Length Of Normal Cervix

The cervix, a vital part of the female reproductive system, plays a crucial role in various aspects of reproductive health. One of the key concerns for many women is understanding the length of a normal cervix and how it can impact their overall well-being. In this blog post, we will delve into the topic of cervical length, exploring its significance, measurement techniques, and the factors that can influence its length.
Understanding Cervical Length

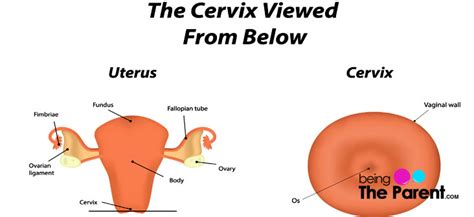
The cervix is a narrow passage that connects the uterus to the vagina. It acts as a gateway, allowing menstrual blood to flow out of the uterus and facilitating the passage of sperm during intercourse. The length of the cervix is an important indicator of a woman's reproductive health and can provide insights into various conditions and potential complications.
Normal Cervical Length
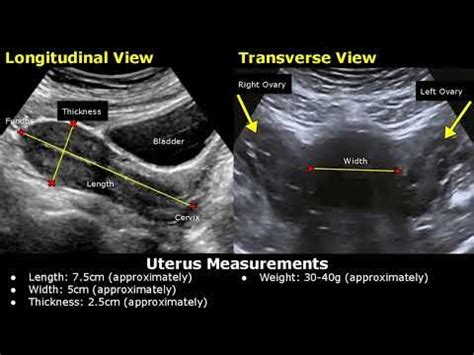
The term "normal" when it comes to cervical length can vary slightly among individuals and across different stages of life. However, a general guideline for a healthy cervical length is considered to be between 2.5 and 3.5 centimeters (cm) during the reproductive years. This range may vary slightly depending on factors such as age, hormonal changes, and pregnancy status.
It's important to note that cervical length can be influenced by various factors, including hormonal fluctuations, pregnancy, and certain medical conditions. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals to understand what is considered normal for your specific situation.
Measuring Cervical Length
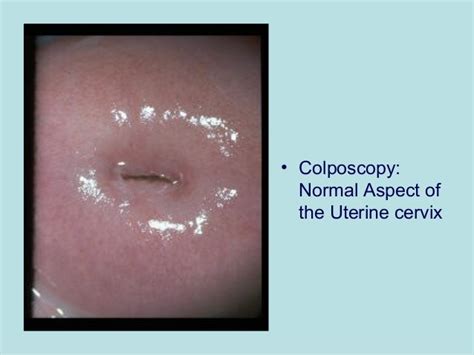
Measuring cervical length is typically done through ultrasound examinations. This non-invasive procedure allows healthcare providers to assess the length, thickness, and overall structure of the cervix. Ultrasound imaging provides detailed information about the cervix and can help identify any abnormalities or potential issues.
During an ultrasound examination, a transducer is gently inserted into the vagina. The transducer emits high-frequency sound waves that create images of the cervix and surrounding structures. These images are then analyzed by healthcare professionals to determine the cervical length and assess its overall health.
Factors Affecting Cervical Length

Hormonal Changes

Hormonal fluctuations throughout a woman's menstrual cycle can impact cervical length. During the menstrual cycle, the cervix undergoes changes in texture and position, which can affect its length. For example, during ovulation, the cervix may become softer and more open, while during menstruation, it may be firmer and closed.
Pregnancy

Pregnancy is a significant factor that can influence cervical length. As the pregnancy progresses, the cervix undergoes several changes to prepare for childbirth. In the early stages of pregnancy, the cervix may become softer and shorter, which is considered a normal adaptation. However, if the cervix becomes significantly shorter than the typical range, it may indicate a condition known as cervical insufficiency or incompetence.
Medical Conditions
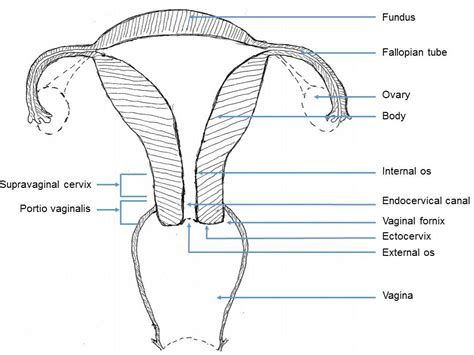
Certain medical conditions can also affect cervical length. For instance, cervical cancer or precancerous conditions may lead to changes in the length and structure of the cervix. Additionally, conditions such as cervical stenosis, where the cervical canal is narrowed, can impact cervical length and cause potential complications.
When to Seek Medical Advice

While a normal cervical length is generally considered to be within the range of 2.5 to 3.5 cm, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns or notice any unusual changes. Here are some situations where seeking medical advice is recommended:
- If you experience abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge.
- If you have a history of cervical insufficiency or cervical cancer.
- During pregnancy, if you notice any changes in cervical length or experience symptoms such as cramping, spotting, or premature contractions.
- If you have a family history of cervical conditions or are at a higher risk due to certain factors.
Regular check-ups and discussions with your healthcare provider can help monitor your cervical health and address any concerns promptly.
Maintaining Cervical Health

Maintaining cervical health is an essential aspect of overall reproductive well-being. Here are some tips to support cervical health:
- Practice safe sex and use protection to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) that can impact cervical health.
- Get regular Pap smear tests as recommended by your healthcare provider. These tests can detect abnormal cells and precancerous conditions.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate hydration.
- Avoid smoking, as it can increase the risk of cervical cancer and other reproductive health issues.
- Manage stress levels and practice self-care to support overall well-being.
By prioritizing cervical health and staying informed about your body, you can take proactive steps to maintain a healthy cervix and address any concerns promptly.
Conclusion
Understanding the length of a normal cervix is an important aspect of reproductive health. While a general guideline suggests a range of 2.5 to 3.5 cm, individual variations and specific circumstances may apply. Regular check-ups, ultrasound examinations, and open communication with healthcare professionals are essential for monitoring cervical health and addressing any potential issues. By staying informed and taking proactive measures, women can ensure the well-being of their cervix and overall reproductive system.
FAQ

Can cervical length vary during different stages of life?

+
Yes, cervical length can vary throughout a woman’s life. It may be longer during childhood and adolescence, shorten during pregnancy, and return to a normal length after childbirth. Hormonal changes and aging can also influence cervical length.
What are the signs of cervical insufficiency or incompetence?

+
Signs of cervical insufficiency or incompetence may include spotting or bleeding during pregnancy, cramping, and premature dilation of the cervix. These symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate course of action.
How often should I get a Pap smear test?

+
The frequency of Pap smear tests can vary depending on your age, medical history, and risk factors. It is recommended to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate screening schedule for you. Generally, women aged 21 to 65 are advised to have regular Pap smear tests.
Can cervical length affect fertility?
+
In some cases, an abnormally short cervix or cervical insufficiency can increase the risk of pregnancy loss or preterm birth. However, with proper monitoring and medical management, many women with cervical insufficiency can have successful pregnancies. It is important to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.



