Mexico And America Border Map
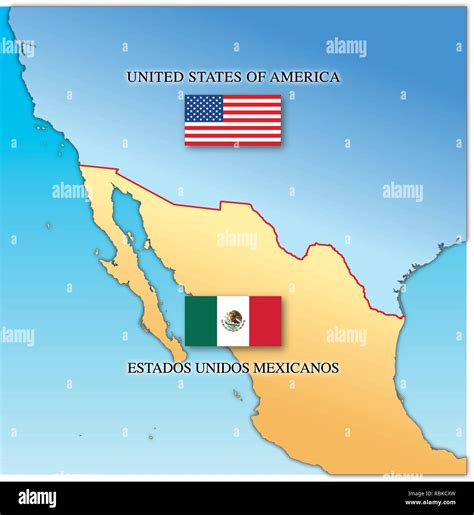
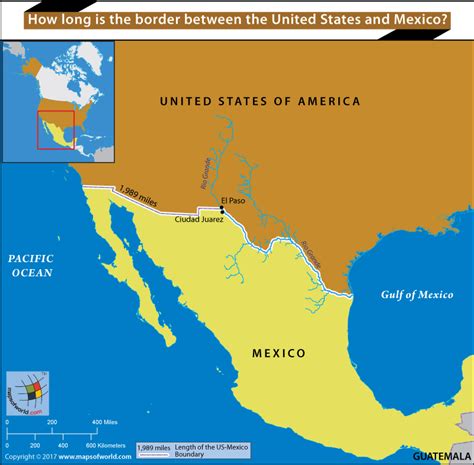
The Mexico-United States border, also known as the International Boundary and Water Commission (IBWC), is a highly significant geographical and political boundary separating two North American countries. This border, stretching approximately 1,954 miles (3,145 km), is not only a physical barrier but also a symbol of the complex relationship between Mexico and the United States.
A Brief History of the Border

The origins of the Mexico-U.S. border can be traced back to the early 19th century. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, signed in 1848, marked the end of the Mexican-American War and established the initial border between the two nations. This treaty, along with the later Gadsden Purchase in 1853, defined the majority of the modern-day border, including the Rio Grande as a natural boundary.
Over the years, the border has undergone various changes and agreements. The IBWC, a joint commission between Mexico and the U.S., was established in 1889 to resolve boundary-related issues and ensure the proper maintenance of the border. The commission has played a crucial role in addressing border-related matters, such as water distribution, flood control, and infrastructure development.
Geographical Features and Border Cities

The Mexico-U.S. border is characterized by diverse landscapes, ranging from rugged mountains to vast deserts. The Rio Grande, which flows through Texas and Mexico, serves as a natural border for a significant portion of the boundary. Other notable geographical features include the Sonoran Desert, the Sierra Madre Occidental mountains, and the Baja California Peninsula.
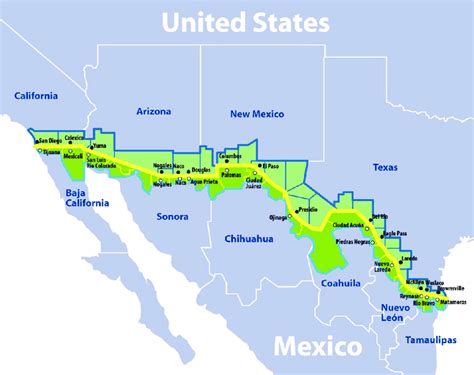
Along the border, numerous cities have developed into vibrant cultural hubs and economic centers. Some of the major border cities include Tijuana and San Diego, Ciudad Juárez and El Paso, and Nuevo Laredo and Laredo. These cities often have close ties and interdependencies, with a significant flow of people, goods, and services across the border.
| Mexican City | U.S. City |
|---|---|
| Tijuana | San Diego |
| Ciudad Juárez | El Paso |
| Nuevo Laredo | Laredo |
| Matamoros | Brownsville |
| Mexicali | Calexico |
Border Security and Immigration

The Mexico-U.S. border has been a subject of intense debate and scrutiny, particularly in the context of border security and immigration policies. The U.S. government has implemented various measures to secure the border, including the construction of physical barriers, increased surveillance, and enhanced border patrol presence. These efforts aim to address concerns related to illegal immigration, drug trafficking, and other cross-border crimes.
Immigration is a complex issue along the border, with many individuals seeking opportunities and a better life in the United States. The border region has witnessed a significant influx of migrants, often facing challenging conditions and a long journey to reach their desired destination. The U.S. government has implemented various policies and programs to manage immigration, including visa requirements, refugee resettlement, and border control measures.
Cross-Border Trade and Economic Impact
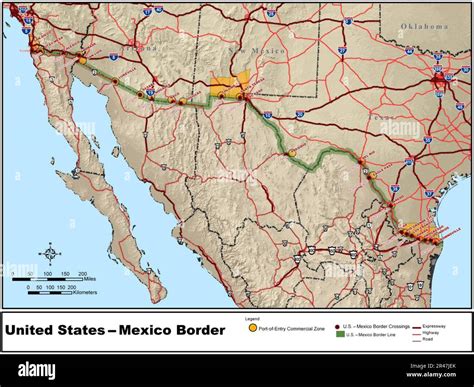
The Mexico-U.S. border plays a vital role in facilitating cross-border trade and economic cooperation. Both countries benefit from a strong economic relationship, with significant trade flows and investment opportunities. The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), later replaced by the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), has further enhanced economic ties and promoted the movement of goods and services across the border.
Border cities and regions have become key hubs for manufacturing, assembly, and logistics, taking advantage of their proximity to the border. The maquiladora industry, for example, has thrived along the border, with many multinational companies establishing manufacturing facilities to take advantage of lower labor costs and efficient supply chains.
Cultural Exchange and Tourism
The Mexico-U.S. border is not just a political and economic boundary but also a cultural bridge. The border region is home to a unique blend of Mexican and American influences, creating a vibrant and diverse cultural landscape. From traditional Mexican cuisine and music to American fast food and pop culture, the border offers a rich and diverse experience for locals and tourists alike.
Tourism is a significant industry along the border, with many visitors attracted to the region's natural beauty, historical sites, and unique cultural offerings. Border cities like Tijuana, Ciudad Juárez, and San Diego have developed robust tourism sectors, offering a range of attractions, accommodations, and entertainment options.
Challenges and Opportunities

While the Mexico-U.S. border presents numerous opportunities for economic growth, cultural exchange, and cooperation, it also faces various challenges. Issues such as border security, immigration, and environmental concerns require ongoing collaboration and innovative solutions.
The border region has been affected by drug-related violence and organized crime, which have impacted the safety and well-being of local communities. Efforts to combat these issues involve collaboration between law enforcement agencies and the implementation of comprehensive security strategies.
Furthermore, the border's unique environmental conditions, including water scarcity and pollution, pose challenges for sustainable development. The IBWC and other organizations work towards addressing these environmental concerns, promoting the responsible use of natural resources, and ensuring the long-term sustainability of the border region.
Final Thoughts

The Mexico-United States border is a dynamic and multifaceted entity, shaping the relationship between two neighboring countries. From its historical origins to its impact on trade, immigration, and cultural exchange, the border continues to be a focal point of attention and discussion. As both nations navigate the complexities of the border, finding a balance between security, economic cooperation, and cultural understanding remains a shared goal.
What is the length of the Mexico-U.S. border?

+
The Mexico-U.S. border is approximately 1,954 miles (3,145 km) long.
What is the role of the International Boundary and Water Commission (IBWC)?

+
The IBWC is a joint commission between Mexico and the U.S. responsible for resolving boundary-related issues and ensuring the proper maintenance of the border. It plays a crucial role in addressing water distribution, flood control, and infrastructure development.
How has the border impacted cross-border trade and economic cooperation?

+
The border has facilitated significant cross-border trade and economic cooperation between Mexico and the U.S. Both countries benefit from a strong economic relationship, with the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) enhancing trade flows and investment opportunities.
What are some of the challenges faced by the border region?

+
The border region faces challenges such as border security, immigration, drug-related violence, and environmental concerns. These issues require ongoing collaboration and innovative solutions to ensure the well-being and sustainability of the border communities.
