Particle Motion Of Plasma

The study of plasma, often referred to as the "fourth state of matter," is a captivating field that delves into the intricate behaviors of highly ionized gases. Among the myriad phenomena within plasma, the particle motion holds a special place, offering insights into the dynamic nature of this unique state of matter.
Understanding Plasma and Its Unique Properties

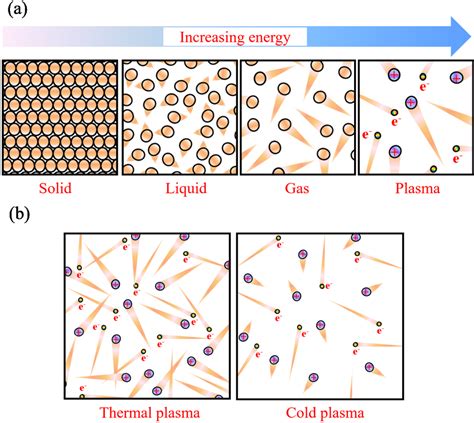
Plasma is a distinctive form of matter that differs significantly from its more familiar counterparts: solids, liquids, and gases. It is characterized by the presence of free electrons and ions, which bestow upon it a range of fascinating properties. Unlike neutral gases, where atoms or molecules are electrically neutral, plasma consists of charged particles, resulting in its ability to conduct electricity and respond to magnetic fields.
This unique composition makes plasma highly responsive to external influences, such as electric and magnetic fields. Consequently, it exhibits a range of complex behaviors, including particle motion, that are not observed in other states of matter. The study of plasma and its particle motion is not only academically intriguing but also has practical applications in various fields, from space physics to fusion energy research.
The Fundamentals of Particle Motion in Plasma

Particle motion in plasma refers to the movement of charged particles, primarily electrons and ions, within the plasma environment. These particles are influenced by a combination of forces, including electric and magnetic fields, as well as collisions with other particles. The resulting motion is a complex interplay of these forces, which can lead to a range of dynamic behaviors.
Key Factors Influencing Particle Motion:
- Electric Fields: The presence of electric fields can accelerate charged particles, causing them to move in a specific direction. This effect is particularly significant in regions of plasma where there are strong electric fields, such as near the edges of a plasma discharge or in the presence of a strong electric current.
- Magnetic Fields: Magnetic fields exert a force on moving charged particles, causing them to follow curved paths. This effect, known as the Lorentz force, is a fundamental aspect of plasma physics and plays a crucial role in the confinement and stability of plasma.
- Collisions: Particles in plasma frequently collide with each other, transferring energy and momentum. These collisions can cause particles to change direction or speed, influencing the overall motion of the plasma.
Types of Particle Motion in Plasma

The particle motion in plasma can manifest in various forms, each with its own unique characteristics and behaviors. Understanding these different types of motion is essential for a comprehensive grasp of plasma physics.
1. Drifting Motion
Drifting motion refers to the collective movement of charged particles in response to external electric and magnetic fields. In this type of motion, particles move as a group, following the direction of the electric field and the curvature of the magnetic field lines. Drifting motion is a fundamental aspect of plasma dynamics and plays a crucial role in the transport of energy and momentum within the plasma.
2. Random Motion (Thermal Motion)

Random motion, also known as thermal motion, describes the chaotic movement of particles due to their thermal energy. In this case, particles move in random directions and at varying speeds, resulting in a constant exchange of energy and momentum. This type of motion is particularly significant in high-temperature plasmas, where the thermal energy of particles is substantial.
3. Oscillatory Motion
Oscillatory motion occurs when charged particles are confined within a magnetic field and subjected to an external electric field. In this scenario, particles move in a periodic, oscillatory manner, following the curvature of the magnetic field lines. This type of motion is a key feature of plasma confinement systems, such as tokamaks and stellarators, where it is utilized to control and stabilize the plasma.
4. Spiral Motion
Spiral motion is a unique type of particle motion observed in plasmas with a strong magnetic field. In this case, charged particles follow spiral trajectories around the magnetic field lines, resulting in a distinctive spiral pattern. This motion is particularly relevant in space physics, where it is observed in the Earth's magnetosphere and other celestial bodies.
Applications of Particle Motion in Plasma
The study of particle motion in plasma has numerous practical applications across various scientific and technological fields. Here are some key areas where an understanding of particle motion is crucial:
1. Fusion Energy Research

One of the most significant applications of plasma physics is in the pursuit of fusion energy. In fusion reactors, such as tokamaks and stellarators, a deep understanding of particle motion is essential for achieving and maintaining the conditions necessary for nuclear fusion. The control of particle motion is critical for confining the hot, ionized plasma and preventing it from touching the reactor walls.
2. Space Physics

The study of particle motion in plasma is vital for understanding the behavior of celestial bodies and their interaction with the solar wind. For instance, the Earth's magnetosphere, which is a region of plasma surrounding our planet, exhibits complex particle motion patterns in response to the solar wind. This knowledge is crucial for space weather forecasting and the protection of satellites and power grids from space-related hazards.
3. Plasma Diagnostics

Particle motion can be used as a diagnostic tool to study the properties of plasma. By analyzing the motion of charged particles, scientists can gain insights into the temperature, density, and other characteristics of the plasma. This information is essential for a wide range of applications, from materials processing to medical treatments using plasma.
4. Plasma-Based Technologies
Plasma is utilized in various technological applications, and an understanding of particle motion is crucial for optimizing these processes. For example, in plasma-based etching and deposition techniques used in the semiconductor industry, the control of particle motion is essential for achieving precise and controlled material removal or deposition.
Challenges and Future Prospects

While significant progress has been made in understanding particle motion in plasma, there are still many challenges and open questions. One of the primary challenges is the complex and highly nonlinear nature of plasma dynamics, which makes it difficult to predict and control the behavior of individual particles. Additionally, the interaction between particles and the plasma environment is often influenced by a multitude of factors, making it a complex and multifaceted problem.
However, with the advancement of computational power and the development of more sophisticated simulation tools, researchers are increasingly able to model and predict the behavior of plasma and its constituent particles. These advancements are paving the way for new and exciting discoveries in the field of plasma physics, with potential applications in energy, space exploration, and materials science.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the study of particle motion in plasma offers a fascinating glimpse into the dynamic and complex world of this unique state of matter. From its fundamental properties to its diverse applications, plasma continues to captivate and challenge scientists and engineers alike. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of plasma and its particle motion, we move closer to harnessing its potential for a sustainable and technologically advanced future.
What is plasma, and how does it differ from other states of matter?

+
Plasma is a unique state of matter characterized by the presence of free electrons and ions. Unlike solids, liquids, and gases, plasma is highly responsive to electric and magnetic fields, making it a dynamic and complex state of matter.
What are the key factors influencing particle motion in plasma?
+The key factors influencing particle motion in plasma include electric and magnetic fields, as well as collisions between particles. These factors work together to create a complex and dynamic motion pattern for charged particles within the plasma.
How is particle motion used in fusion energy research?
+In fusion energy research, a deep understanding of particle motion is crucial for achieving and maintaining the conditions necessary for nuclear fusion. By controlling the motion of charged particles, scientists can confine the hot plasma and prevent it from touching the reactor walls.

