What Is Net Force

Net force is a fundamental concept in physics, particularly in the study of mechanics. It plays a crucial role in understanding the motion of objects and the forces acting upon them. In this blog post, we will delve into the definition of net force, explore its calculation, and discuss its significance in various physical scenarios.
Understanding Net Force

Net force, often denoted as Fnet, represents the resultant force acting on an object when multiple forces are applied to it. It is the vector sum of all the individual forces acting on the object. In simpler terms, net force is the combined effect of all forces acting on an object, taking into account both their magnitudes and directions.
The concept of net force is essential because it helps us determine how an object will move or change its motion. When multiple forces act on an object, the net force determines whether the object will accelerate, decelerate, or remain at rest.
Calculating Net Force

To calculate the net force on an object, we need to consider all the forces acting upon it. These forces can be classified into two categories: balanced forces and unbalanced forces.
Balanced Forces
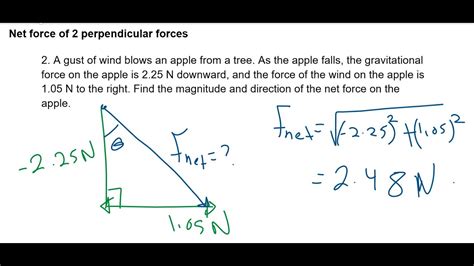
Balanced forces occur when the magnitude and direction of two or more forces are equal and opposite. In such cases, the net force is zero, and the object remains in a state of equilibrium, meaning it does not experience any acceleration.
Unbalanced Forces

Unbalanced forces, on the other hand, occur when the magnitude and direction of forces are not equal and opposite. In this scenario, the net force is non-zero, and the object experiences acceleration in the direction of the net force.
The calculation of net force involves vector addition. Let's consider an example where two forces, F1 and F2, are acting on an object.
| Force | Magnitude (N) | Direction |
|---|---|---|
| F1 | 10 | East |
| F2 | 5 | West |

To find the net force, we can use the following formula:
Fnet = F1 + F2
In this case, the net force would be:
Fnet = 10 N (East) + 5 N (West) = 5 N (East)
Therefore, the net force on the object is 5 Newtons in the eastern direction.
Significance of Net Force

Net force is a vital concept in physics for several reasons:
- Understanding Motion: Net force helps us predict and explain an object's motion. It determines whether an object will accelerate, decelerate, or maintain a constant velocity.
- Newton's Second Law: Net force is closely related to Newton's Second Law of Motion, which states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.
- Equilibrium and Stability: In situations where the net force is zero, objects are in a state of equilibrium, which is crucial for understanding the stability of structures and systems.
- Complex Systems: Net force becomes particularly important when dealing with multiple forces acting on an object simultaneously, such as in mechanical systems or celestial mechanics.
Real-Life Applications

The concept of net force has numerous real-life applications across various fields:
- Engineering: Engineers use net force calculations to design structures, vehicles, and machines that can withstand external forces and remain stable.
- Physics Experiments: Understanding net force is essential for conducting experiments involving motion, such as studying the behavior of particles in a collision or analyzing the motion of planets in the solar system.
- Sports and Athletics: Athletes and coaches rely on net force principles to optimize performance. For example, understanding the net force acting on a baseball or a sprinter can improve training techniques.
- Aerodynamics: In aviation and aerospace, net force calculations are crucial for designing aircraft and spacecraft that can withstand the forces of lift, drag, and thrust.
Key Takeaways

In summary, net force is the resultant force acting on an object when multiple forces are applied. It is calculated by vector addition of individual forces. Net force plays a crucial role in understanding motion, equilibrium, and stability. Its applications extend across various scientific and engineering disciplines, making it a fundamental concept in the field of physics.
What is the difference between net force and individual forces?

+
Net force represents the combined effect of all forces acting on an object, while individual forces are the specific forces applied to the object. Net force takes into account the magnitude and direction of each force to determine the overall force acting on the object.
How does net force affect an object’s motion?

+
Net force determines whether an object will accelerate, decelerate, or remain at rest. If the net force is non-zero, the object will experience acceleration in the direction of the net force. If the net force is zero, the object will remain in a state of equilibrium.
Can net force be negative?

+
Yes, net force can be negative. This occurs when the combined effect of forces results in a force acting in the opposite direction of the initial force. In such cases, the object experiences acceleration in the opposite direction.


