World War Two Military Ranks

Understanding the military ranks during World War II is crucial for anyone interested in military history, especially when delving into the complex organizational structure of armed forces during this significant global conflict. The rank system not only defines an individual's position within the military hierarchy but also highlights the diverse roles and responsibilities that contributed to the war effort.
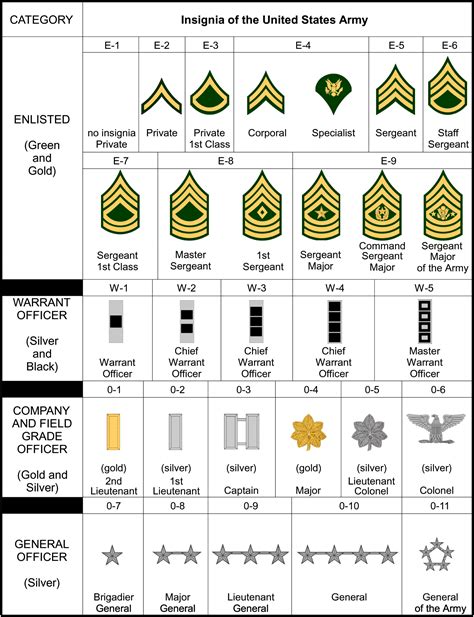
Army Ranks

The army, being the largest branch of the military, had a comprehensive rank structure. Here's an overview of the key ranks, starting from the highest:
- General of the Army - This rank was equivalent to a five-star general and was held by only a few individuals during World War II. It denoted the highest level of military command and was reserved for those with exceptional leadership and strategic skills.
- Lieutenant General - A three-star general, often commanding an army-sized unit or serving as a senior military advisor.
- Major General - A two-star general, typically commanding a division or serving in a senior staff position.
- Brigadier General - A one-star general, often leading a brigade or serving as a senior commander within a division.
- Colonel - The highest field officer rank, commanding a regiment or serving as a senior staff officer.
- Lieutenant Colonel - A mid-level field officer, often commanding a battalion or serving as a senior staff officer within a regiment.
- Major - A senior officer, typically commanding a battalion or serving as a staff officer within a brigade.
- Captain - The first officer rank, commanding a company or serving as a staff officer within a battalion.
- First Lieutenant - A junior officer, often serving as a platoon leader or a staff officer within a company.
- Second Lieutenant - The lowest officer rank, typically serving as a platoon leader or a junior staff officer.
- Warrant Officer - A specialized rank, usually with technical expertise, performing specific duties and providing technical guidance to other officers.
- Sergeant Major - The highest enlisted rank, serving as the principal advisor to senior officers and overseeing the administration and discipline of the unit.
- First Sergeant - A senior non-commissioned officer, often serving as the first sergeant of a company and responsible for the administration and discipline of the unit.
- Master Sergeant - A highly experienced non-commissioned officer, typically serving as a squad leader or performing specialized tasks.
- Sergeant - A mid-level non-commissioned officer, often leading a squad or serving as a platoon sergeant.
- Corporal - A junior non-commissioned officer, typically leading a small team or serving as a squad member.
- Private First Class - A rank above the basic private, often serving as a squad member or a specialist.
- Private - The lowest enlisted rank, serving as a basic soldier and undergoing training to advance to higher ranks.
Navy Ranks

The navy, with its unique structure and responsibilities, had a different rank system. Here are the key navy ranks during World War II:
- Fleet Admiral - The highest naval rank, equivalent to a five-star admiral, commanding the entire navy or serving as a senior naval advisor.
- Admiral - A four-star admiral, often commanding a fleet or serving in a senior naval command position.
- Vice Admiral - A three-star admiral, typically commanding a fleet or serving as a senior naval commander.
- Rear Admiral - A two-star admiral, often commanding a squadron or serving in a senior naval staff position.
- Captain - The highest officer rank in the navy, commanding a ship or serving as a senior staff officer.
- Commander - A mid-level officer, often commanding a smaller ship or serving as a senior staff officer on a larger vessel.
- Lieutenant Commander - A junior officer, typically commanding a small ship or serving as a department head on a larger vessel.
- Lieutenant - A junior officer, often serving as a division officer or a watch officer.
- Lieutenant (Junior Grade) - A rank below lieutenant, typically serving as a junior division officer or a watch officer.
- Ensign - The lowest officer rank in the navy, often serving as a junior officer or a trainee.
- Chief Petty Officer - The highest enlisted rank, serving as the principal advisor to senior officers and overseeing the administration and discipline of the ship.
- Petty Officer First Class - A senior non-commissioned officer, often serving as a department head or a senior specialist.
- Petty Officer Second Class - A mid-level non-commissioned officer, typically serving as a section leader or a senior specialist.
- Petty Officer Third Class - A junior non-commissioned officer, often serving as a team leader or a specialist.
- Seaman - The lowest enlisted rank, serving as a basic sailor and undergoing training to advance to higher ranks.
Air Force Ranks

The air force, a relatively new branch during World War II, had a rank structure that reflected its unique role in aerial warfare. Here are the key air force ranks:
- General of the Air Force - The highest air force rank, equivalent to a five-star general, commanding the entire air force or serving as a senior air force advisor.
- General - A four-star general, often commanding a numbered air force or serving in a senior air force command position.
- Lieutenant General - A three-star general, typically commanding a major air command or serving as a senior air force commander.
- Major General - A two-star general, often commanding a wing or serving in a senior staff position.
- Brigadier General - A one-star general, typically commanding a group or serving as a senior commander within a wing.
- Colonel - The highest field officer rank, commanding a wing or serving as a senior staff officer.
- Lieutenant Colonel - A mid-level field officer, often commanding a group or serving as a senior staff officer within a wing.
- Major - A senior officer, typically commanding a squadron or serving as a staff officer within a group.
- Captain - The first officer rank, commanding a flight or serving as a staff officer within a squadron.
- First Lieutenant - A junior officer, often serving as a flight leader or a staff officer within a flight.
- Second Lieutenant - The lowest officer rank, typically serving as a flight leader or a junior staff officer.
- Warrant Officer - A specialized rank, usually with technical expertise, performing specific duties and providing technical guidance to other officers.
- Master Sergeant - The highest enlisted rank, serving as the principal advisor to senior officers and overseeing the administration and discipline of the unit.
- Technical Sergeant - A senior non-commissioned officer, often serving as a section leader or a senior specialist.
- Staff Sergeant - A mid-level non-commissioned officer, typically serving as a team leader or a specialist.
- Sergeant - A junior non-commissioned officer, often serving as a squad leader or a team member.
- Airman First Class - A rank above the basic airman, often serving as a squad member or a specialist.
- Airman - The lowest enlisted rank, serving as a basic airman and undergoing training to advance to higher ranks.
Other Military Branches

Other military branches, such as the Marine Corps and Coast Guard, had their own unique rank structures, but they followed similar patterns to the army, navy, and air force. The ranks and responsibilities varied based on the specific roles and missions of each branch.
Comparing Military Ranks

It's important to note that the rank structures and titles varied slightly between different countries and even within the same country over the course of the war. Additionally, the responsibilities and authority associated with each rank could also vary based on the specific military branch and the context of the war effort.
Understanding these military ranks provides valuable insights into the complex organizational structure of the armed forces during World War II. It highlights the diverse roles and responsibilities that contributed to the war effort, from the highest-ranking generals and admirals to the lowest-ranking privates and seamen.
A Visual Guide to Military Ranks

To better visualize the military rank structures, here's a simplified table comparing the ranks across the army, navy, and air force:
| Rank | Army | Navy | Air Force |
|---|---|---|---|
| General of the Army / Fleet Admiral | Five-Star General | Five-Star Admiral | Five-Star General |
| Lieutenant General / Admiral | Three-Star General | Four-Star Admiral | Four-Star General |
| Major General / Vice Admiral | Two-Star General | Three-Star Admiral | Three-Star General |
| Brigadier General / Rear Admiral | One-Star General | Two-Star Admiral | Two-Star General |
| Colonel / Captain | Highest Field Officer | Highest Officer | Highest Field Officer |
| Lieutenant Colonel / Commander | Mid-Level Field Officer | Mid-Level Officer | Mid-Level Field Officer |
| Major / Lieutenant Commander | Senior Officer | Junior Officer | Senior Officer |
| Captain / Lieutenant | First Officer | Junior Officer | First Officer |
| First Lieutenant / Lieutenant (Junior Grade) | Junior Officer | Junior Officer | Junior Officer |
| Second Lieutenant / Ensign | Lowest Officer | Lowest Officer | Lowest Officer |
| Warrant Officer | Specialized Rank | Specialized Rank | Specialized Rank |
| Sergeant Major / Chief Petty Officer / Master Sergeant | Highest Enlisted | Highest Enlisted | Highest Enlisted |
| First Sergeant / Petty Officer First Class / Technical Sergeant | Senior NCO | Senior NCO | Senior NCO |
| Master Sergeant / Petty Officer Second Class / Staff Sergeant | Experienced NCO | Experienced NCO | Experienced NCO |
| Sergeant / Petty Officer Third Class | Mid-Level NCO | Mid-Level NCO | Mid-Level NCO |
| Corporal / Seaman | Junior NCO | Junior NCO | Junior NCO |
| Private First Class / Airman First Class | Above Basic | Above Basic | Above Basic |
| Private / Airman | Lowest Enlisted | Lowest Enlisted | Lowest Enlisted |
⚙️ Note: This table provides a simplified comparison of military ranks across different branches. The actual rank structures and titles may vary based on specific countries and their military organizations.
Conclusion

Understanding the military ranks of World War II is essential for appreciating the complexity and organization of the armed forces during this pivotal period in history. From the highest-ranking generals to the lowest-ranking enlisted personnel, each rank played a vital role in the war effort. The rank system not only defined an individual's position within the military hierarchy but also highlighted the diverse skills, expertise, and leadership required to win the war.
FAQ

What was the highest military rank during World War II?

+
The highest military rank during World War II was General of the Army (five-star general) in the army, Fleet Admiral (five-star admiral) in the navy, and General of the Air Force (five-star general) in the air force.
What were the responsibilities of a sergeant major in the army?

+
A sergeant major in the army served as the highest enlisted rank, acting as the principal advisor to senior officers and overseeing the administration and discipline of the unit.
How did the rank structure of the navy differ from the army and air force?

+
The navy’s rank structure had unique titles and responsibilities, reflecting its maritime role. For example, the highest officer rank was Captain, and the highest enlisted rank was Chief Petty Officer.
Were there any differences in rank structures between countries during World War II?
+
Yes, rank structures and titles varied slightly between different countries and even within the same country over the course of the war. The responsibilities and authority associated with each rank could also differ based on the specific military branch and the context of the war effort.
What was the role of a warrant officer in the military?
+
A warrant officer was a specialized rank, usually with technical expertise, performing specific duties and providing technical guidance to other officers. They often served as specialists in fields like aviation, engineering, or communications.


