Unlocking The Ultimate A1c Conversion: The Expert's Guide
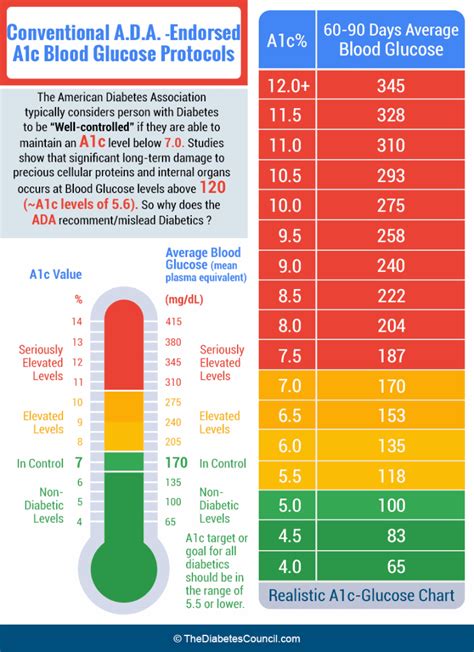
Managing diabetes effectively often involves monitoring and understanding various metrics, one of which is the A1C level. This parameter provides crucial insights into your average blood sugar control over the past two to three months. However, interpreting A1C values and converting them into more familiar units like mg/dL or mmol/L can be challenging for many individuals. In this comprehensive guide, we aim to demystify the A1C conversion process, providing you with the tools and knowledge to make informed decisions about your diabetes management.
Understanding A1C: The Basics
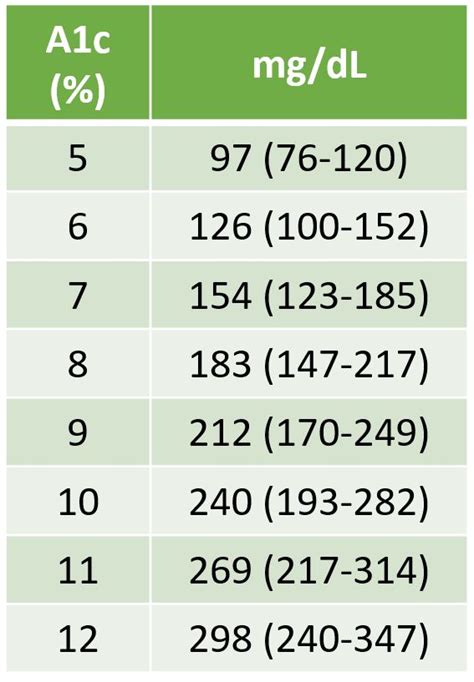
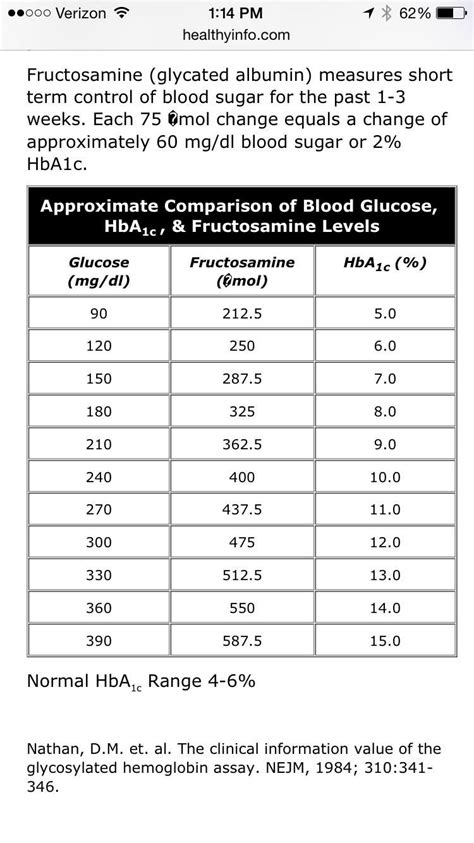
The A1C, also known as the hemoglobin A1C or HbA1c, is a critical metric for individuals with diabetes. It reflects the average level of glucose in your bloodstream over an extended period, typically two to three months. This long-term perspective is invaluable as it helps healthcare professionals and individuals with diabetes assess the effectiveness of their treatment plans and make necessary adjustments.
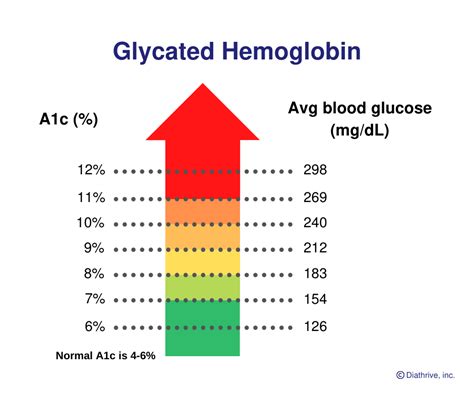
The A1C value is expressed as a percentage, indicating the proportion of hemoglobin in the blood that has glucose attached to it. A higher A1C percentage signifies poorer blood sugar control, while a lower percentage indicates better management. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends an A1C target of < 7% for most adults with diabetes, although this target may vary based on individual circumstances and medical advice.
The Importance of A1C Conversion

While the A1C percentage provides a valuable overview of blood sugar control, it may not be the most intuitive metric for everyone. Many individuals with diabetes are more accustomed to monitoring their blood glucose levels in mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) or mmol/L (millimoles per liter). Converting A1C values into these familiar units can offer a more tangible understanding of one's diabetes management and help identify patterns or trends more easily.
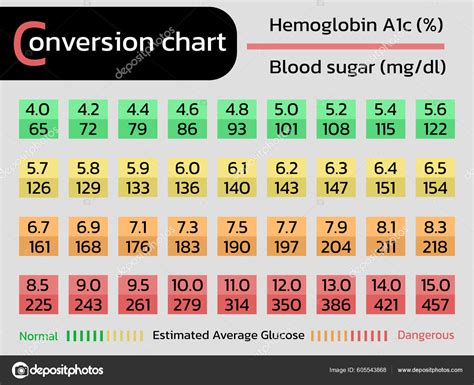
Converting A1C to mg/dL and mmol/L
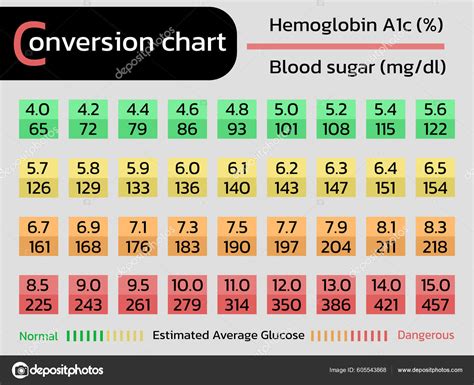
Converting A1C to mg/dL or mmol/L involves a series of calculations that take into account the relationship between average blood glucose levels and the A1C percentage. While these calculations can be complex, we've simplified the process for you with the following formulas:
Converting A1C to mg/dL
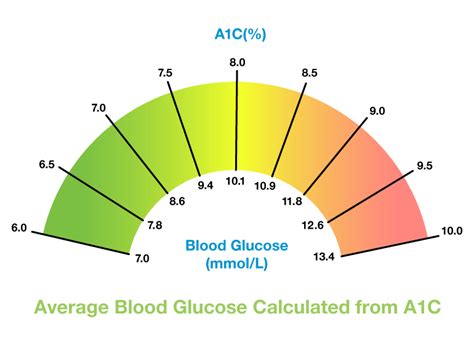
The formula for converting A1C to mg/dL is as follows:
mg/dL = (A1C x 33.3) - 83
For example, if your A1C is 7%, the calculation would be:
mg/dL = (7 x 33.3) - 83
mg/dL = 233 - 83
mg/dL = 150
So, an A1C of 7% would correspond to an average blood glucose level of approximately 150 mg/dL.
Converting A1C to mmol/L
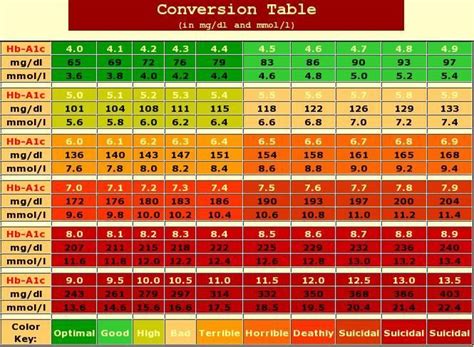
To convert A1C to mmol/L, use the following formula:
mmol/L = (A1C x 1.59) - 2.59
Using the same A1C value of 7% as an example:
mmol/L = (7 x 1.59) - 2.59
mmol/L = 11.13 - 2.59
mmol/L = 8.54
Thus, an A1C of 7% would correspond to an average blood glucose level of approximately 8.54 mmol/L.
Practical Steps for A1C Conversion

To make the A1C conversion process more accessible, consider the following steps:
- Obtain Your A1C Result: Start by getting your most recent A1C test result from your healthcare provider. This result is typically provided as a percentage.
- Use Online Calculators: There are numerous online tools and calculators available that can perform the A1C conversion for you. Simply input your A1C value, and the calculator will provide the corresponding mg/dL or mmol/L values.
- Manual Calculation: If you prefer a more hands-on approach, use the formulas provided above to calculate your A1C conversion manually. Ensure you have a calculator or a device with a calculator app to assist you.
- Track Your Progress: Once you have your A1C conversion, compare it to your previous results to track your progress. Monitoring trends over time can help you identify areas where your diabetes management may need adjustment.
Interpreting Your A1C Conversion

Understanding the implications of your A1C conversion is crucial for effective diabetes management. Here's a simplified breakdown of what your A1C conversion might indicate:
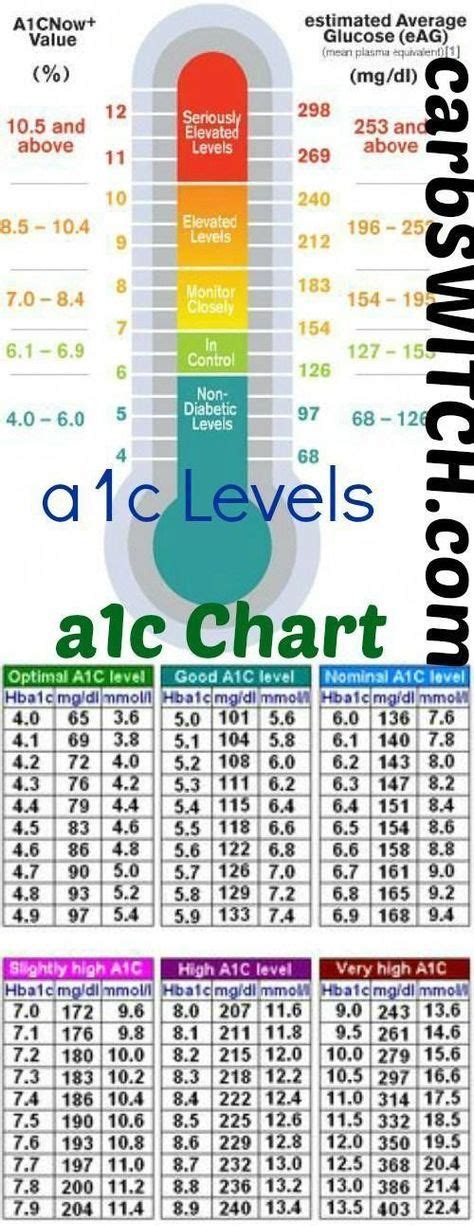
| A1C Percentage | Average Blood Glucose Level (mg/dL) | Average Blood Glucose Level (mmol/L) | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5.7% or below | 110 mg/dL or below | 6.1 mmol/L or below | Excellent blood sugar control. Keep up the good work! |
| 5.8% - 6.4% | 111 - 140 mg/dL | 6.2 - 7.8 mmol/L | Moderate blood sugar control. Consider making adjustments to your diet and exercise routine. |
| 6.5% - 7.9% | 141 - 190 mg/dL | 7.9 - 10.5 mmol/L | Poor blood sugar control. Consult with your healthcare provider to discuss treatment options and lifestyle changes. |
| 8% or above | 191 mg/dL or above | 10.6 mmol/L or above | Very poor blood sugar control. Urgent medical attention is required to prevent complications. |

Please note that these interpretations are general guidelines, and individual circumstances may vary. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance based on your specific situation.
Tips for Better Diabetes Management

In addition to understanding your A1C conversion, here are some tips to help you manage your diabetes more effectively:
- Regular Monitoring: Monitor your blood glucose levels regularly using a glucometer. This provides real-time data and helps you make informed decisions about your diet and medication.
- Healthy Diet: Adopt a balanced diet rich in whole foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates. Limit processed foods and sugary snacks.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity and manage blood sugar levels. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best exercise routine for you.
- Medication Adherence: Follow your prescribed medication regimen as directed by your healthcare provider. Do not skip doses or adjust medication without medical advice.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can impact blood sugar control. Practice stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to maintain proper hydration and support healthy kidney function.
- Regular Check-Ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your diabetes and discuss any concerns or questions you may have.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals

Your healthcare team, including endocrinologists, diabetes educators, and dietitians, plays a vital role in your diabetes management journey. They can provide personalized guidance, answer your questions, and offer support to help you achieve your A1C goals. Regular communication with your healthcare team is essential for optimizing your diabetes management plan.
Conclusion: Unlocking Better Diabetes Management

Understanding and converting your A1C values is a powerful tool in your diabetes management arsenal. By interpreting your A1C conversion and implementing the tips outlined in this guide, you can take control of your diabetes and work towards achieving optimal blood sugar control. Remember, effective diabetes management is a journey, and with the right knowledge and support, you can unlock a healthier and more fulfilling life.
What is the significance of the A1C test for individuals with diabetes?

+
The A1C test provides a long-term perspective on blood sugar control, helping individuals and healthcare professionals assess the effectiveness of diabetes management plans and make necessary adjustments.
Why is A1C conversion important for diabetes management?
+
A1C conversion allows individuals with diabetes to understand their blood sugar control in more familiar units like mg/dL or mmol/L, making it easier to identify patterns and trends in their diabetes management.
How often should I get an A1C test done?
+
The frequency of A1C testing depends on individual circumstances and medical advice. Generally, it is recommended to get an A1C test done at least twice a year, but your healthcare provider may suggest more frequent testing if needed.
Can I manage my diabetes without understanding A1C conversion?
+
While it is possible to manage diabetes without understanding A1C conversion, having this knowledge can provide a more comprehensive understanding of your blood sugar control and help you make more informed decisions about your diabetes management.
Are there any online tools or apps that can help with A1C conversion?
+
Yes, there are several online calculators and apps available that can perform A1C conversions for you. These tools can simplify the process and provide instant results.
