per capita is lower compared to some of its regional neighbors, such as Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. However, it is higher than countries like India. These comparisons provide a broader context for understanding Iran's economic position and the factors influencing its GDP per capita.
Conclusion
Iran's GDP per capita is a complex metric influenced by a multitude of factors, including oil dependency, geopolitical dynamics, economic policies, and population growth. The country's economic history, marked by periods of growth and challenges, has shaped its GDP per capita and the standard of living for its citizens. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for policymakers, investors, and individuals seeking to comprehend Iran's economic landscape and its potential for future development.
What is the current GDP per capita of Iran?

+
As of my last update in January 2023, Iran’s GDP per capita is estimated to be around $5,760.
How does Iran’s GDP per capita compare to other countries in the region?

+
Iran’s GDP per capita is lower compared to some of its regional neighbors, such as Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. However, it is higher than countries like India.
What are the main challenges facing Iran’s economy?

+
Iran’s economy faces challenges such as oil dependency, international sanctions, geopolitical tensions, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. These factors have impacted its GDP per capita and overall economic growth.



