The Normal Brain Model: A Comprehensive Guide To Brain Function
Understanding the Normal Brain: An Exploration of Neurological Wonders

Delving into the intricacies of the human brain is akin to embarking on a journey through a vast and complex universe, where each neuron fires a unique story and every synapse ignites a new discovery. Among the myriad of brain models, the Normal Brain Model stands as a cornerstone, offering a comprehensive insight into the fundamental workings of this incredible organ. This guide aims to demystify the Normal Brain Model, unraveling its components, functions, and significance in our daily lives.
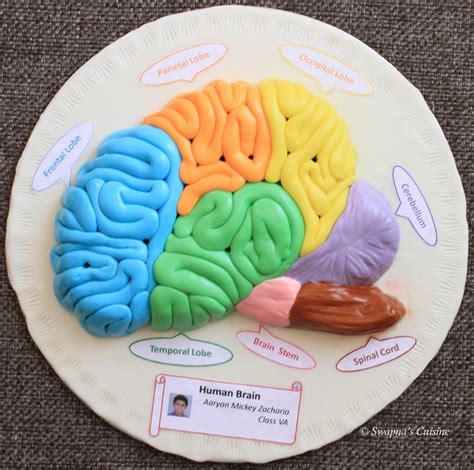
The Anatomy of a Normal Brain
The Normal Brain, a masterpiece of nature’s design, is a highly organized structure composed of billions of neurons and support cells. These neurons, the fundamental units of the nervous system, communicate through electrical and chemical signals, forming an intricate network that underpins all cognitive processes.
Key Components:
- Neurons: These are the information processing cells of the brain. Each neuron consists of a cell body, dendrites (which receive signals), and an axon (which transmits signals).
- Glial Cells: Often referred to as the “support cells,” glial cells provide structural and metabolic support to neurons. They play a crucial role in maintaining the brain’s environment and facilitating neuronal communication.
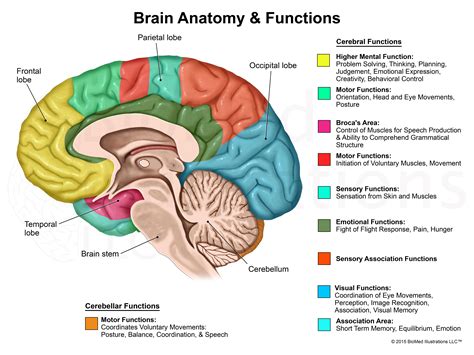
- Cerebral Cortex: The outer layer of the cerebrum, the cerebral cortex is responsible for higher cognitive functions, including memory, attention, perception, awareness, thought, language, and consciousness.
- Cerebrum: The largest part of the brain, the cerebrum is divided into two hemispheres—the left and right. It controls movement, coordination, temperature regulation, and learning.
- Cerebellum: Located at the back of the brain, the cerebellum is involved in coordination, balance, and muscle movement.
- Brain Stem: Connecting the brain to the spinal cord, the brain stem controls vital functions like breathing, heart rate, and digestion.
Brain Function and its Complexities
The Normal Brain Model encapsulates the intricate processes that enable us to think, feel, and act. These processes, often referred to as “brain functions,” are diverse and far-reaching, encompassing everything from basic physiological responses to complex cognitive tasks.
Key Brain Functions:
- Cognition: This involves thinking, learning, memory, and perception. The brain’s ability to process and interpret information is a key aspect of cognition.
- Emotion: The brain is responsible for our emotional responses, from joy and happiness to fear and anger. These emotions are regulated by various brain regions, including the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex.
- Motor Control: The brain controls all voluntary and involuntary movements, from walking and running to breathing and swallowing.
- Sensory Processing: The brain receives and interprets sensory information, allowing us to perceive the world around us through our senses.
- Sleep and Wakefulness: The brain regulates our sleep-wake cycles, ensuring we get the rest we need and are alert when we need to be.
Unraveling the Normal Brain Model
Understanding the Normal Brain Model is crucial for grasping the basics of neurological function. By studying this model, researchers and medical professionals can gain insights into how the brain typically operates, which forms the basis for identifying and treating neurological disorders.
Key Insights:
- Brain Connectivity: The Normal Brain Model highlights the intricate connections between different brain regions, emphasizing the importance of communication and coordination in cognitive processes.
- Neuroplasticity: This model also underscores the brain’s ability to adapt and change, a phenomenon known as neuroplasticity. This adaptability allows us to learn, remember, and recover from brain injuries.
- Homeostasis: The brain maintains a stable internal environment, ensuring optimal functioning. This process, known as homeostasis, is crucial for overall brain health.
Exploring the Wonders of the Normal Brain
The Normal Brain Model opens a window into the fascinating world of neuroscience, offering a glimpse into the mechanisms that make us who we are. By understanding the normal brain, we can appreciate the complexity and beauty of our cognitive abilities and the importance of maintaining brain health.
Embracing Brain Health:
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and B vitamins is essential for brain health.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves cognitive function and reduces the risk of cognitive decline.
- Mental Stimulation: Engaging in activities that challenge the brain, such as learning a new skill or playing brain games, can enhance cognitive reserve and protect against cognitive decline.
- Social Engagement: Maintaining strong social connections and engaging in meaningful social activities can positively impact brain health.
Visualizing the Normal Brain

This image depicts a cross-section of the Normal Brain, highlighting key regions and their functions. From the cerebral cortex to the brain stem, each part plays a crucial role in maintaining our cognitive, emotional, and physical well-being.
Conclusion:
The Normal Brain Model is a testament to the incredible complexity and beauty of the human brain. By understanding its anatomy, functions, and the insights it provides, we can appreciate the delicate balance that underpins our thoughts, emotions, and actions. Embracing brain health and understanding the Normal Brain Model can empower us to make informed decisions about our cognitive well-being and appreciate the wonders of our neurological universe.
FAQ Section
What is the role of neurons in the Normal Brain Model?
+Neurons are the fundamental units of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals. In the Normal Brain Model, neurons form an intricate network, facilitating communication and coordination between different brain regions.
How does the Normal Brain Model contribute to our understanding of neurological disorders?
+By studying the Normal Brain Model, researchers can identify deviations from typical brain function, which can help in diagnosing and treating neurological disorders. Understanding the normal brain provides a baseline for identifying abnormalities and developing effective interventions.
What are some common brain functions influenced by the Normal Brain Model?
+The Normal Brain Model encompasses a wide range of brain functions, including cognition, emotion, motor control, sensory processing, and sleep-wake cycles. These functions are integral to our daily lives and are influenced by the intricate workings of the Normal Brain.
How can we promote brain health and maintain a normal brain function?
+Promoting brain health involves adopting a holistic approach that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, mental stimulation, and social engagement. These lifestyle factors can enhance cognitive function, reduce the risk of cognitive decline, and support overall brain health.
What is the significance of neuroplasticity in the Normal Brain Model?
+Neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to adapt and change, is a key concept in the Normal Brain Model. It allows the brain to learn, remember, and recover from injuries, highlighting the brain’s remarkable resilience and capacity for change.