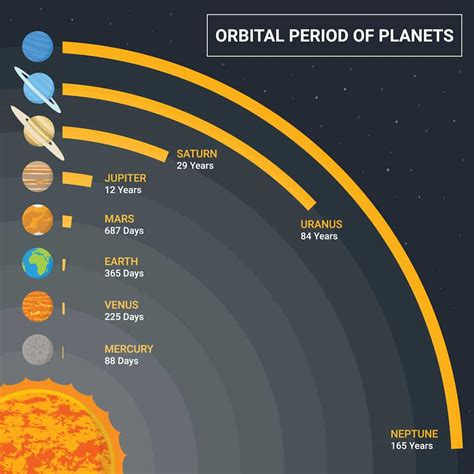
Planets Distance To The Sun

The solar system is a fascinating place, with a diverse range of planets orbiting our star, the Sun. Each planet has its own unique characteristics and distance from the Sun, which plays a significant role in shaping its environment and conditions. Let's explore the distances of these celestial bodies and uncover some intriguing facts about their positions in our cosmic neighborhood.
Mercury: The Closest to the Sun

Mercury, the smallest and innermost planet in our solar system, holds the title of being the closest to the Sun. With an average distance of approximately 58 million kilometers (36 million miles) from the Sun, Mercury experiences extreme temperature variations. Its proximity to the Sun means it receives intense solar radiation, resulting in scorching temperatures during the day. However, due to its lack of atmosphere, the nights on Mercury are incredibly cold.
Venus: The Second Planet

Venus, often referred to as Earth’s “sister planet,” is the second planet from the Sun. It is situated at an average distance of around 108 million kilometers (67 million miles) from our star. Venus is known for its thick atmosphere, which consists primarily of carbon dioxide. This atmosphere creates a runaway greenhouse effect, leading to extremely high temperatures on the planet’s surface, making it the hottest planet in our solar system.
Earth: Our Home Planet

Earth, the third planet from the Sun, is where we call home. It is located at a distance of approximately 150 million kilometers (93 million miles) from the Sun. Our planet’s distance from the Sun is just right, providing the ideal conditions for life as we know it. Earth’s atmosphere, composed of various gases, plays a crucial role in regulating temperature and supporting the diverse ecosystems that thrive on its surface.
Mars: The Red Planet

Mars, the fourth planet from the Sun, is often referred to as the “Red Planet” due to its distinct reddish appearance. It is situated at an average distance of around 228 million kilometers (142 million miles) from the Sun. Mars has a thin atmosphere primarily composed of carbon dioxide, which contributes to its cold and dry conditions. Despite its challenging environment, Mars has captured the interest of scientists and space enthusiasts alike, with ongoing missions exploring its potential for past or present habitability.
The Gas Giants: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune

Beyond Mars, we enter the realm of the gas giants. These planets, known for their massive sizes and gaseous compositions, include Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
Jupiter: The Largest Planet

Jupiter, the fifth planet from the Sun, is the largest planet in our solar system. It is located at an average distance of approximately 778 million kilometers (483 million miles) from the Sun. Jupiter’s massive size and powerful gravitational pull make it a dominant force in the solar system. Its iconic Great Red Spot, a giant storm, has been observed for centuries and showcases the planet’s dynamic atmosphere.
Saturn: The Ringed Beauty

Saturn, the sixth planet from the Sun, is renowned for its breathtaking ring system. It is situated at an average distance of around 1.4 billion kilometers (886 million miles) from the Sun. Saturn’s rings, composed primarily of ice and rock particles, are a stunning celestial display. The planet’s atmosphere, primarily made up of hydrogen and helium, gives rise to its distinctive banded appearance.
Uranus: The Sideways Planet
Uranus, the seventh planet from the Sun, has a unique feature: it rotates on its side! This peculiar tilt is believed to be the result of a massive impact in its early history. Uranus is located at an average distance of approximately 2.9 billion kilometers (1.8 billion miles) from the Sun. Its atmosphere, primarily composed of hydrogen, helium, and methane, gives it a distinctive blue-green color.
Neptune: The Distant Ice Giant

Neptune, the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun, is an ice giant. It is situated at an average distance of around 4.5 billion kilometers (2.8 billion miles) from our star. Neptune’s atmosphere, similar to Uranus, contains hydrogen, helium, and methane, contributing to its deep blue hue. The planet is known for its powerful winds and the presence of its largest moon, Triton.
Dwarf Planets: Pluto and Beyond

In addition to the eight major planets, our solar system also includes dwarf planets, such as Pluto. Pluto, once considered the ninth planet, is now classified as a dwarf planet due to its size and orbital characteristics. It is located in the Kuiper Belt, a region beyond Neptune, at an average distance of approximately 5.9 billion kilometers (3.7 billion miles) from the Sun. Other dwarf planets, like Eris and Haumea, also reside in this distant region of our solar system.
The Sun’s Influence
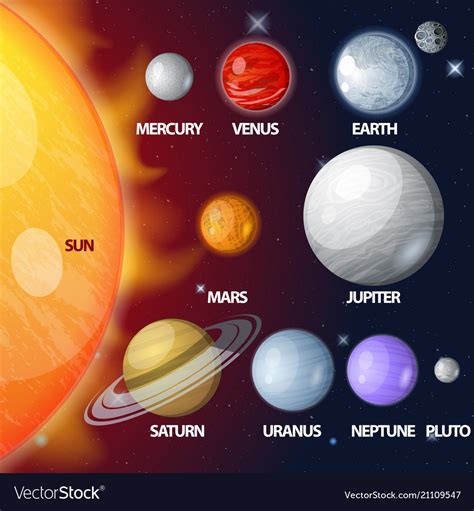
The distances of the planets from the Sun are not merely numbers; they have a profound impact on the characteristics and conditions of each celestial body. The Sun’s heat and light play a crucial role in shaping the planets’ atmospheres, temperatures, and overall environments. From the scorching heat of Mercury to the frigid conditions of Neptune, the varying distances create a diverse range of worlds, each with its own unique story to tell.
Exploring the Planets

Human curiosity and exploration have led to numerous missions and discoveries about the planets in our solar system. Space agencies around the world have sent spacecraft and rovers to study these distant worlds, providing valuable insights into their geology, atmospheres, and potential for supporting life. From the Mars rovers to the Cassini mission to Saturn, our understanding of the planets continues to evolve, fueling our fascination with the cosmos.
A Journey Through the Solar System

The solar system is a vast and captivating place, with each planet offering a unique experience. From the extreme temperatures of Mercury to the breathtaking rings of Saturn and the distant ice giants, there is an abundance of wonders to explore. As we continue to push the boundaries of space exploration, we uncover more secrets and mysteries, inspiring us to dream bigger and reach for the stars.
Table: Planet Distances to the Sun

| Planet | Average Distance from the Sun (km) | Average Distance from the Sun (miles) |
|---|---|---|
| Mercury | 58 million | 36 million |
| Venus | 108 million | 67 million |
| Earth | 150 million | 93 million |
| Mars | 228 million | 142 million |
| Jupiter | 778 million | 483 million |
| Saturn | 1.4 billion | 886 million |
| Uranus | 2.9 billion | 1.8 billion |
| Neptune | 4.5 billion | 2.8 billion |

💡 Note: The distances mentioned are average distances, as the planets follow elliptical orbits around the Sun.
Final Thoughts
The solar system is a captivating realm, filled with diverse planets and a wealth of scientific discoveries waiting to be made. As we continue to explore and learn more about these celestial bodies, we gain a deeper understanding of our place in the universe. The distances of the planets from the Sun are not just numerical values but key factors that shape the unique characteristics of each world. From the scorching heat of Mercury to the distant ice giants, our solar system never fails to amaze and inspire.
How do the distances of the planets affect their conditions?

+
The distances of the planets from the Sun significantly impact their conditions. Closer planets experience higher temperatures due to increased solar radiation, while more distant planets are colder. This distance-related factor influences the formation of atmospheres, the presence of liquid water, and the potential for life.
What is the significance of the gas giants in our solar system?

+
The gas giants, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, play a crucial role in our solar system. Their massive sizes and gravitational influence help maintain the stability of the solar system. Additionally, their unique atmospheres and dynamic weather patterns provide valuable insights into planetary formation and evolution.
Are there any other dwarf planets beyond Pluto?

+
Yes, beyond Pluto, there are several other dwarf planets in our solar system. Some notable examples include Eris, Makemake, and Haumea. These distant worlds offer valuable insights into the diverse range of celestial bodies and the complexities of planetary formation.