Why Did Sample Blood Clot
Blood clotting, or coagulation, is a vital process that helps prevent excessive bleeding when our bodies suffer an injury. However, sometimes blood clots can form unexpectedly and lead to serious health issues. Understanding why blood clots occur is crucial for maintaining our well-being and recognizing potential risks.
In this blog post, we will delve into the fascinating world of blood clotting, exploring the various factors that contribute to its formation. From our body's natural defense mechanisms to underlying medical conditions, we will uncover the reasons behind why blood clots occur and how they can impact our health.
The Role of Platelets and Coagulation Factors
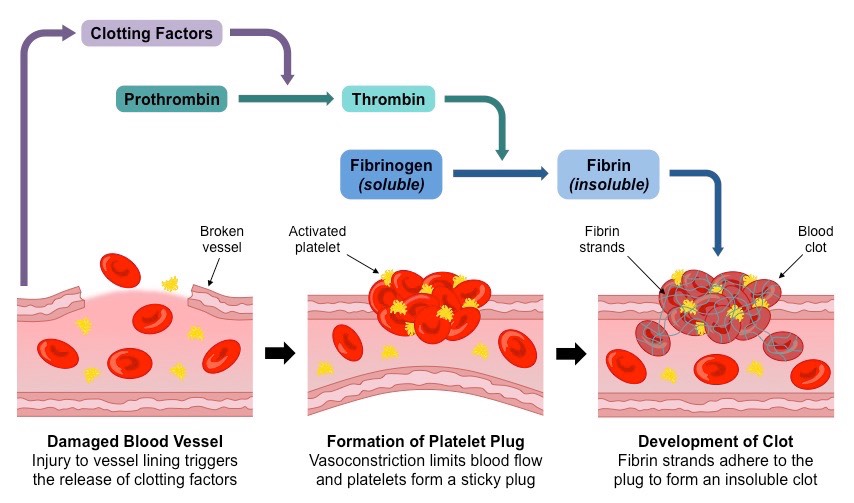
Blood clotting is a complex process involving several components of our blood. One of the key players is platelets, small cell fragments that circulate in our bloodstream. When we sustain an injury, platelets rush to the site and aggregate, forming a plug to stop the bleeding. This initial response is known as primary hemostasis.
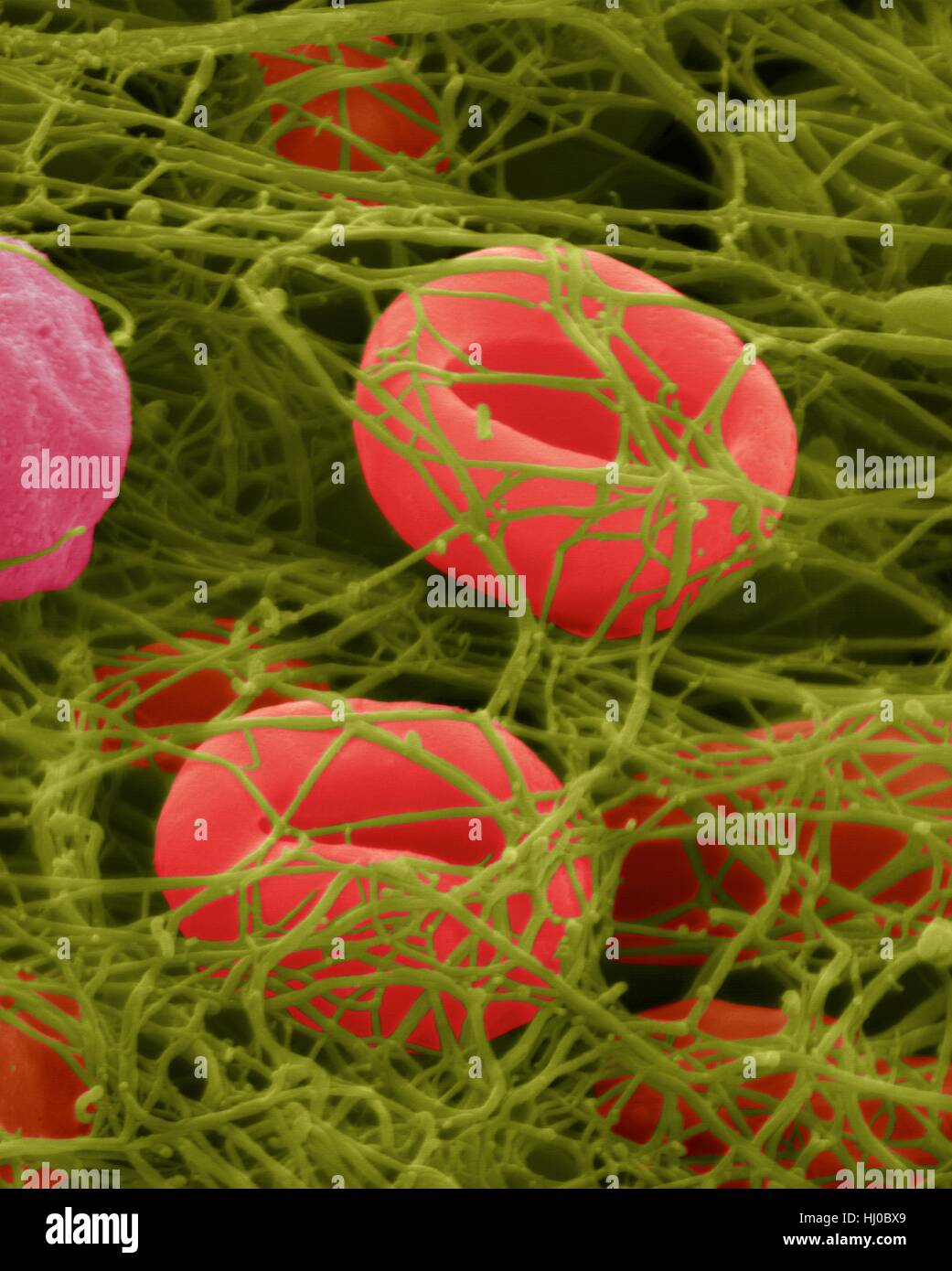
However, for a blood clot to fully form, a series of coagulation factors come into play. These factors are proteins that trigger a cascade of reactions, ultimately leading to the formation of a fibrin mesh. The fibrin mesh acts as a net, trapping red blood cells and platelets to create a solid clot. This process, known as secondary hemostasis, ensures that the wound is sealed and protected until it heals.
The Intricate Balance of Blood Clotting

Blood clotting is a finely tuned process that requires a delicate balance between promoting clot formation and preventing excessive clotting. Our bodies have evolved a sophisticated system to maintain this equilibrium. Anticoagulant proteins and fibrinolytic enzymes work together to regulate clot formation and breakdown, ensuring that clots only form when necessary and are promptly removed once their job is done.
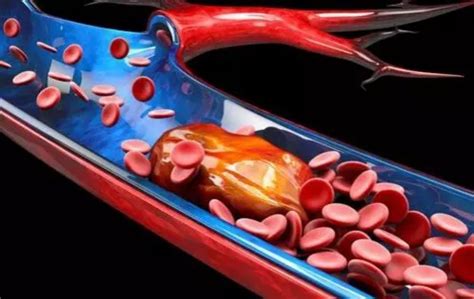
When this balance is disrupted, it can lead to either excessive clotting or inadequate clotting. In the case of excessive clotting, blood clots can form in blood vessels, obstructing blood flow and potentially causing serious complications. This condition is known as thrombosis and can result in deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism, or even a heart attack or stroke.
Underlying Medical Conditions and Risk Factors
Several underlying medical conditions and risk factors can contribute to the formation of blood clots. One common condition is atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up in the arteries, narrowing the blood vessels and increasing the likelihood of clot formation.
- Atherosclerosis: The buildup of plaque in arteries can lead to the narrowing of blood vessels, making it easier for clots to form and obstruct blood flow.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing blood clots due to the disease's impact on blood vessel health and circulation.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension can damage the walls of blood vessels, making them more susceptible to clot formation.
- Obesity: Excess body weight is associated with an increased risk of blood clots, as it can contribute to various metabolic and cardiovascular issues.
- Smoking: Smoking cigarettes is a significant risk factor for blood clots, as it damages blood vessels and promotes the formation of plaque.
Additionally, certain medical procedures and conditions can increase the likelihood of blood clot formation. Prolonged periods of immobility, such as during long-distance travel or after surgery, can slow down blood flow and allow clots to develop. Conditions like cancer, certain genetic disorders, and pregnancy can also raise the risk of blood clots.
Identifying Symptoms and Seeking Medical Attention

Recognizing the symptoms of a blood clot is crucial for early detection and timely medical intervention. While symptoms can vary depending on the location of the clot, some common signs include:
- Pain and Swelling: Blood clots in the legs or arms may cause localized pain, tenderness, and swelling.
- Warmth and Redness: The affected area may feel warm to the touch and appear red or discolored.
- Chest Pain: Blood clots in the lungs (pulmonary embolism) can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and a rapid heartbeat.
- Headache and Dizziness: Blood clots in the brain (stroke) can lead to severe headaches, dizziness, and difficulty speaking or understanding speech.
- Abdominal Pain: Blood clots in the abdomen may cause severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare professional can conduct a thorough evaluation, including blood tests and imaging scans, to determine the presence of a blood clot and provide appropriate treatment.
Prevention and Management Strategies
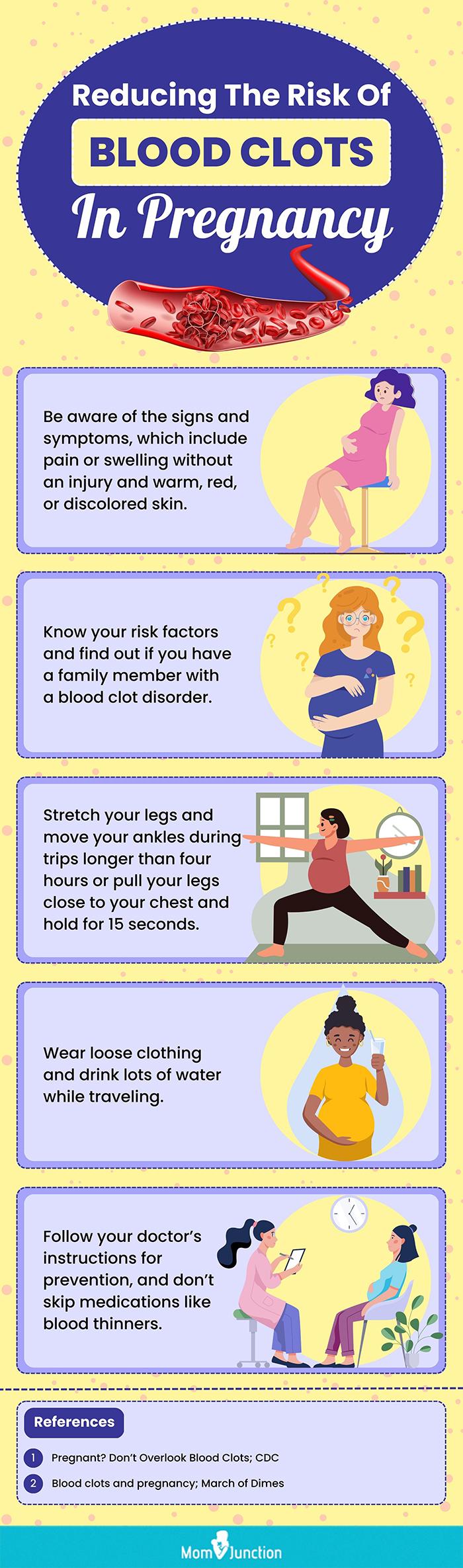
Preventing blood clots and managing existing ones is crucial for maintaining good health. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of blood clots. This includes regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking.
- Manage Underlying Conditions: If you have any underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, it is essential to manage them effectively through medication and lifestyle modifications.
- Compression Stockings: Wearing compression stockings can help improve blood flow in the legs and reduce the risk of blood clots, especially during periods of immobility.
- Medication: In some cases, healthcare professionals may prescribe anticoagulant medications to prevent or treat blood clots. These medications thin the blood and inhibit clot formation.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups and screenings can help identify any potential risk factors for blood clots and allow for early intervention.
It is important to note that the management of blood clots should always be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice and treatment plans based on your specific circumstances and medical history.
Conclusion
Blood clotting is a fascinating and intricate process that plays a vital role in our body's defense mechanism. While it is a natural response to injuries, understanding the underlying causes and risk factors is crucial for maintaining our overall health. By recognizing the symptoms, adopting preventive measures, and seeking timely medical attention, we can effectively manage blood clots and reduce the risk of serious complications.
What are the common signs of a blood clot in the legs?
+Common signs of a blood clot in the legs include pain, swelling, warmth, and redness in the affected area. The skin may also appear discolored, and the leg may feel tender to the touch.
Can blood clots be prevented during long-distance travel?
+Yes, there are several measures you can take to reduce the risk of blood clots during long-distance travel. These include staying hydrated, wearing compression stockings, taking regular breaks to stretch and walk around, and performing simple leg exercises while seated.
Are blood clots more common in certain age groups?
+Blood clots can occur at any age, but the risk tends to increase with age. Older individuals are more susceptible to blood clots due to various factors, including reduced mobility, underlying medical conditions, and changes in blood vessel health.
Can blood clots be life-threatening?
+Yes, blood clots can be life-threatening if they obstruct vital blood vessels or travel to critical organs. For example, a blood clot in the lungs (pulmonary embolism) or the brain (stroke) can have severe consequences and require immediate medical attention.
How are blood clots treated?
+The treatment for blood clots depends on their location and severity. Common treatments include anticoagulant medications to prevent further clotting, thrombolytic therapy to dissolve existing clots, and, in some cases, surgical intervention to remove the clot.