Tardigrade On Finger: 5+ Weird Facts You Never Knew

A Tiny Creature with an Even Tinier World

Tardigrades, often referred to as water bears or moss piglets, are microscopic creatures that have captivated scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. These tiny organisms, no bigger than a pinpoint, possess an extraordinary ability to thrive in some of the harshest environments on Earth. From the depths of the ocean to the desolate deserts, tardigrades have adapted to survive where few other life forms can. But what makes these tiny creatures so fascinating? Let’s delve into some of the weird and wonderful facts about tardigrades that will leave you in awe of their resilience and uniqueness.
1. Masters of Extremes: Surviving the Unsurvivable

Tardigrades are renowned for their extraordinary survival skills. They can withstand conditions that would be fatal to most other living organisms. Here’s a glimpse into their superpowers:
- Extreme Temperatures: These tiny creatures can survive temperatures as low as -272°C (-457.6°F) and as high as 151°C (303.8°F). Imagine withstanding the cold of absolute zero or the heat of a boiling pot!
- Radiation Resistance: Tardigrades have an incredible tolerance to radiation, making them almost indestructible. They can survive doses of radiation that would be lethal to humans and most other animals.
- Dehydration and Revivification: One of the most astonishing abilities of tardigrades is their capacity to enter a state of suspended animation called cryptobiosis. They can survive extreme dehydration, losing up to 99% of their body water, and remain in this state for years. When water becomes available again, they revive and continue their life cycle.
- High-Pressure Environments: Tardigrades have been found thriving in the deep sea, where pressures are thousands of times greater than at the surface. They can also survive the vacuum of space, making them true intergalactic explorers.
2. Tiny but Mighty: The Physiology of Tardigrades

Despite their minuscule size, tardigrades have a complex and fascinating physiology. Here are some intriguing details:
- Microscopic Size: Most tardigrades are just 0.1-1.5 mm long, making them barely visible to the naked eye. Their small stature allows them to inhabit a wide range of environments.
- Segmented Bodies: Their bodies are divided into segments, with four pairs of legs, each ending in tiny claws. This design provides them with excellent maneuverability and the ability to navigate through their microscopic world.
- Specialized Mouthparts: Tardigrades have a unique mouth structure called a stylet, which they use to pierce the cells of their prey and feed on their contents.
- Transparent Bodies: Their transparent bodies allow for easy observation of their internal organs and life processes, making them a favorite subject for scientists.
3. A Diet for the Adventurous

Tardigrades are not picky eaters; they have a diverse diet that reflects their adaptability. Here’s a glimpse into their culinary preferences:
- Plant-based Diet: Many tardigrade species are herbivores, feeding on algae, moss, and other plant matter. They play a crucial role in maintaining the health of their ecosystems.
- Carnivorous Delights: Some tardigrades are predators, feasting on other tiny organisms like rotifers and even smaller tardigrades. They use their stylets to inject digestive enzymes into their prey, breaking down their tissues for consumption.
- Scavengers: Certain tardigrade species are scavengers, feeding on decaying organic matter. They contribute to the breakdown of organic materials, playing a vital role in nutrient cycling.
- Opportunistic Eaters: Tardigrades are opportunistic feeders, consuming whatever food sources are available in their environment. This flexibility allows them to survive in diverse habitats.
4. The Art of Reproduction

Tardigrades have unique and varied reproductive strategies, ensuring the survival of their species:
- Sexual and Asexual Reproduction: Some tardigrades reproduce sexually, while others can reproduce asexually through parthenogenesis. This versatility allows them to adapt to different environmental conditions.
- Long Lifespan: Tardigrades have a relatively long lifespan for their size, with some species living up to 2 years. This longevity gives them more opportunities to reproduce and pass on their genes.
- Rapid Reproduction: In favorable conditions, tardigrades can reproduce rapidly, with some species producing multiple generations per year. This quick turnover helps them colonize new habitats and respond to environmental changes.
- Brood Care: Certain tardigrade species exhibit brood care, protecting their eggs and young until they are ready to hatch. This behavior increases the survival rate of their offspring.
5. Tardigrades in Popular Culture

Tardigrades have made their mark in popular culture, appearing in various forms of media:
- Scientific Inspiration: Their incredible survival abilities have inspired scientists to develop new technologies, such as radiation-resistant materials and methods to preserve biological samples.
- Art and Literature: Tardigrades have been featured in art, literature, and poetry, often symbolizing resilience and adaptability. Their unique appearance and mysterious nature have captured the imagination of artists and writers.
- Film and Animation: Tardigrades have made appearances in films and animated series, often portrayed as cute and lovable characters. Their tiny size and distinctive shape make them popular subjects for animation.
- Internet Sensation: With their adorable appearance and incredible abilities, tardigrades have become an internet sensation. Memes, gifs, and videos featuring these tiny creatures have gone viral, spreading awareness and fascination about their existence.
6. Discovering the Tiny Wonders of Nature
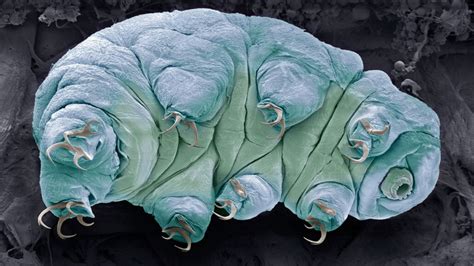
Tardigrades are a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of life on Earth. Their ability to thrive in extreme conditions and their unique physiological adaptations make them a subject of fascination for scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. By studying these tiny creatures, we gain a deeper understanding of the wonders of nature and the incredible resilience of life.
🌍 Note: Tardigrades are a fascinating example of how life can adapt and thrive in the most extreme environments. Their unique abilities inspire us to explore and appreciate the diversity of our planet.
FAQ

How big are tardigrades?
+Tardigrades are incredibly small, ranging from 0.1 to 1.5 mm in length. Some species can be even smaller, making them barely visible to the naked eye.
Can tardigrades survive in space?
+Yes, tardigrades have demonstrated an incredible ability to survive in the vacuum of space. They can withstand the extreme conditions of space, including radiation and low pressure.
What do tardigrades eat?
+Tardigrades have a diverse diet. Some are herbivores, feeding on algae and moss, while others are predators, consuming other tiny organisms like rotifers. Certain species are also scavengers, feeding on decaying matter.
How long can tardigrades survive in a dehydrated state?
+Tardigrades can survive extreme dehydration for years. They enter a state of cryptobiosis, where they lose almost all their body water and enter a state of suspended animation. When water becomes available again, they revive and continue their life cycle.
Are tardigrades dangerous to humans?
+No, tardigrades are not dangerous to humans. They are too small to pose any threat and typically live in microscopic environments, far from human interaction.

